Forty six years ago in 1979 I wrote my BSc final dissertation, Phantom Eye. Now I aim to simplify, update, expand and improve the atrophied and absent external Phantom/ Primal eye framework, not least in the current 'mental health epidemic'.
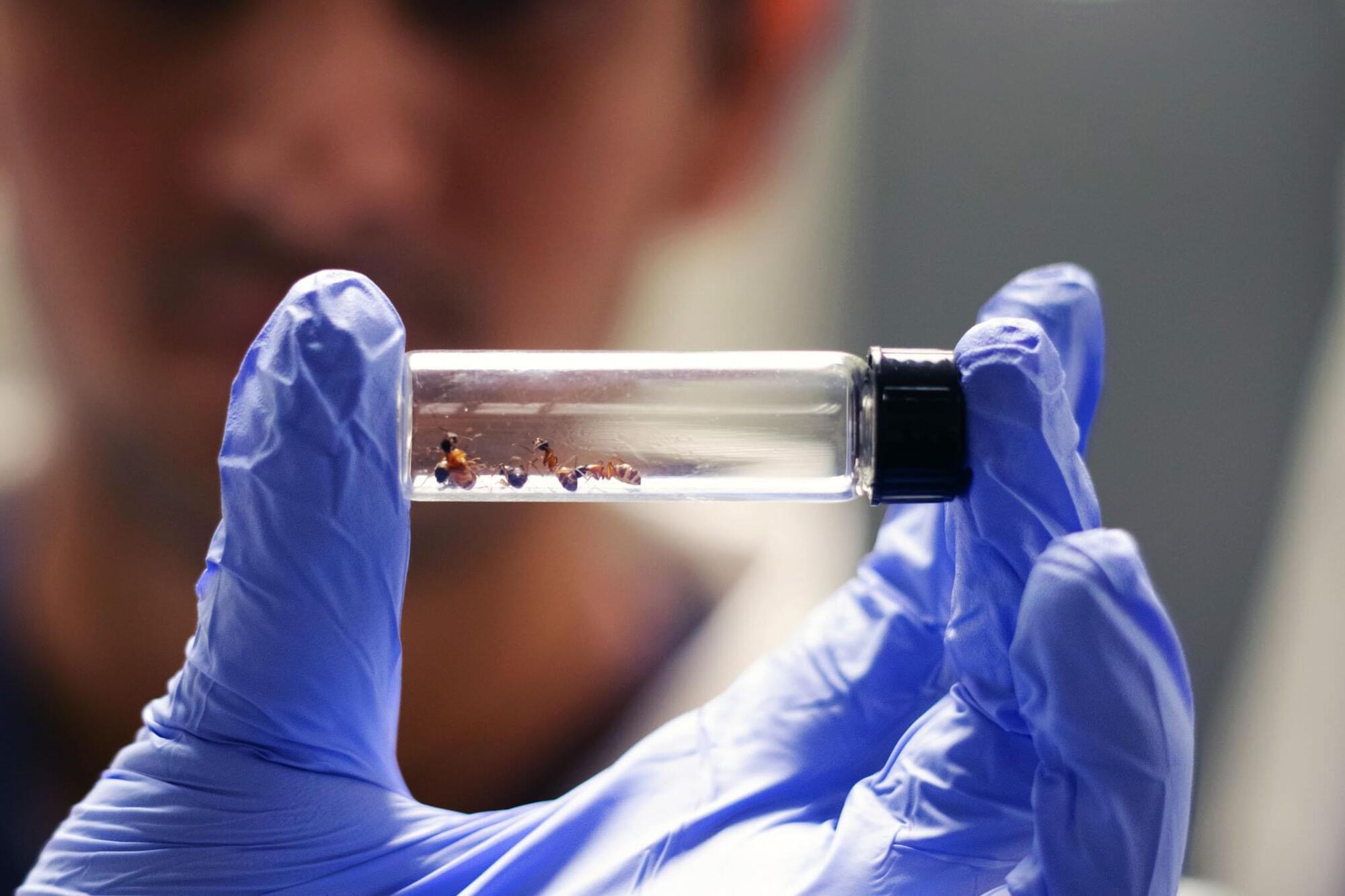





Has a crucial component to the development of human medicine been hiding under our feet? Auburn University Assistant Professor of Entomology Clint Penick and a team of graduate students may have found that ants are far ahead of humans in antibiotic innovation. “In our study, we tested how ants use antibiotic compounds to fight off pathogens and asked why their chemical defenses remain effective over evolutionary time,” Penick said.
