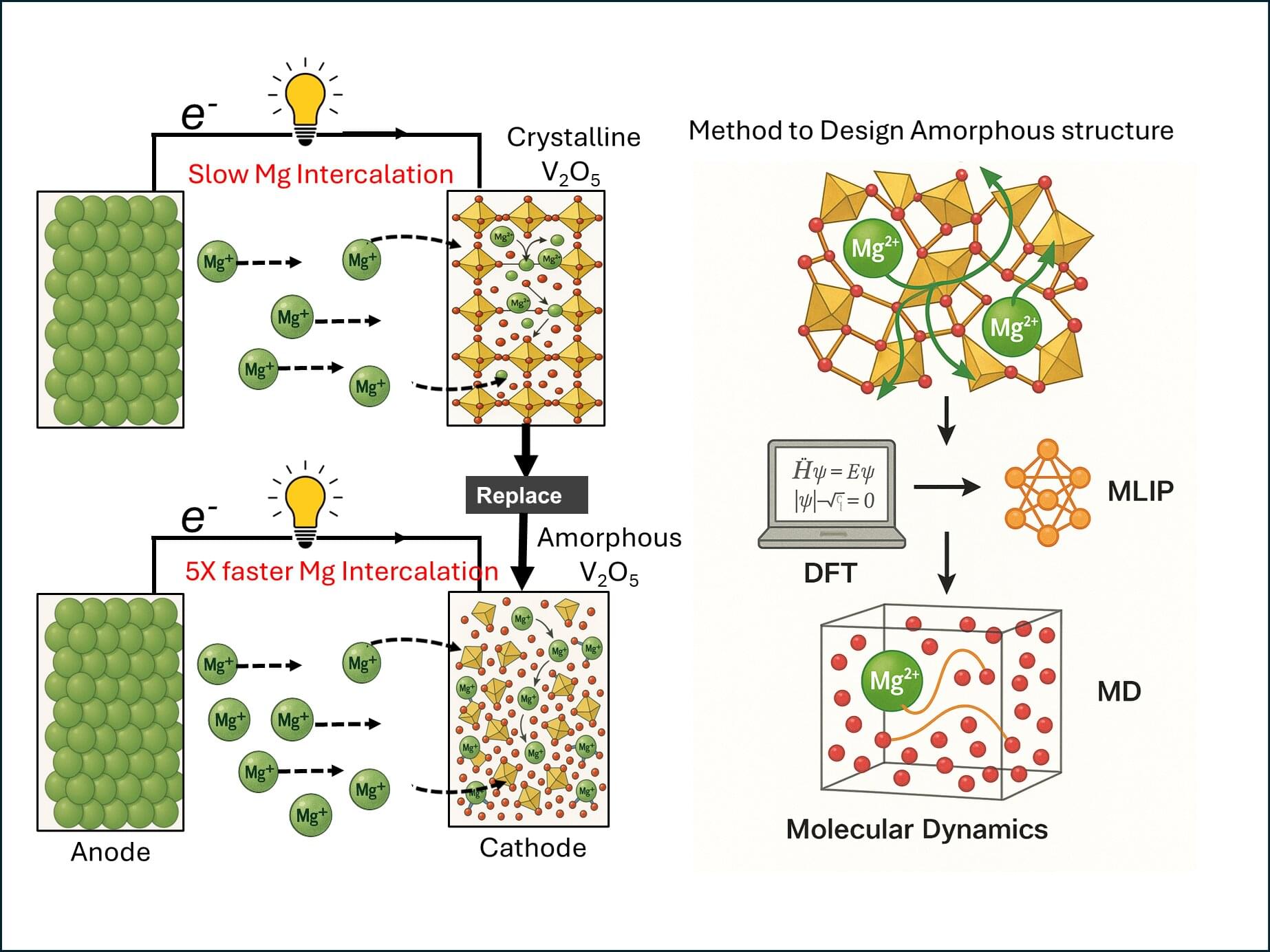
Young asteroids—which formed much later than those that were created during the formation of our solar system—are typically created when larger asteroids, planetesimals, or comets collide and break up into smaller pieces. These smaller pieces form “asteroid families” that share certain properties, like their semimajor axis, eccentricity, and inclination—all of which describe their orbital paths.
