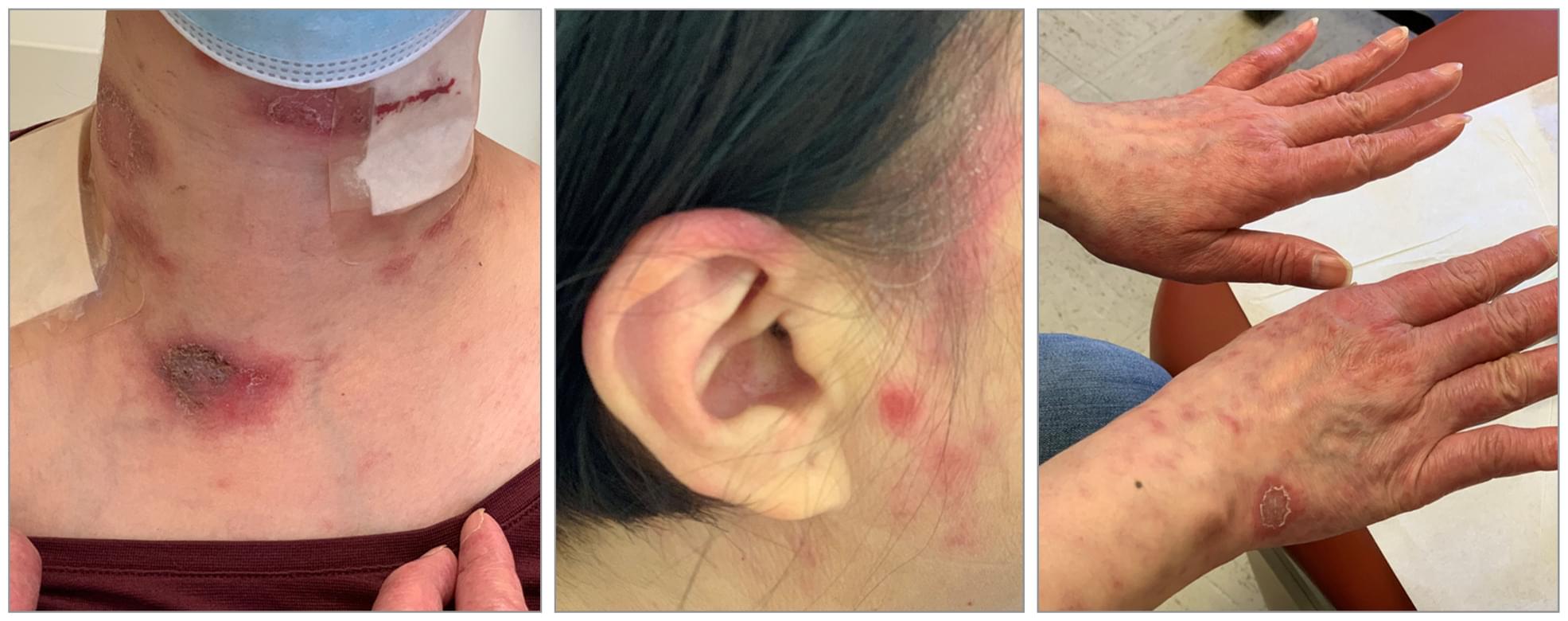
A patient receiving adalimumab for rheumatoid arthritis had ulcerated plaques on the anterior and lateral aspects of the neck, upper chest, and nape and erythroderma on the dorsum of the hands.
What is the diagnosis, and what would you do next?
Build your website in minutes with Odoo — free domain for the first year + your first app free for life!
Start here: https://www.odoo.com/r/PR8
…
When people hear the word “paradox,” they usually think of something like a logic puzzle or a brain teaser. Something strange, but mostly harmless. But in quantum physics, paradoxes aren’t just puzzles. They point to something much deeper—a place where our understanding of reality breaks down.
1:13 Quantum Paradox.
8:53 The Quantum Eraser Paradox.
13:52 Wigner’s Friend (Observer vs. Observer)
19:50 Time Symmetry and Retrocausality.
26:26 Quantum Pseudo-Telepathy.
32:28 Quantum Cheshire Cat.
38:18 The Quantum Suicide Twist.
44:20 The Black Hole Information Paradox.
51:02 The Measurement Problem.
57:42 Closing the Loop.
Thank you for watching, and don’t forget to subscribe smile
Einstein never liked the idea that nature is uncertain and he once said “does that mean the Moon is not there when I am not looking at it”. He believed we live in an orderly Universe which is fundamentally rational and that there should always be a reason why thing happen. But there is a way to have the objective Universe of Einstein and the uncertainty of quantum physics and that is by explaining quantum mechanics as the physics of ‘time’ with the future as an emergent property.
In this radical theory the mathematics of quantum mechanics represents the physics of ‘time’ as a physical process with classical physics representing process over a period of time as in Newton’s differential equations. This is a process formed by the spontaneous absorption and emission of light photon energy. This forms a continuous process of energy exchange that forms the ever changing world of our everyday life.
