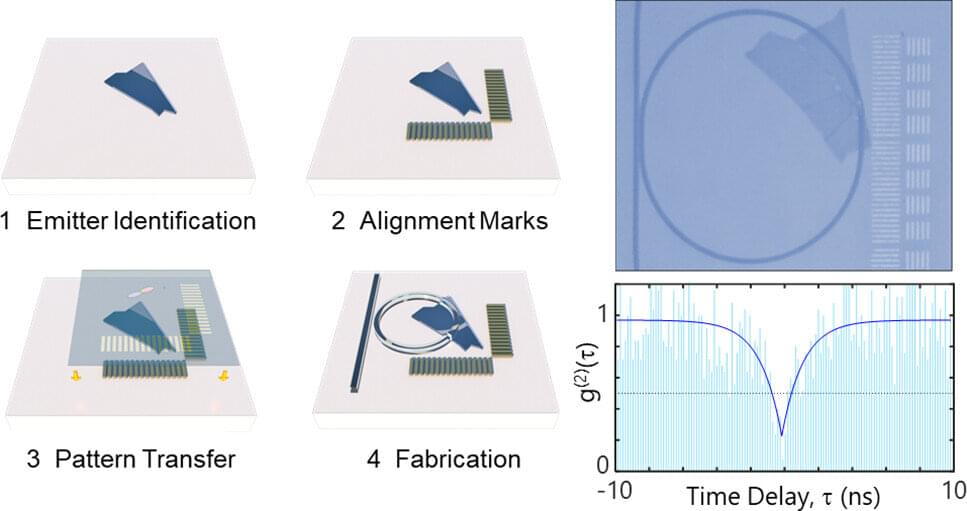
Jan 18, 2023
Driving the era of silicon photonics with integrated lasers
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: innovation, robotics/AI
During the past several decades, silicon has undeniably been the crown jewel of the semiconductor industry’s transformation. But with the plateauing of Moore’s Law, the increasing complexity of circuits, and the explosive growth of data-intensive applications, companies need even more innovative ways to compute, store, and move data faster. As a result, scale, speed, and power have become underlying forces to handle both advanced intelligence and computing needs.
Silicon photonics has already earned a stronghold for its impressive performance, power efficiency, and reliability compared to conventional electronic integrated circuits. Overall speed requirements have become fast enough, benefiting the technology’s strengths to transfer data efficiently over ever-shortening distances. Meanwhile, artificial intelligence (AI) is pushing computing to a point where electronic components need to communicate over distances to combine and integrate multiple XPUs (application-specific processing units).