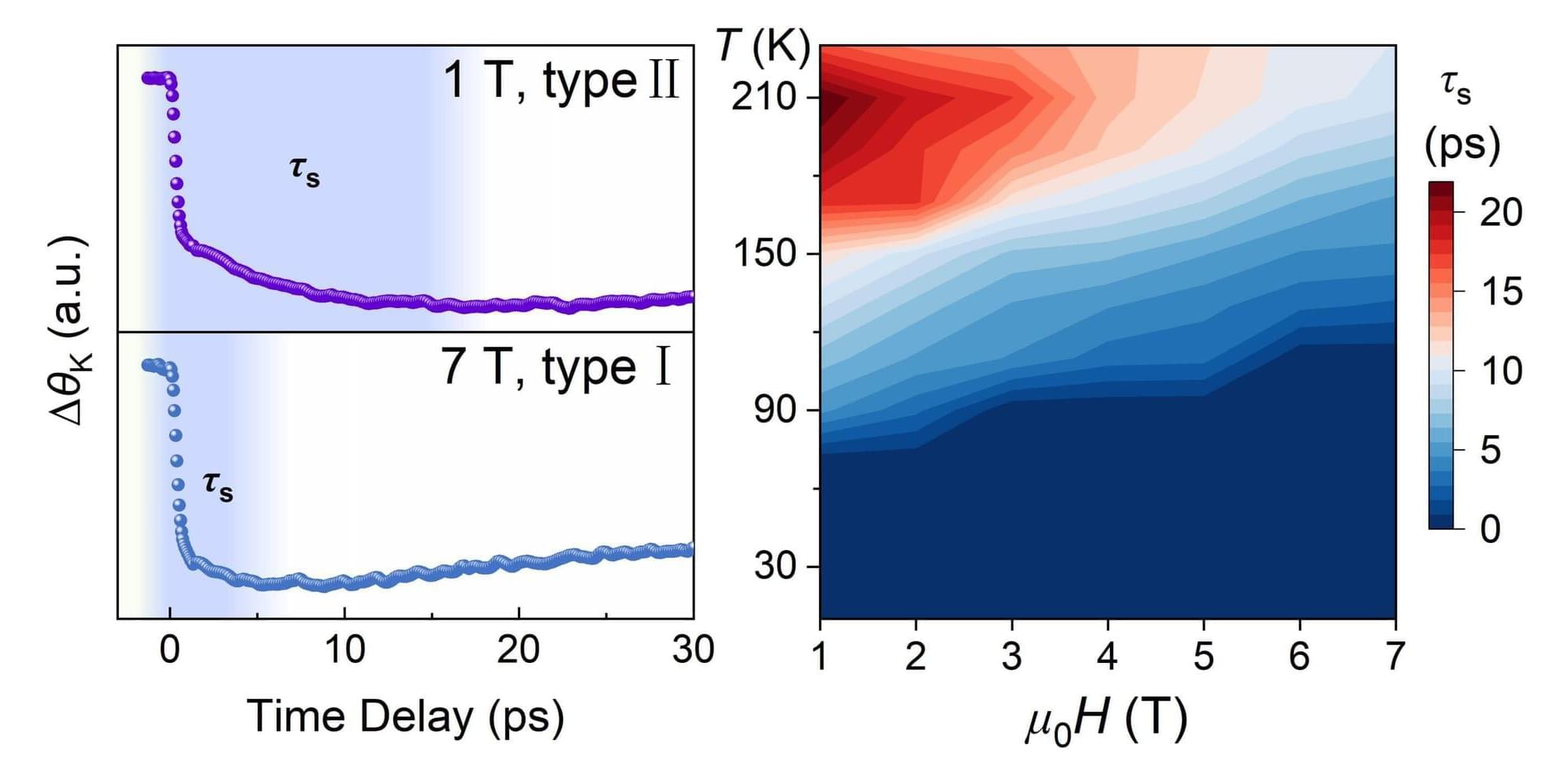
A research team led by Prof. Sheng Zhigao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. A.V. Kimel from Radboud University, has demonstrated that strong magnetic fields can effectively regulate laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in a two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals (vdW) ferromagnet.