“Humans have relied on antibiotics for less than a century, yet many pathogens have already evolved resistance, giving rise to ‘superbugs.’ Ants, by contrast, have been using antibiotics for tens of millions of years, and they might hold the key to using these powerful drugs more wisely.”
Ants as a source of antibiotics The team looked at just six ant species, all found easily in the Southeastern United States.
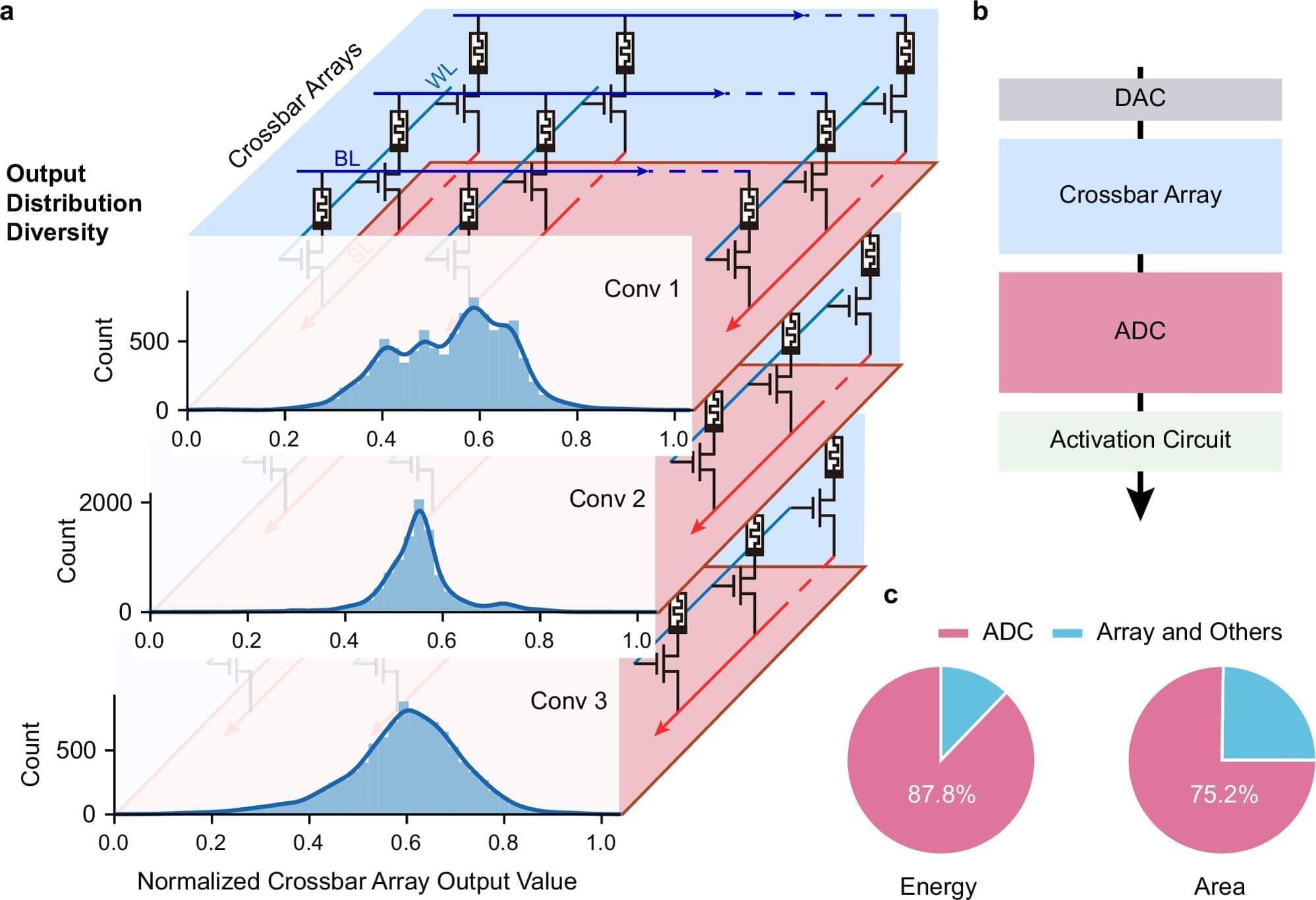
A cross-institutional team led by researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE), under the Faculty of Engineering at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), have achieved a major breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware by developing a new type of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that uses innovative memristor technology. The work is published in Nature Communications.
