Over half (53.3%) of data scientists and engineers say they plan to deploy large language model (LLM) applications into production in the next 12 months or “as soon as possible” Learn more about why and how this massive retooling is happening — and how enterprises can be ready.
I’ve got two questions for you that you’ve undoubtedly generically heard of before. Prepare yourself mentally. First, have we hit the wall? Second, does size matter? Both of those questions have deeply entered into the behind-the-scenes news about the latest in generative AI.
Generative AI is the type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that can generate various outputs by the entry of text prompts. You’ve likely used or known about ChatGPT by AI maker OpenAI which allows you to enter a text prompt and get a generated essay in response, referred to as a text-to-text or text-to-essay style of generative AI, for my analysis of how this works see the link here.
A recent remark by the OpenAI CEO has brought to the fore an ongoing debate whether generative AI such as ChatGPT is nearing a wall and getting bigger won’t make a difference. Here’s the inside scoop on that hefty debate.
The push for the smartest web browser is officially on. Just a month after Microsoft announced an AI-powered version of its search engine Bing, Google has announced it will be also be adding AI functionality to allow users to interact with it in more human ways. Right now, the substance of the announcement is all speculation. There is no known release date (yet) for its AI-powered engine, and no specific AI model has been chosen. Still, Google, which has invested billions on AI in just the past few years, is throwing its hat in the ring as a clear sign that the race for AI leadership is far from over. Its recent announcement merging its DeepMind and Brain divisions further reiterates that.
The addition of Generative AI capabilities to Google Search will be critical if Google intends to remain the top search engine globally. And while there are more questions than answers at this time, Google is going to be adding conversational to its search platform and it should be well received.
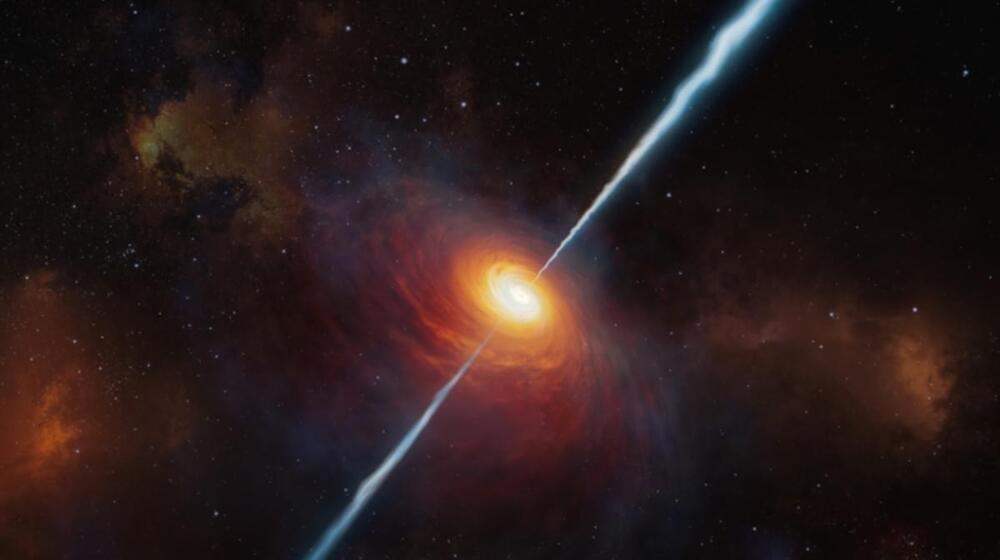
Quasars are the most radiant and powerful objects in the entire universe, but nobody knew how they were triggered—until now.
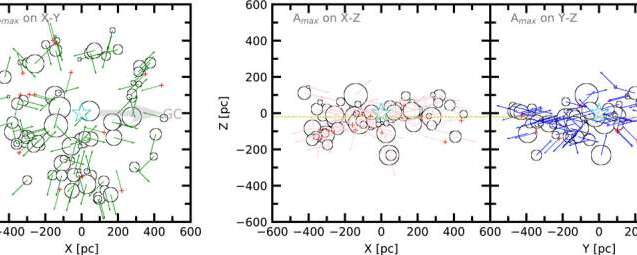
Morphological study of open clusters can provide observational evidence for tracing the formation mechanism of star clusters and help to explore the evolution of star clusters.
The morphology of open clusters on the two-dimensional (2D) projection planes mostly conforms to the core-shell structure. However, whether this layered structure actually exists in three-dimensional (3D) space is not known.
Recently, researchers from the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a rose diagram overlaying method based on Gaia data to study the 3D layered structure of open cluster samples within 500 parsec (pc) near the sun.
