Scientists harnessed the unique properties of gallium to create the ink, which can be produced using conventional printing methods.


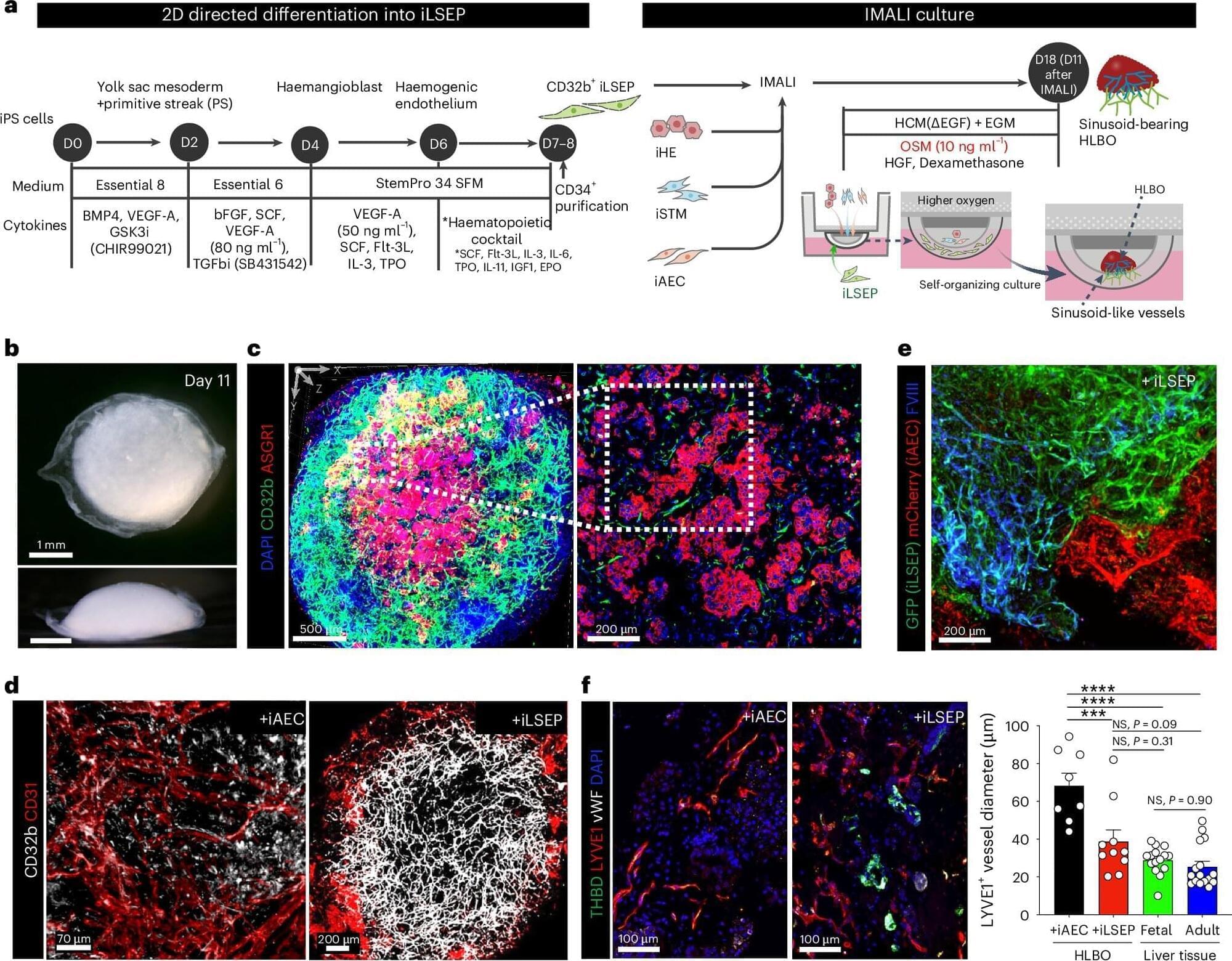
Scientists from Cincinnati Children’s and colleagues based in Japan report achieving a major step forward in organoid technology: producing liver tissue that grows its own internal blood vessels.
This significant advance could lead to new ways to help people living with hemophilia and other coagulation disorders while also taking another step closer to producing transplantable repair tissues for people with damaged livers.
