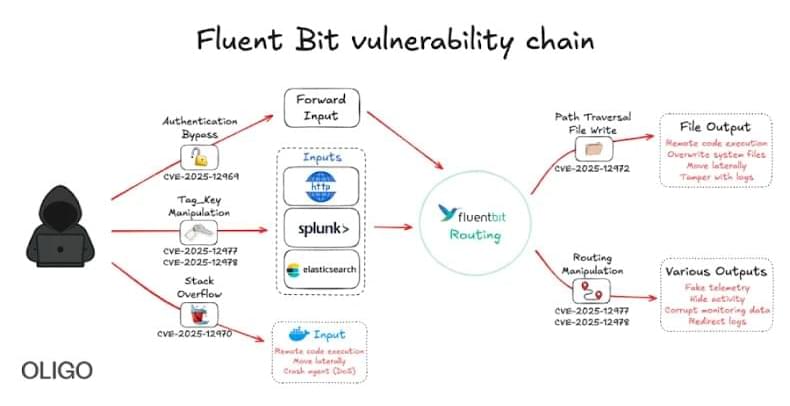
Fluent Bit, deployed in billions of containers, has five new flaws enabling log tampering, remote code execution, and cloud takeover paths.

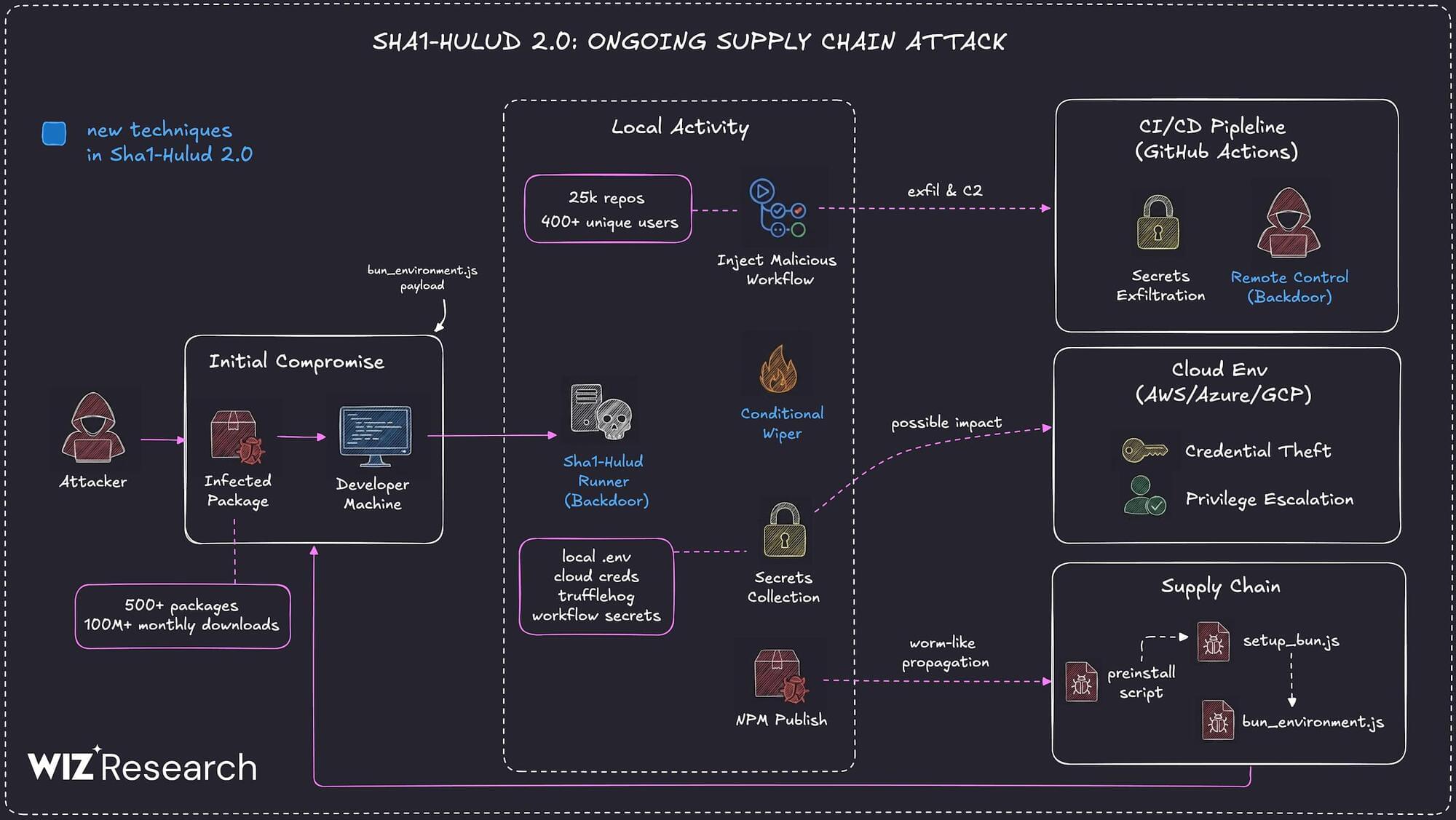
Multiple security vendors are sounding the alarm about a second wave of attacks targeting the npm registry in a manner that’s reminiscent of the Shai-Hulud attack.
The new supply chain campaign, dubbed Sha1-Hulud, has compromised hundreds of npm packages, according to reports from Aikido, HelixGuard, JFrog, Koi Security, ReversingLabs, SafeDep, Socket, Step Security, and Wiz. The trojanized npm packages were uploaded to npm between November 21 and 23, 2025. The attack has impacted popular packages from Zapier, ENS Domains, PostHog, and Postman, among others.
“The campaign introduces a new variant that executes malicious code during the preinstall phase, significantly increasing potential exposure in build and runtime environments,” Wiz researchers Hila Ramati, Merav Bar, Gal Benmocha, and Gili Tikochinski said.

