An AI just helped guide a NASA rover across Mars, marking a major leap in autonomous space exploration. 🚀
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.




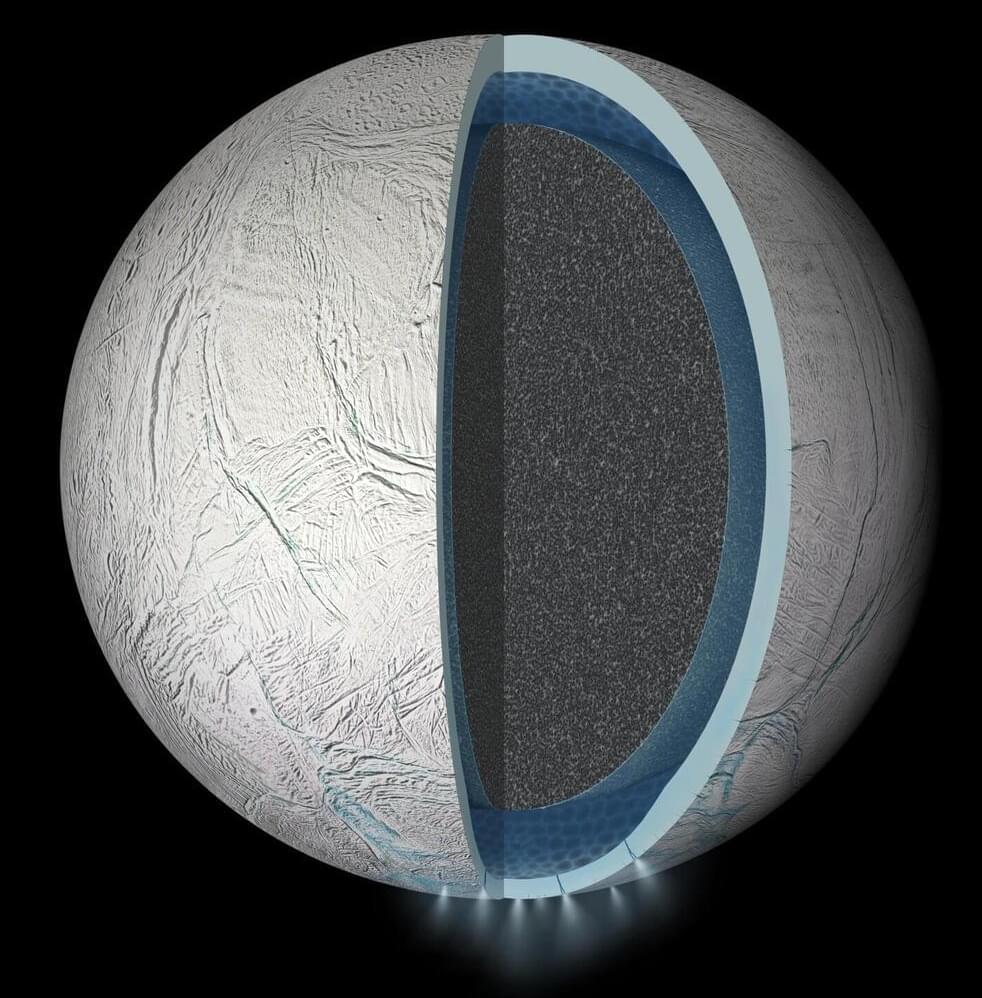
Experiments bring Enceladus’ subsurface ocean into the lab
Through new experiments, researchers in Japan and Germany have recreated the chemical conditions found in the subsurface ocean of Saturn’s moon, Enceladus. Published in Icarus, the results show that these conditions can readily produce many of the organic compounds observed by the Cassini mission, strengthening evidence that the distant world could harbor the molecular building blocks of life.
Beneath its thick outer shell of ice, astronomers widely predict that Saturn’s sixth largest moon hosts an ocean of liquid water in its south polar region. The main evidence for this ocean is a water-rich plume which frequently erupts from fractures in Enceladus’ surface, leaving a trail of ice particles in its orbital paths which contributes to one of its host planet’s iconic rings.
Between 2004 and 2017, NASA’s Cassini probe passed through this E-ring and plume several times. Equipped with instruments including mass spectrometers and an ultraviolet imaging spectrograph, it detected a diverse array of organic compounds: from simple carbon dioxide to larger hydrocarbon chains, which on Earth are essential molecular precursors to complex biomolecules.