The study, led by Takanori Takebe, MD, Ph.D., director for commercial innovation at the Cincinnati Children’s Center for Stem Cell and Organoid Research and Medicine (CuSTOM), was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
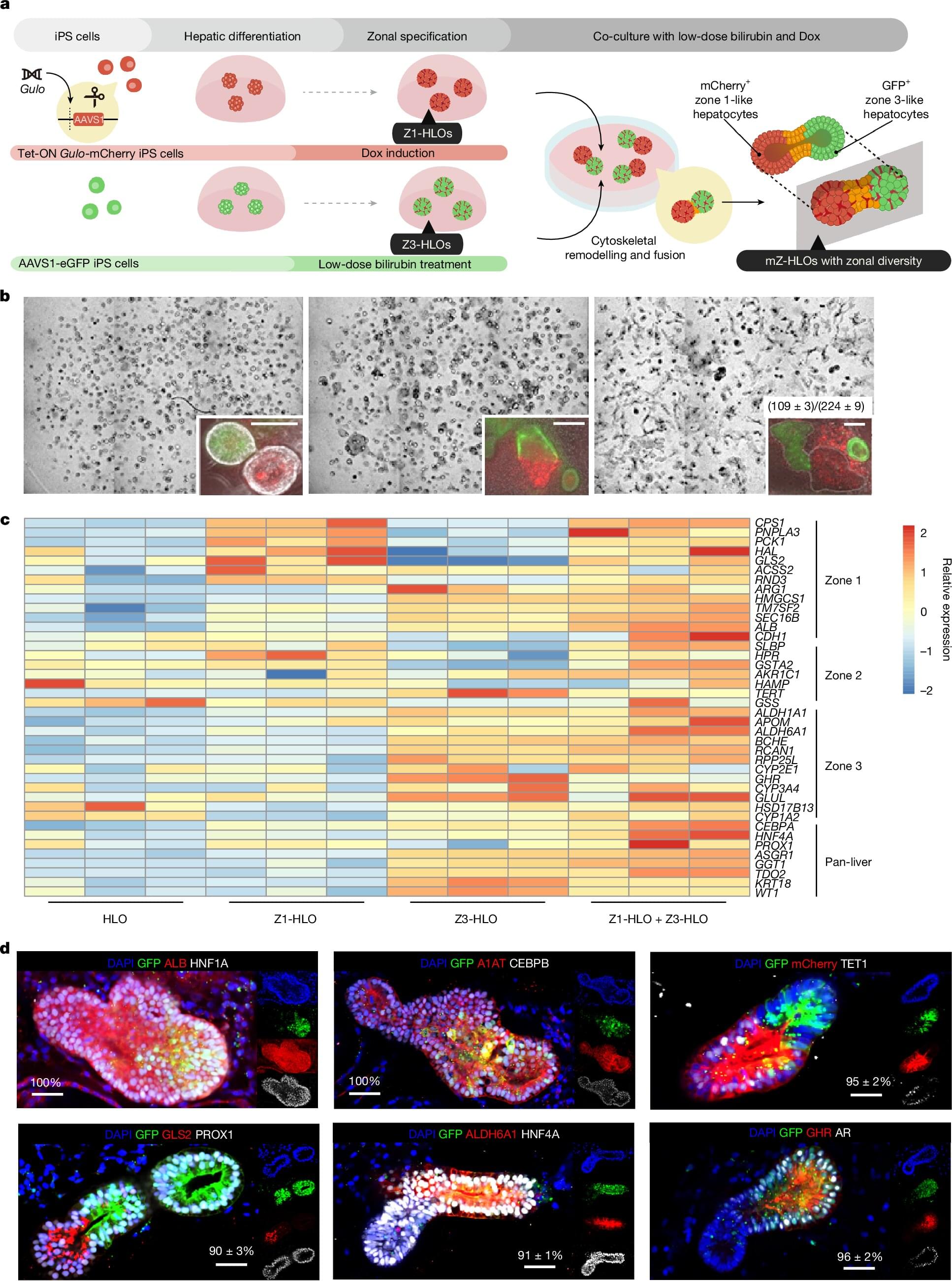
One reason why our livers excel at clearing waste from our blood system is that the organ functions according to three key “zones” that perform specific major tasks. So, if scientists hope to create self-growing patches of liver organoid tissue that could help repair damaged organs, it’s important that the lab-grown tissue faithfully reproduce such zones.
In a groundbreaking paper published April 16, 2025Nature, a team of organoid medicine experts at Cincinnati Children’s reports achieving just such a milestone—made from human stem cells. When these humanized organoids were transplanted into rodents whose own liver-bile duct system had been disconnected, the improved organoids nearly doubled the rodents’ survival rate.
“The research community has long needed a better model for studying human liver biology and disease, because there are outstanding hepatocyte diversity and associated functional orchestrations in the human liver that do not exist in rodents,” says Takanori Takebe, MD, Ph.D., the study’s corresponding author. “This new system paves the way for studying, and eventually treating, a wide range of otherwise fatal liver disorders.”
