Strategic agreement calls for fleet of Boston Dynamics robots to be deployed across more than 20 facilities over the next two years, to position retailer for the future.
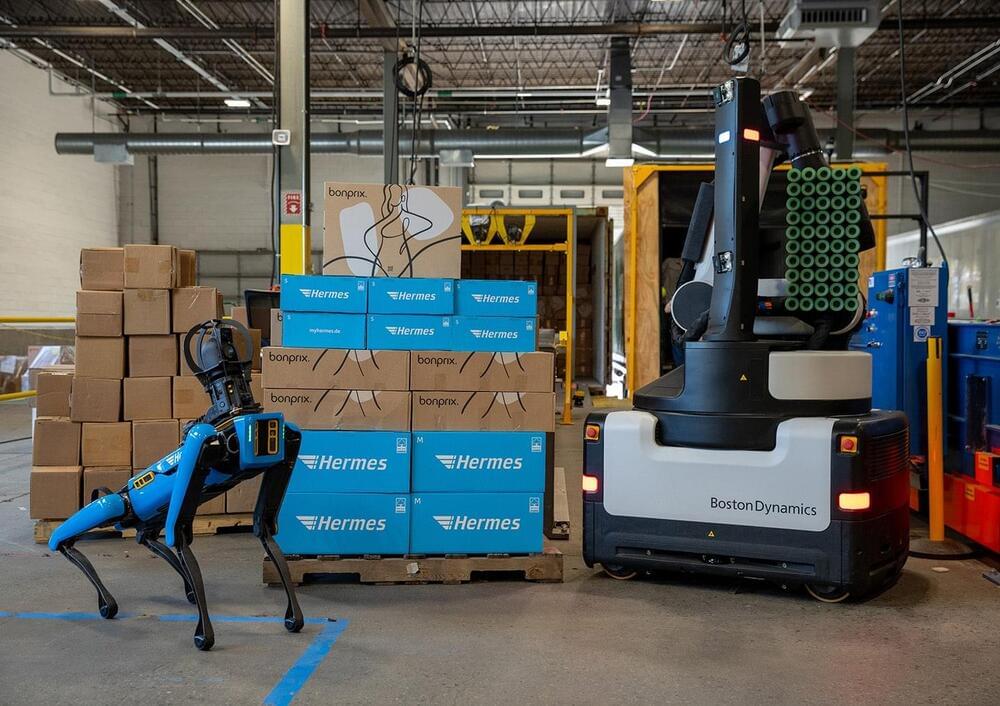
Hamburg, Germany / Waltham, MA, USA – September 11, 2023 – The Otto Group, one of the world’s largest e-commerce retailers, has signed a strategic agreement with Boston Dynamics, the global leader in mobile robotics, to continue automating its logistics operations. The plan is to deploy Boston Dynamics’ Spot® robots in more than 10 and Stretch™ robots in more than 20 of the group’s facilities over the next two years, beginning with Hermes Fulfilment. The deployment supports Otto Group’s efforts to improve safety, increase operational efficiency and address labor shortages for specific types of warehouse work and the agreement marks the first time both of Boston Dynamics’ commercially available robots will be deployed together at enterprise scale.
Under the terms of the agreement, Spot, the four-legged mobile robot from Boston Dynamics, will support tunnel inspections and predictive maintenance activities for operations equipment, including thermal monitoring, analog gauge reading and acoustic detection of pressurized air and gas leaks. The Spot fleet will also run autonomous missions, collecting data for machine learning models to support tasks like fire exit egress monitoring and detecting slight changes in storage racks to keep Otto Group’s warehouses even safer. In addition, the Otto Group will be utilizing Stretch, Boston Dynamics’ box-moving robot designed for warehouse applications. Stretch will begin unloading containers at 10 facilities next year, with the goal of having all sites operational by the end of 2025. Stretch, which is particularly useful for unloading heavy packages in the container sector, will provide technological support for physically demanding activities.