Once installed, the malware is designed to launch a core module that’s responsible for loading other plugins embedded in the shellcode into memory. It also comes fitted with a variety of anti-detection and persistence techniques. The activity has not been attributed to any known threat actor or group.
“After the proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for the vulnerability was publicly released, attackers quickly weaponized it to distribute ShadowPad malware via WSUS servers,” AhnLab said. “This vulnerability is critical because it allows remote code execution with system-level permission, significantly increasing the potential impact.”
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.

Microsoft has warned IT administrators to prepare for the removal of Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) from Windows Server releases starting in November 2034.
The legacy WINS computer name registration and resolution service has been deprecated with the release of Windows Server 2022 in August 2021, when Microsoft stopped active development and working on new features.
Windows Server 2025 will be the final Long-Term Servicing Channel release to come with WINS support, with the feature to be removed from future releases.

A Russian-linked campaign delivers the StealC V2 information stealer malware through malicious Blender files uploaded to 3D model marketplaces like CGTrader.
Blender is a powerful open-source 3D creation suite that can execute Python scripts for automation, custom user interface panels, add-ons, rendering processes, rigging tools, and pipeline integration.
If the Auto Run feature is enabled, when a user opens a character rig, a Python script can automatically load the facial controls and custom UI panels with the required buttons and sliders.

ClickFix attack variants have been observed where threat actors trick users with a realistic-looking Windows Update animation in a full-screen browser page and hide the malicious code inside images.
ClickFix is a social-engineering attack where users are convinced to paste and execute in Windows Command Prompt code or commands that lead to running malware on the system.
The attack has been widely adopted by cybercriminals across all tiers due to its high effectiveness and has continually evolved, with increasingly advanced and deceptive lures.

SitusAMC, a company that provides back-end services for top banks and lenders, disclosed on Saturday a data breach it had discovered earlier this month that impacted customer data.
As a real-estate (commercial and residential) financing firm, SitusAMC handles back-office operations in areas like mortgage origination, servicing, and compliance for banks and investors.
The company generates around $1 billion in annual revenue from 1,500 clients, some of whom are banking giants like Citi, Morgan Stanley, and JPMorgan Chase.


Hundreds of trojanized versions of well-known packages such as Zapier, ENS Domains, PostHog, and Postman have been planted in the npm registry in a new Shai-Hulud supply-chain campaign.
The malicious packages have been added to NPM (Node Package Manager) over the weekend to steal developer and continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) secrets. The data is automatically posted on GitHub in encoded form.
At publishing time, GitHub returned 27,600 results corresponding to entries related to the recent attack.