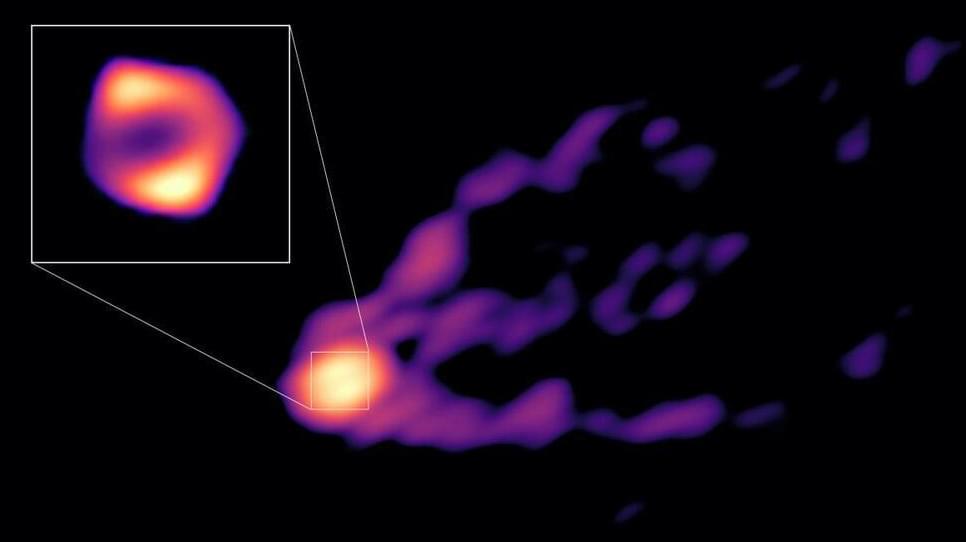
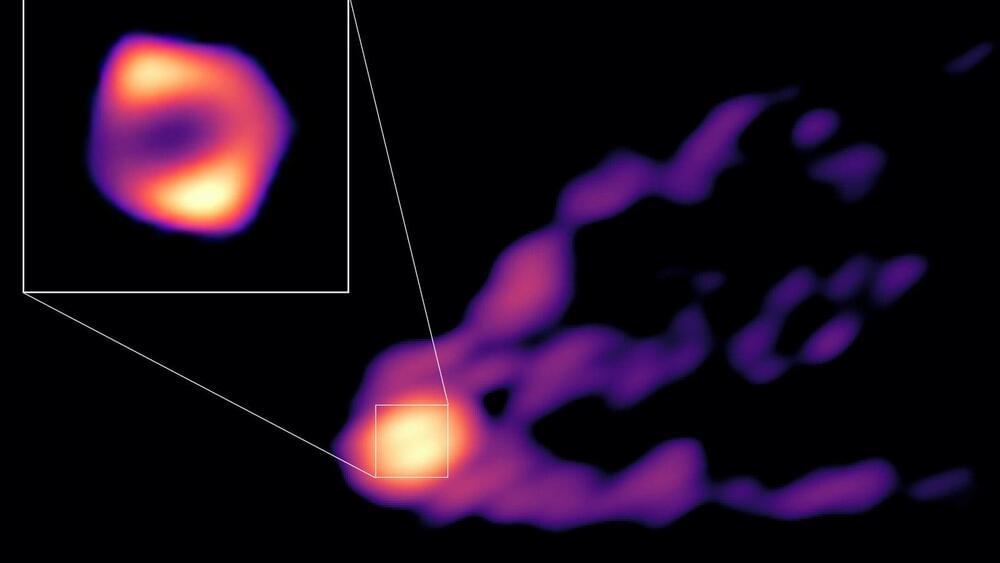
Astronomers have captured the first direct image of a black hole as it blasts out a powerful jet.
The new photo features the monstrous supermassive black hole at the heart of the galaxy Messier 87 (M87), the first black hole ever directly imaged by humanity.
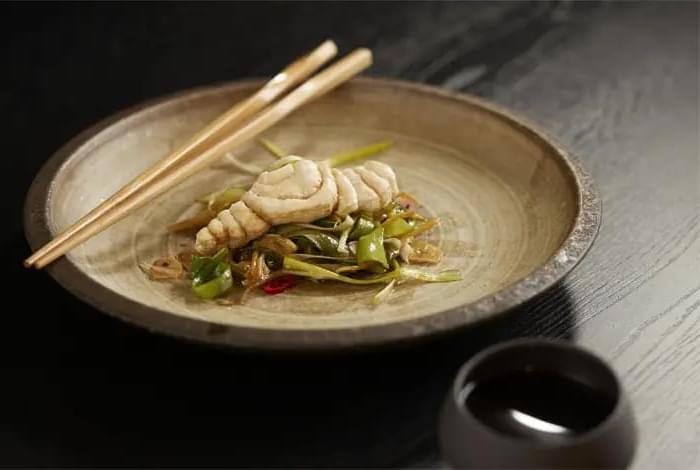
World’s first cultivated grouper fillet
Posted in food
Israeli company Steakholder Foods has announced that it successfully 3D printed the first ready-to-cook cultivated grouper fish product.
