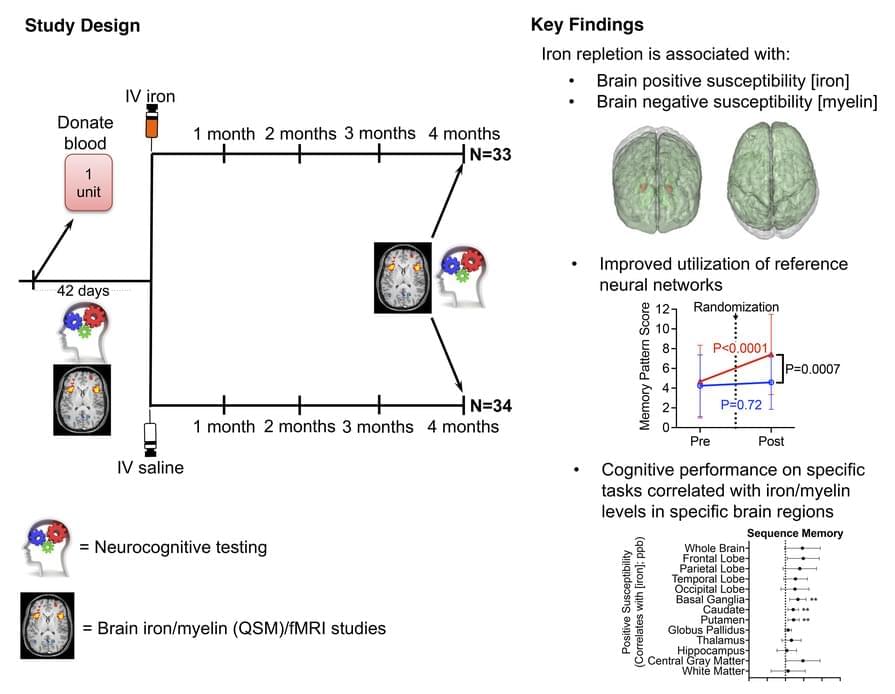
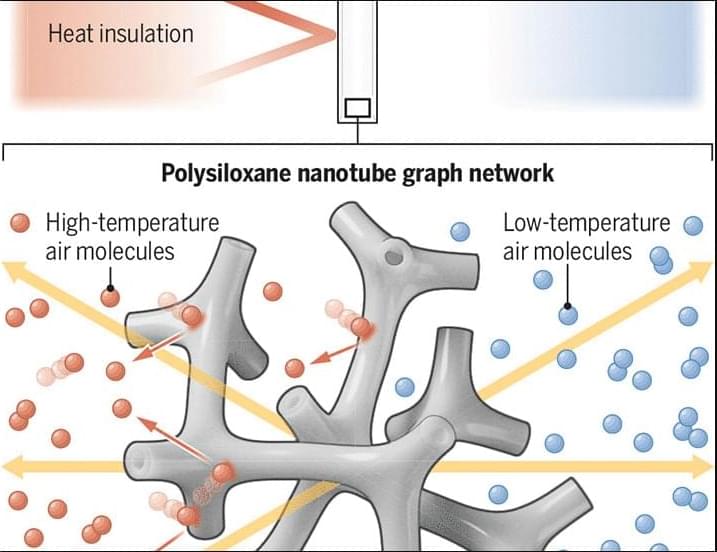
Steven L. Spitalnik & team report on a double-blind randomized trial for iron-deficient blood donors, finding treatment appears to affect brain function, brain iron, and myelin levels:
The heatmap images highlight the trend for increased iron in most brain regions.
1Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, and.
2Cognitive Neuroscience Division in Neurology, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, New York, USA.
3Department of Radiology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, New York, USA.