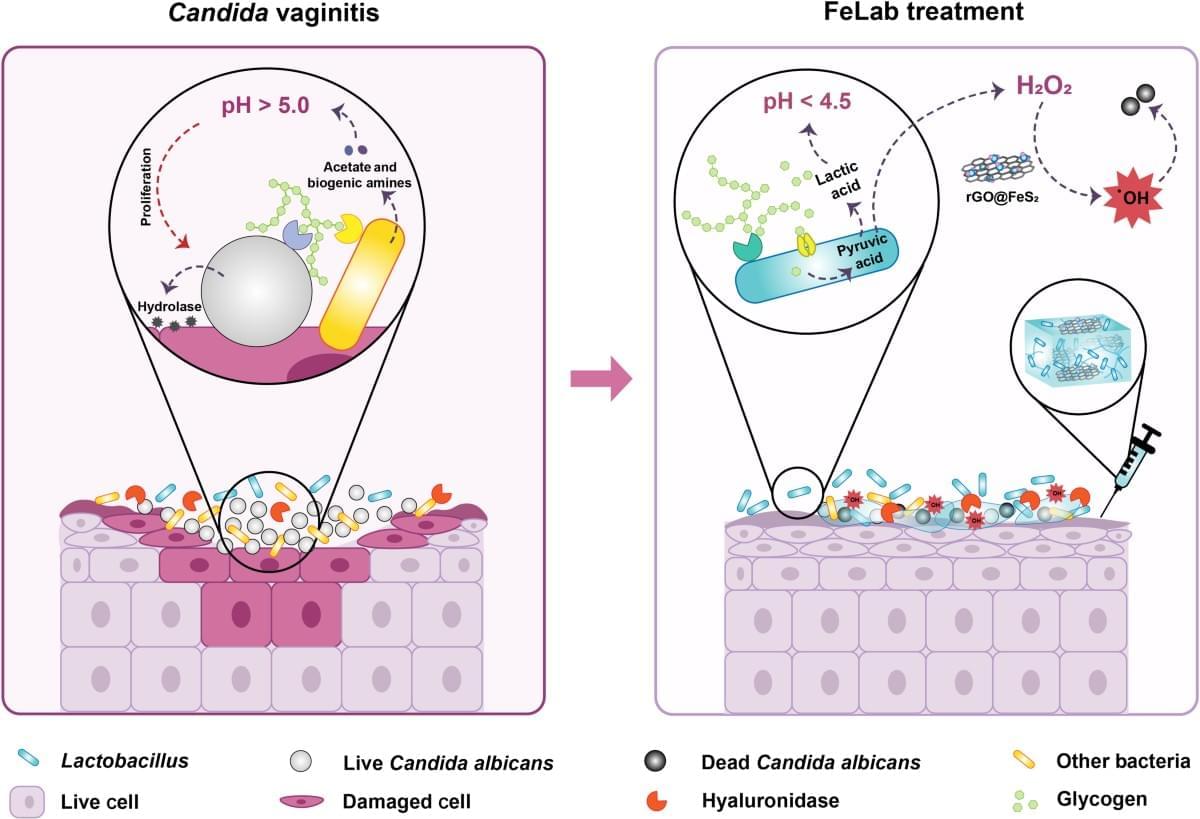
Sleep supports memory consolidation, but can it also facilitate memory reorganization? This study reveals that N2 sleep, but not N1 sleep during a nap, increases the likelihood of having an ‘aha’ moment about a previous decision-making task, and that spectral slopes of EEG power spectra predict future insights.
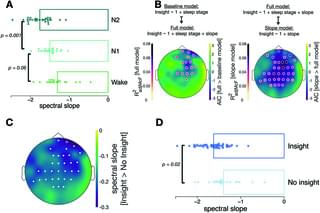
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) continues to devastate the global swine industry, yet the structural basis of how small molecules block its entry into host cells remains unclear. Researchers at the University of Tsukuba and Mahidol University developed a refined model of the PRRSV receptor domain CD163-SRCR5 using state-of-the-art computational approaches, offering new avenues for rational drug design.
While traditional drug discovery often relies on static crystal structures, many biologically important proteins, including the scavenger receptor CD163-SRCR5, contain flexible loop regions poorly captured by crystallography. These loops are critical for recognizing ligands and viral proteins, making them challenging yet attractive drug targets.
In their new study published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, the researchers used molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, ensemble docking, and fragment molecular orbital calculations to generate a dynamic, physiologically relevant structural model of the CD163-SRCR5 domain.