The Universe is a continuum with the future coming into existence photon by photon with each new photon electron coupling or dipole moment. This forms the movement of positive and negative charge with the continuous flow of electromagnetic fields.
Consciousness in the form of electrical activity in the brain is the most advanced part of this process and can therefore comprehend this process as ‘time’. With a past that has gone forever and a future that is always uncertain in the form of a probability function or quantum wave particle function that is explained mathematically by Schrödinger’s wave equation Ψ. Therefore each individual is in the centre of their own reference frame as an interactive part of this process. With their own time line from the past into the future being able to look back in time in all directions at the beauty of the stars! It is this personalization of the brain being in ‘the moment of now’ in the center of its own reference frame that gives us the concept of ‘mind’ with each one of us having our own personal view of the beauty and uncertainty of life.
It is not that there is uncertainty if the Moon is there or not if nobody looks. It is that the physical act of looking will form new light photon oscillations or vibrations relative to the actions of the observer in a continuous flow of cause and effect. The wave particle duality of light is acting like the bits or zeros and ones of a computer. This forms an interactive process continuously forming a blank canvas that we can interact with turning the possible into the actual! Any observation of the Moon will be over a period of time with the wave nature of light explaining diffraction, interference, reflection and refraction. But the particle nature of light the ‘photon’ will only come into existence when the light comes in contact with the lenses and mirrors of the telescope being used. And finally with new photons be formed in the eye of the observer the uncertainty of the observation will be completed using both the wave and particle nature of light!
What we see in our everyday life as an uncertain future is formed by a physical process that at the smallest scale is represented mathematically by Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle ∆×∆p×≥h/4π with the Planck constant ħ=h/2π being a constant of action in the dynamics geometry of space and time! This theory takes quantum potential, electrical potential and gravitational potential and combines them into one universal process. That explains why we all have a potential future in our everyday life that is always uncertain. This is done by making the future an emergent property energy ∆E slows the rate that time ∆t flows creating a future relative to the energy and momentum of each object or life form. For in this theory creation is truly in the hand and eye of the beholder with an objective reality in the form of a dynamic interactive process that forms an infinity of possibilities. Please share and subscribe it will help the promotion of this theory!
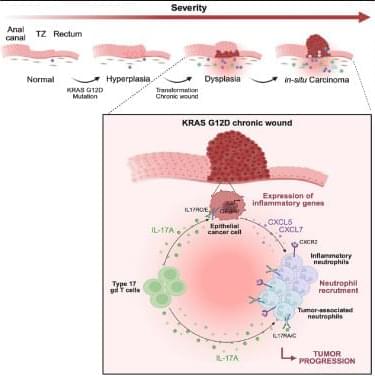
Petitpas et al. dissect the single-cell transcriptome underlying the sequential steps of pre-malignant lesions and early anorectal cancer, mimicking disease evolution seen in patients, at the epithelial and immune level. They reveal a key epithelial-immune cell crosstalk involving IL-17-producing T lymphocytes and neutrophils as essential for the dysplasia-carcinoma progression.
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDjOS0VHEr4Please support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:- LMNT: https://drinkLM…
Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDjOS0VHEr4Please support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:- LMNT: https://drinkLM…

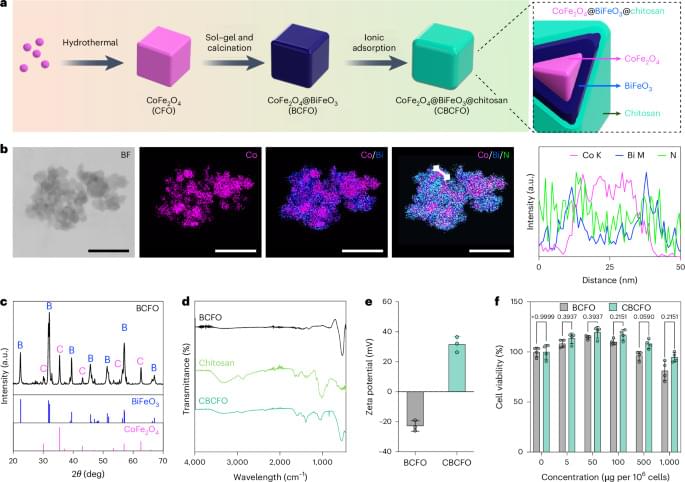
An intriguing paper by Lin et al. where cells were engineered to express a signaling pathway that transcribes a gene of interest upon generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by CBCFO nanoparticles in response to applied electromagnetic fields. When implanted in a mouse model of diabetes, nanoparticle-treated genetically engineered cells produced insulin and decreased blood glucose levels in the mice after electromagnetic field application.
Wireless magnetic control of gene expression in mammalian cells has been developed based on intracellular nanointerface and ROS-mediated signalling. The approach allows remotely tunable insulin release and regulates blood glucose in diabetic mice.