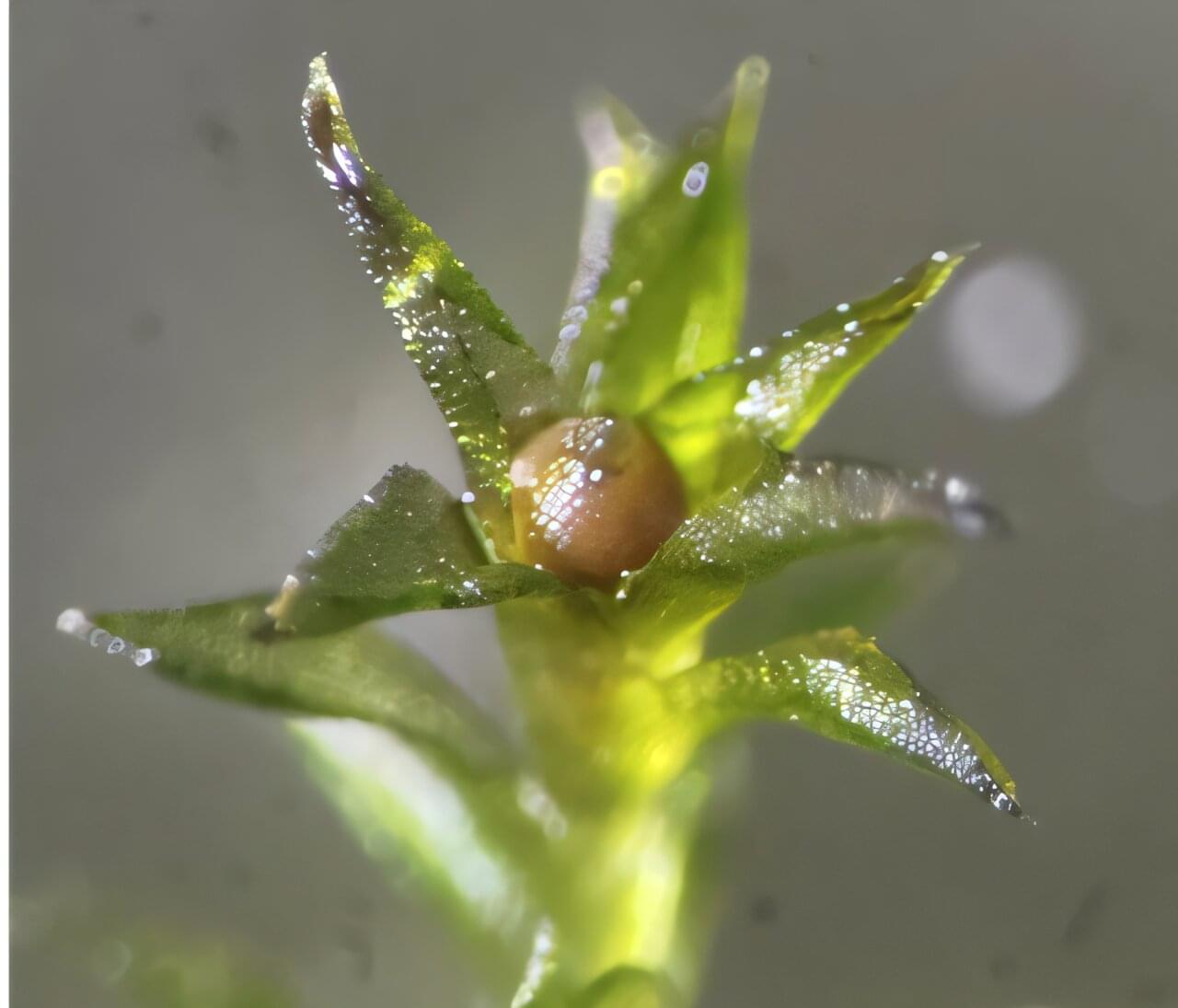
Mosses thrive in the most extreme environments on Earth, from the peaks of the Himalayas to the sands of Death Valley, the Antarctic tundra to the lava fields of active volcanoes. Inspired by moss’s resilience, researchers sent moss sporophytes—reproductive structures that encase spores—to the most extreme environment yet: space.
Their results, published in the journal iScience on November 20, show that more than 80% of the spores survived nine months outside of the International Space Station (ISS) and made it back to Earth still capable of reproducing, demonstrating for the first time that an early land plant can survive long-term exposure to the elements of space.
“Most living organisms, including humans, cannot survive even briefly in the vacuum of space,” says lead author Tomomichi Fujita of Hokkaido University. “However, the moss spores retained their vitality after nine months of direct exposure. This provides striking evidence that the life that has evolved on Earth possesses, at the cellular level, intrinsic mechanisms to endure the conditions of space.”