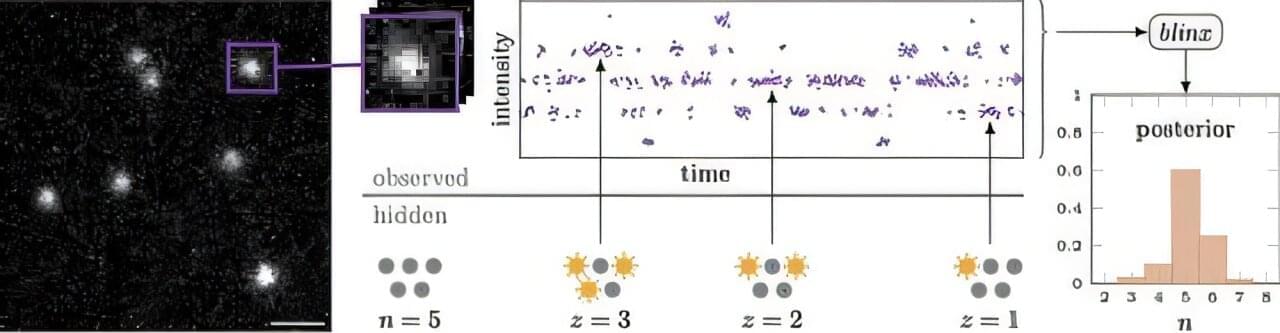
Imagine you’re sitting at a pond, listening to the din of croaking frogs. You want to know how many frogs are in the pond, but you can’t pick out the individual croaks—only the combined sound rising and falling in volume as frogs start and stop communicating.
But what if you were able to examine these volume changes to figure out how many frogs are in the pond?
That’s the idea behind a new method developed by the Funke Lab at Janelia to count the individual molecules contained in a single spot of light detected by a fluorescence microscope—a quantity important for understanding the underlying biology of a living system. The paper is published in the journal Nano Letters.
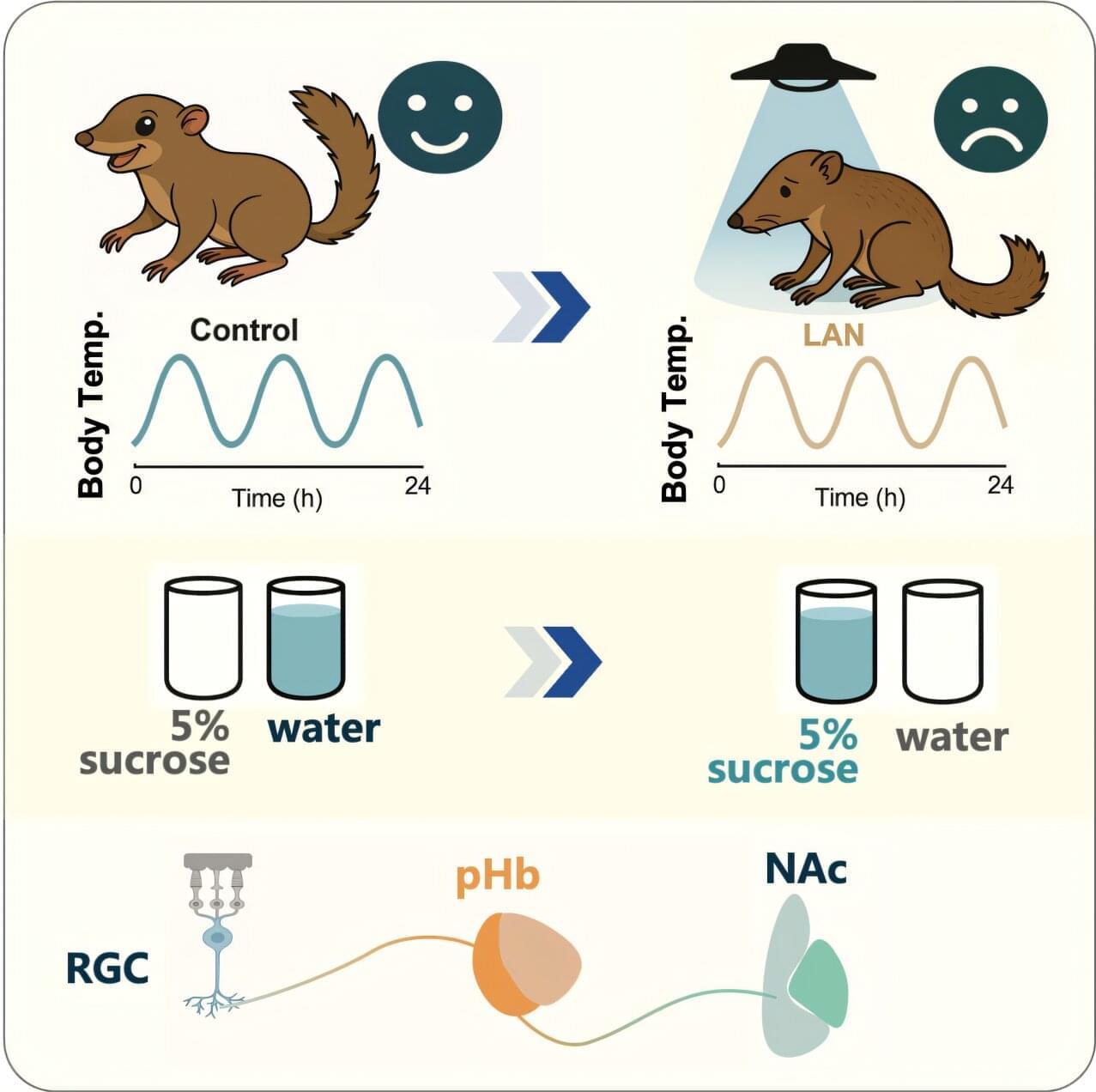
A new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals that chronic exposure to artificial light at night (LAN) can trigger depression-like behaviors by activating a specific neural pathway in the brain.
The study, conducted on tree shrews—diurnal mammals genetically close to primates that are active during the day like humans—offers critical insights into how nighttime light may disrupt mood regulation, potentially affecting human mental health in increasingly illuminated urban environments.
The research team, led by Prof. Xue Tian from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), Prof. Yao Yonggang of the Kunming Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and Prof. Zhao Huan of Hefei University, exposed tree shrews to blue light (comparable to bright indoor lighting) for two hours each night for three weeks.
You wouldn’t microwave fish around your worst enemy—the smell lingers both in kitchen and memory. It is one few of us like, let alone have positive associations with. But what makes our brains decide a smell is stinky?