Challenges with conventional AI hardware Conventional AI accelerators face challenges because the essential components that convert analog signals into digital form are often bulky and power-consuming. Led by Professor Ngai Wong, Professor Can Li and Dr. Zhengwu Liu of HKU EEE, in collaboration with researchers from Xidian University and the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the cross-disciplinary research team developed a new type of ADC that uses innovative memristor technology. This new converter can process signals more efficiently and accurately, paving the way for faster, more energy-efficient AI chips.
Adaptive system and efficiency gains The research team created an adaptive system that automatically adjusts its settings based on the data it receives, i.e., dynamically fine-tuning how signals are converted. This results in a 15.1× improvement in energy efficiency and a 12.9× reduction in circuit area compared with state-of-the-art solutions.
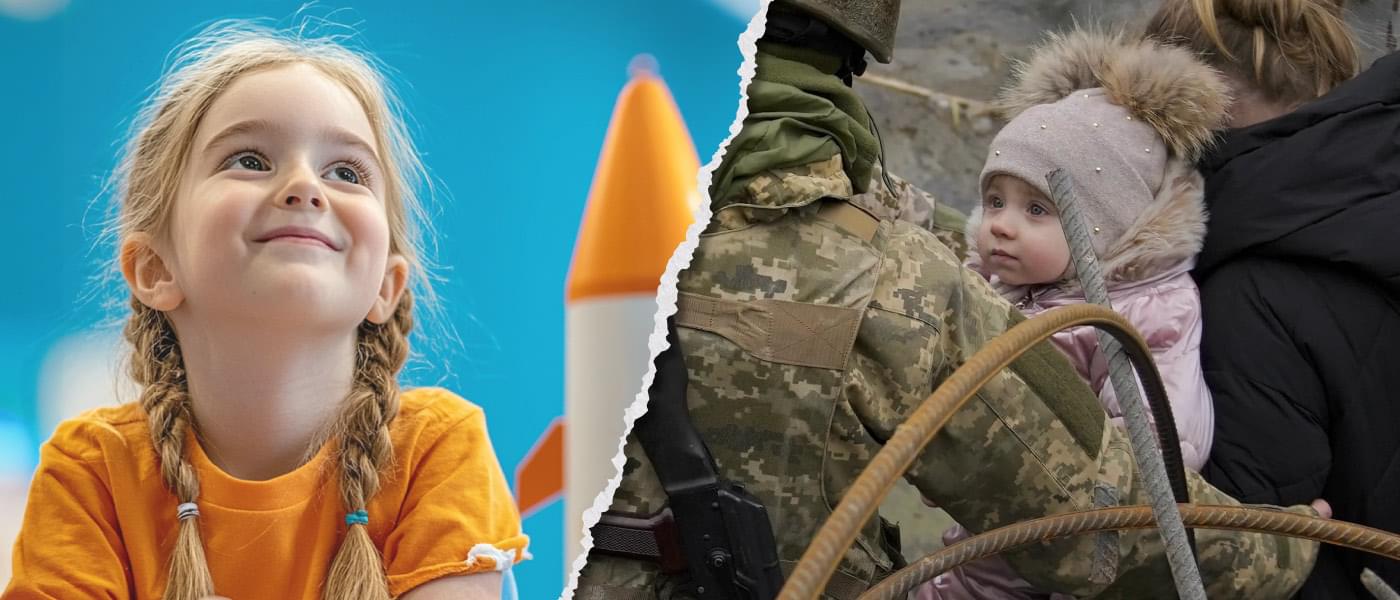

Help us help the kids of Ukraine to dream about the future.