Credit: Steakholder Foods.
The grouper is a species of fish that belongs to the subfamily Epinephelinae and is known for its large size and unique appearance. There are various species found in different parts of the world, including the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, the Mediterranean, and the Indo-Pacific region.
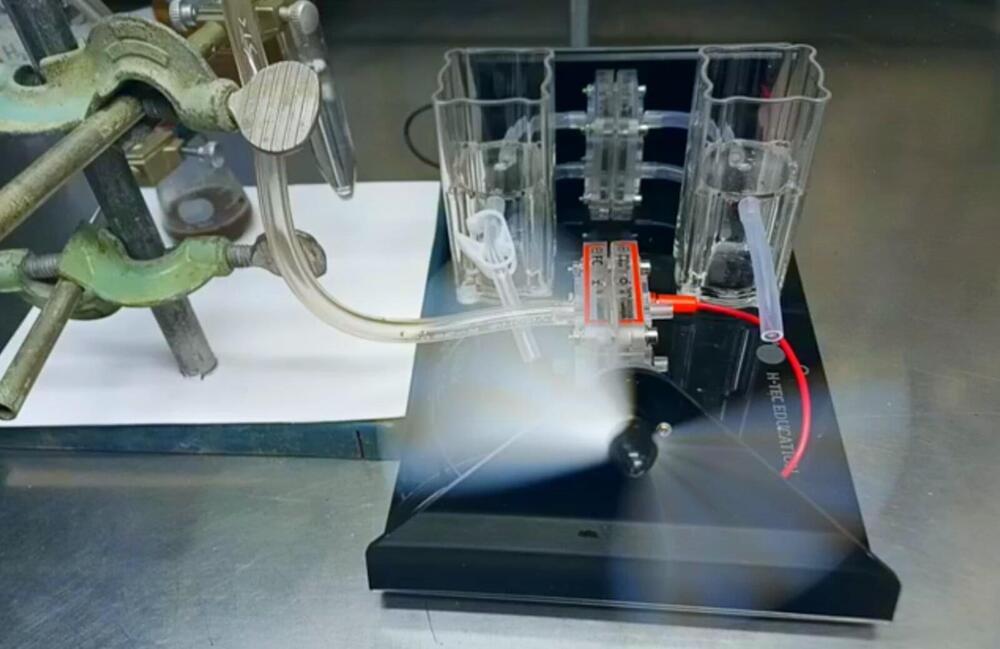
University of Alberta researchers have developed a new catalyst that could revolutionize how we generate power and purify water. When placed in any type of water and provided with a small amount of power, the catalyst produces hydrogen that can be fed into a fuel cell to generate electricity along with distilled water that is safe to drink.
The catalyst was discovered almost entirely by chance when Robin Hamilton was creating an electrode for an undergraduate student working on a waste biomass upcycling project. He mixed up a combination of powders and allowed them to sit overnight in water, intending to finish the cell the following day. When he returned in the morning, the mixture was bubbling—a reaction that was extremely out of the ordinary.
“It ends up being that when you mix these two things together, they interact, they work together and hydrogen comes off. It floored us,” says Hamilton, a senior research associate in the Department of Chemistry.
The supermassive black hole has a mass billions of times that of the sun and is around 55 million light-years from Earth. Scientists used data gathered from more than a dozen telescopes worldwide to compile the picture.
Suvorexant (Belsomra), a dual orexin receptor antagonist approved for insomnia, reduced levels of tau phosphorylation and amyloid beta, a small clinical trialopens in a new tab or window showed.
The ratio of phosphorylated tau-threonine-181 (p-tau-181) to unphosphorylated tau-threonine-181 decreased 10% to 15% in cognitively normal adults treated with suvorexant 20 mg compared with placebo, reported Brendan Lucey, MD, MSCI, of Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, and co-authors.
Amyloid-beta levels fell 10% to 20% compared with placebo starting 5 hours after suvorexant administration, the researchers wrote in Annals of Neurologyopens in a new tab or window.
— Both amyloid and tau levels fell in early trial.