A new study from UF Health researchers reveals the mechanisms behind how your brain decides you dislike—even loathe—a smell. The findings are published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Or as first author and graduate research fellow Sarah Sniffen puts it: How do odors come to acquire some sort of emotional charge?
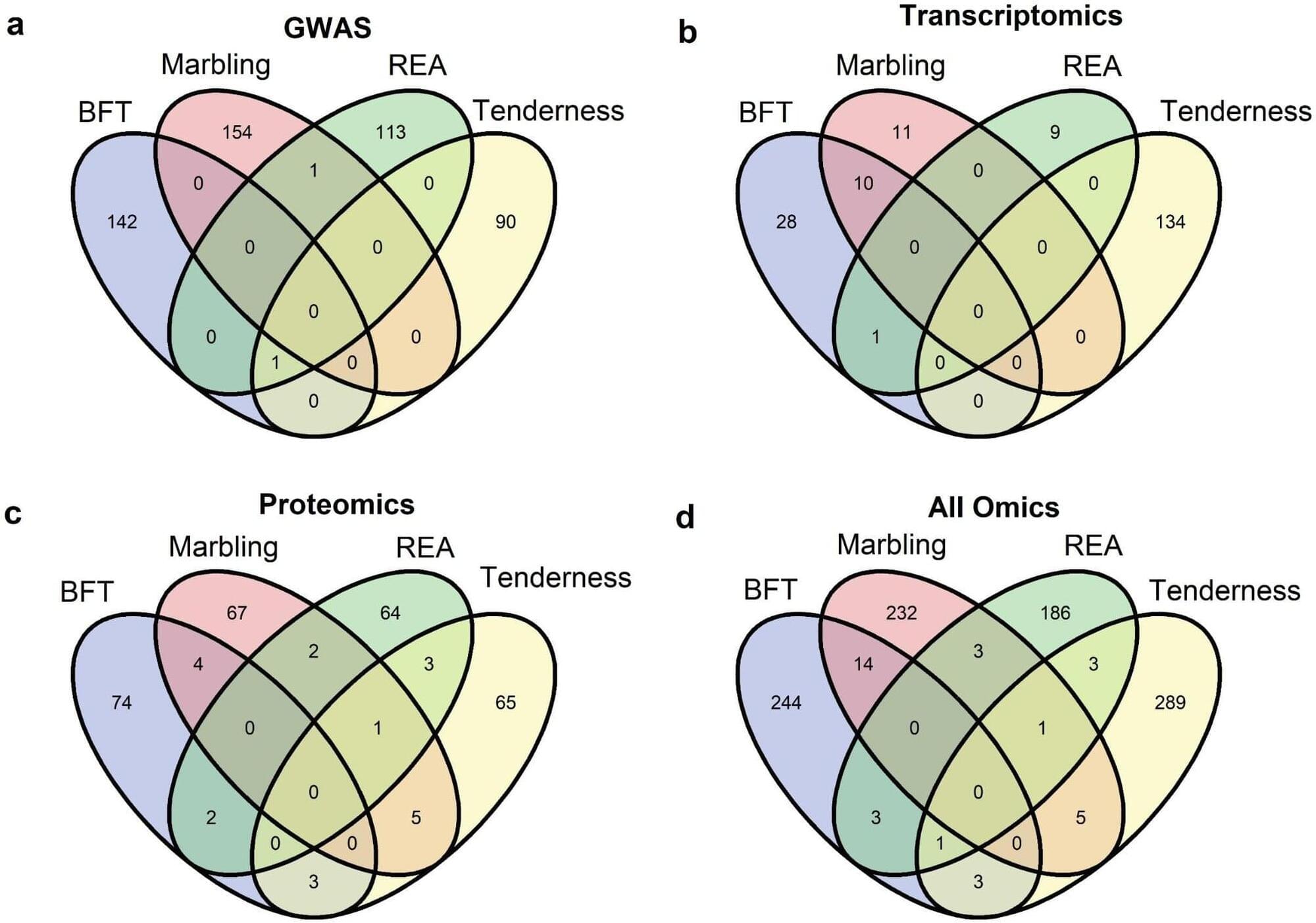
Researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil have identified a robust set of genetic markers associated with meat quality in the Nelore cattle breed (Bos taurus indicus) genome. The results pave the way for substantial progress in the genetic enhancement of the Zebu breed, which accounts for about 80% of the Brazilian beef herd.
The research has direct implications for the productivity and quality of Brazilian beef, reinforcing the country’s standing as a major beef exporter. The results are published in the journal Scientific Reports.
In previous studies, the group had identified genes and proteins by studying meat and carcass characteristics separately using different techniques. For the current study, however, the researchers integrated these techniques and examined multiple characteristics using data from 6,910 young Nelore bulls from four commercial genetic improvement programs.
Research has shown that large language models (LLMs) tend to overemphasize information at the beginning and end of a document or conversation, while neglecting the middle.
This “position bias” means that if a lawyer is using an LLM-powered virtual assistant to retrieve a certain phrase in a 30-page affidavit, the LLM is more likely to find the right text if it is on the initial or final pages.
MIT researchers have discovered the mechanism behind this phenomenon.
The concatenation of both ideas allows us to conclude that entropy exchanges tend to zero when the temperature tends to zero (which is Nernst’s theorem) and that absolute zero is inaccessible.