Space, hope, and a great cause on the side of freedom. Follow the links. Make the donation, put a telescope, model rocket or robot in the hands of a kid who very badly needs Permission to Dream!
Space4 Ukraine empowers young Ukrainians whose education has been disrupted by war, giving them access to the tools, training, and opportunities they need to rebuild their future—and ours. Because no human potential should ever be wasted.
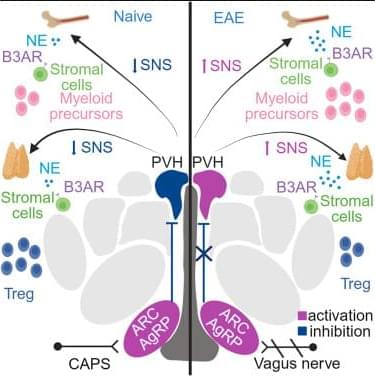
In this work, Vigo et al. demonstrate that norepinephrine (NE) promotes myeloid hematopoiesis in BM and regulates thymic Tregs via B3ARs in EAE. B3ARs are controlled by hypothalamic AgRP neurons, which are dysfunctional in EAE. Serum levels of AgRP are elevated in people with MS and correlate with disease severity.

Winter’s chill impacts children’s health, increasing illness and affecting growth due to reduced sunlight, indoor confinement, and dietary shifts. Experts advise parents to prioritize balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and physical activity. Simple measures like hygiene, vaccinations, and sun exposure are crucial for keeping kids healthy and thriving throughout the colder months.
A heart attack is a medical emergency that requires an immediate call to the emergency services. However, there are sometimes warning signs that can show up weeks in advance that should prompt you to visit your doctor.
Firstly, what exactly happens during a heart attack? A heart attack occurs when the vessels that supply the heart itself with oxygen and nutrients—known as coronary arteries—become blocked. One cause is calcium deposits building up in them, says the German Heart Foundation.
As this is a gradual process, symptoms often appear before the blockage occurs, when the vessels are already narrowed in what is referred to as coronary heart disease.

Scientists in China have performed an experiment first proposed by Albert Einstein almost a century ago when he sought to disprove the quantum mechanical principle of complementarity put forth by Niels Bohr and his school of physicists. Bohr claimed there are properties of particles that cannot simultaneously be measured. The new result backs up the Copenhagen school yet again, with the potential to shed light on other, less settled questions in quantum mechanics.
When they met at physics conferences, Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr liked to kick back and debate about quantum mechanics. Einstein, always skeptical of the standard picture of quantum mechanics then being developed, liked to claim he had found holes and inconsistencies in Bohr’s interpretation, and Bohr was always up for the challenge.
At the 1927 Solvay conference in Brussels, the two Nobel Laureates had perhaps their most famous parley, with Einstein famously proclaiming, “God does not play dice with the universe.” In particular, Einstein proposed an experiment he thought would reveal the essential contradiction in the principle of complementarity, which held that pairs of properties of particles, such as position and momentum, and frequency and lifetime, cannot be measured at the same time. Complementarity undergirds the concepts of wave-particle duality and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.