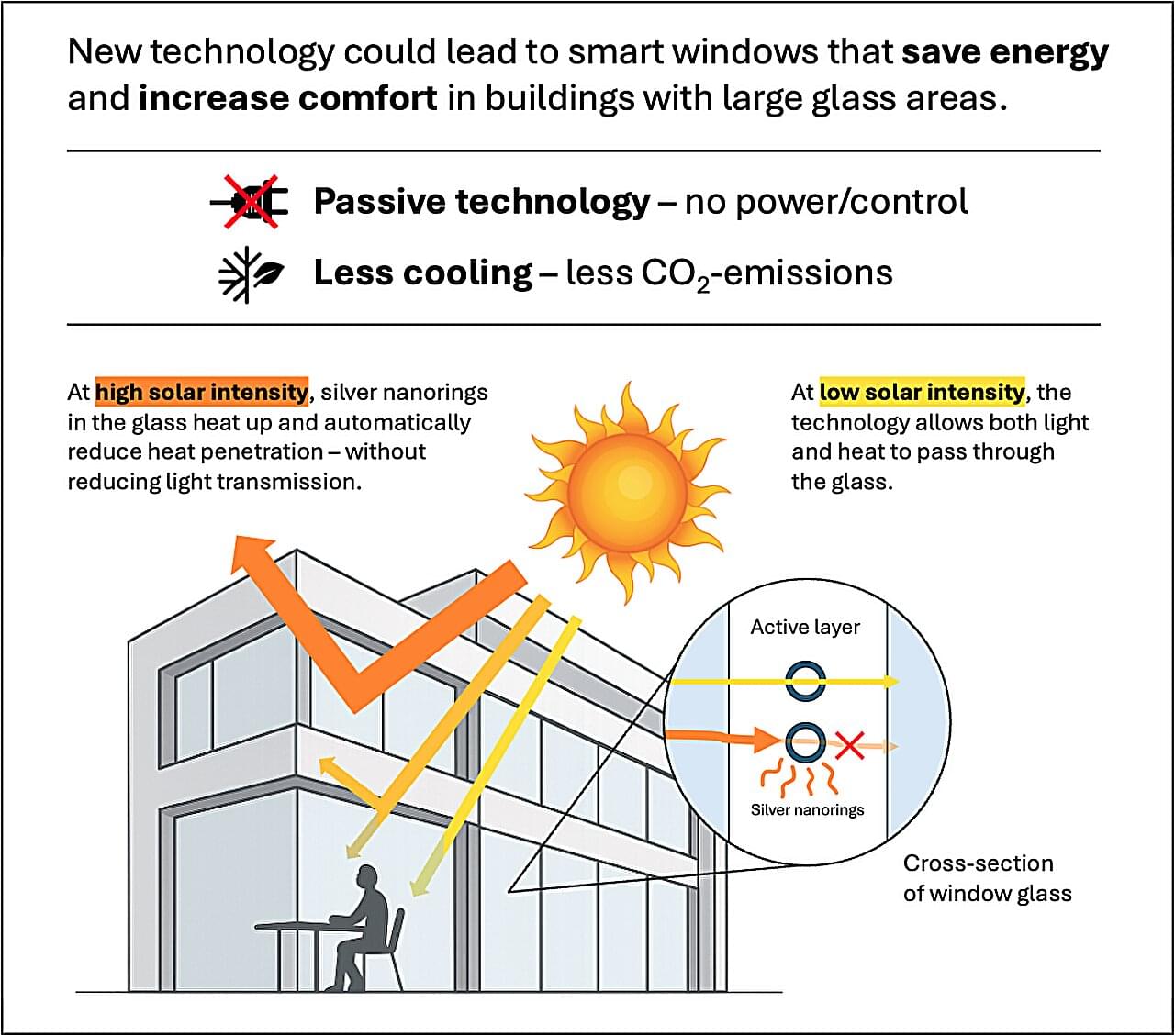
A new Danish research breakthrough could make buildings far more energy-efficient in the future. Researchers from Aarhus University’s Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Center (iNANO) have developed a light-responsive hybrid material based on so-called silver nanorings that automatically responds to solar intensity and regulates how much heat penetrates through windows.
The microscopic silver rings increasingly block near-infrared light as sunlight becomes stronger—without making the glass less transparent.
The technology functions without the use of power, sensors, or electronics—and could potentially be applied as a window coating in, for example, office buildings and modern residential buildings where large glass areas are common and heat radiation from the sun can be a challenge. This makes the solution particularly relevant at a time when energy consumption for cooling exceeds the need for heating in large parts of the world.