Martin-Olalla points out that a fundamental problem in thermodynamics is to distinguish the sensation of temperature, the sensations of hot and cold, from the abstract concept of temperature as a physical quantity. In the discussion between Nernst and Einstein, temperature was merely an empirical parameter: the absolute zero condition was represented by the condition that the pressure or volume of a gas became close to zero.
Formally, the second principle of thermodynamics provides a more concrete idea of the natural zero of temperature. The idea is not related to any sensation, but to that engine imagined by Nernst but which has to be virtual. This radically changes the approach to the proof of the theorem.
Lasers have widespread applications as a light source in a variety of fields, including manufacturing, medicine, high-speed communications, electronics, and scientific research.
In recent years, the demand for lasers with increased control over their output has grown significantly. In particular, ultranarrow bandwidth mode-locked lasers, which can produce extremely short laser pulses (short bursts of light) ranging from picoseconds to nanoseconds, have received considerable attention. Such short laser pulses are extremely beneficial for many applications—from diamond cutting to semiconductor manufacture. However, these applications can be further improved with the incorporation of lasers with tunable pulse duration.
A laser works by reflecting light back and forth between a highly reflective and a selective reflective mirror inside a cavity, and then amplifying it using a material called the gain medium. Conventional continuous-wave lasers emit a continuous beam of light waves (modes) with different wavelengths and random phases.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
How Charles Babbage built the first computer—laying the foundation for modern computing, automation, and AI that still shape our world today.