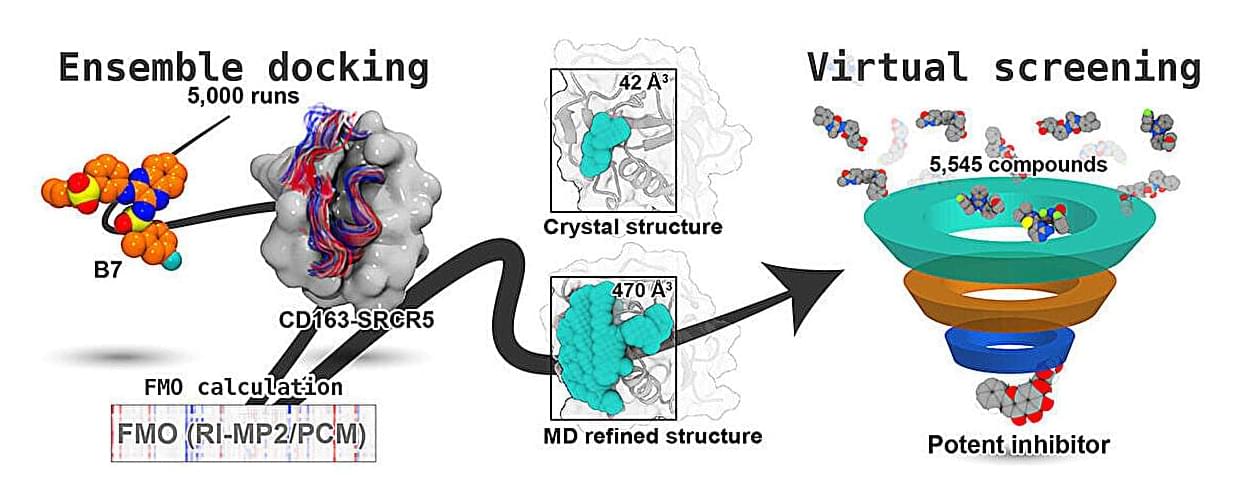
Superconductivity is an advantageous physical phenomenon observed in some materials, which entails an electrical resistance of zero below specific critical temperatures. This phenomenon is known to arise following the formation of so-called Cooper pairs (i.e., pairs of electrons).
There are two known types of superconductivity, known as conventional and unconventional superconductivity. In conventional superconductors, the formation of Cooper pairs is mediated by the interaction between electrons and phonons (i.e., vibrations in a crystal’s lattice), as explained by Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory.
Unconventional superconductors, on the other hand, are materials that exhibit a superconductivity that is not prompted by electron–phonon interactions. While many past studies have tried to shed light on the mechanisms underpinning unconventional superconductivity, its underlying physics remains poorly understood.
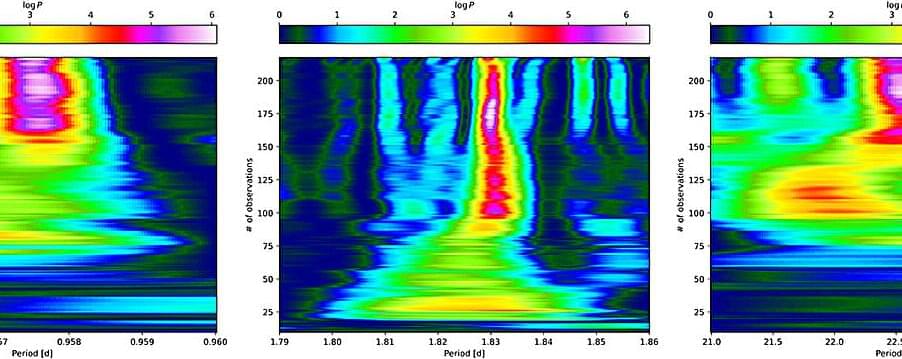
According to the latest studies led by Heidelberg University astronomers, low-mass stars quite often host Earth-like planets. Data collected as part of the CARMENES project were the basis of this finding. By analyzing the data, an international research team succeeded in identifying four new exoplanets and determining their properties.
At the same time, the researchers were able to show that Earth-like planets are found quite frequently in the orbit of stars with less than a sixth of the mass of our sun. These findings could support the search for potentially life-sustaining worlds in our cosmic neighborhood. The work is published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The CARMENES spectrograph system at the Calar Alto Observatory near Almería (Spain) was developed and built at the Königstuhl Observatory of Heidelberg University. It aids astronomers in the search for exoplanets that orbit so-called M-dwarfs. These stars have a mass of less than one-tenth to half the mass of our sun. M-dwarfs are the most abundant stars in our galaxy. They exhibit tiny periodic movements caused by the gravitational pull of orbiting planets, from which researchers can infer the existence of previously undiscovered worlds.