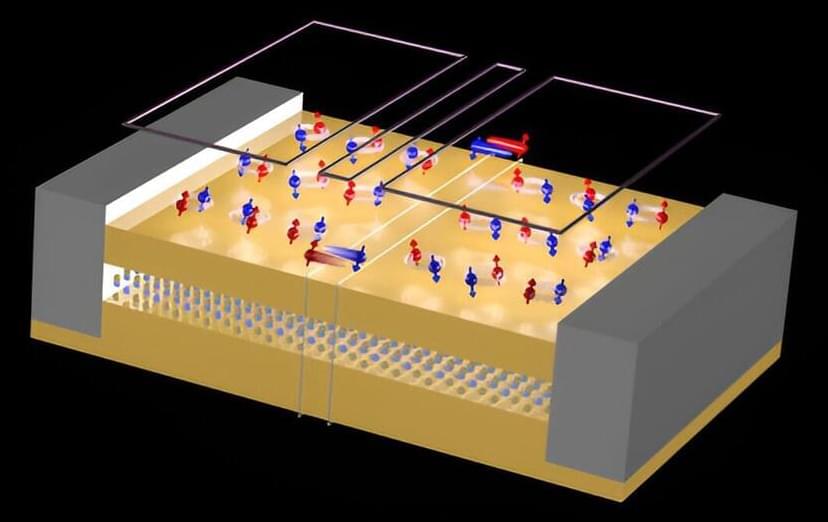
Physicists at RIKEN have developed an electronic device that hosts unusual states of matter, which could one day be useful for quantum computation.
When a material exists as an ultrathin layer—a mere one or a few atoms thick—it has totally different properties from thicker samples of the same material. That’s because confining electrons to a 2D plane gives rise to exotic states. Because of their flat dimensions and their broad compatibility with existing semiconductor technologies, such 2D materials are promising for harnessing new phenomenon in electronic devices.
These states include quantum spin Hall insulators, which conduct electricity along their edges but are electrically insulating in their interiors. Such systems when coupled with superconductivity have been proposed as a route toward engineering topological superconducting states that have potential application in future topological quantum computers.