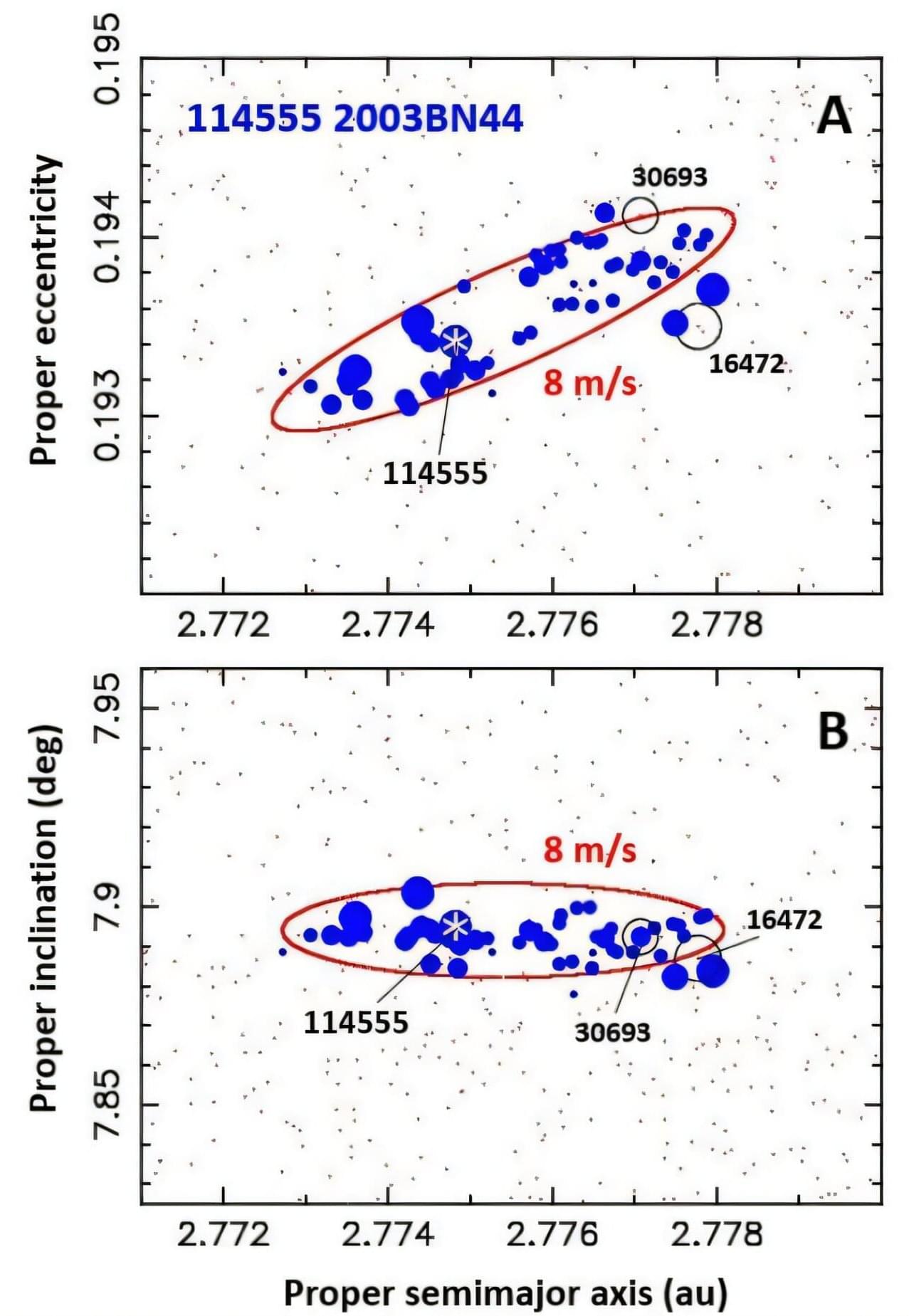
Scientists generally describe young asteroid families as being less than around 10–15 million years old and consisting of at least three members. New research, published in the journal Icarus, just revealed 63 newly discovered young asteroid families less than around 10 million years old. While many of these young families are likely to exist in our solar system, only 43 had been previously documented. The new study used a five-dimensional Hierarchical Clustering Method (HCM) with a catalog of 1.25 million asteroid orbits, which enabled the team to bring the total number of known young asteroid families to 106.
The team searched for clustering in proper orbital elements (semimajor axis, eccentricity, inclination, nodal and perihelion longitudes) at various times in the past 10 million years to find groups with similar elements.