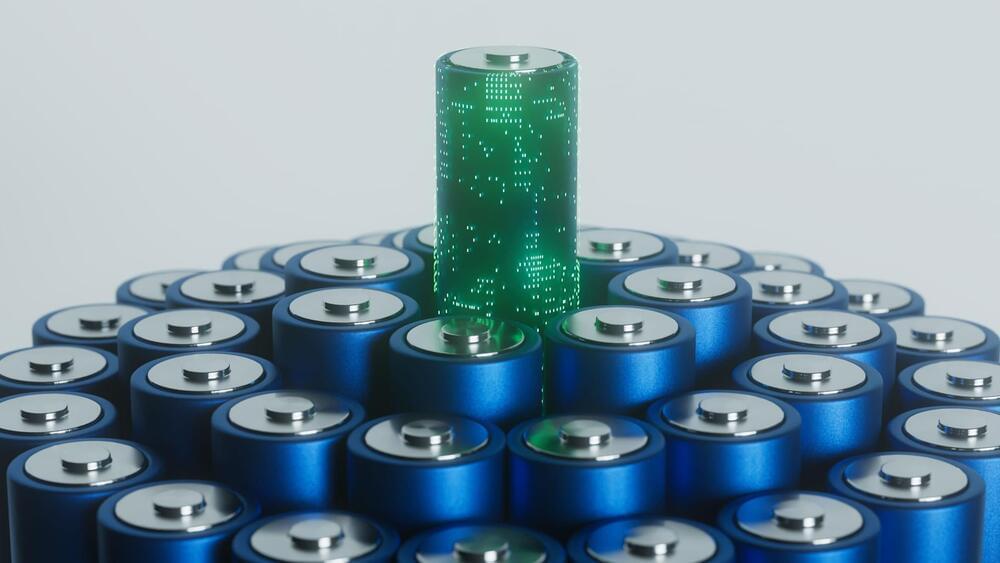
Researchers from Germany and China have created a new method to produce lithium-metal batteries that are solid-state, safer, and more durable.


OUR LANDS ARE GREEN, AND SKIES ARE BLUUUEEEE

The successful transfer of a gene that produces HMW-HA paves the way for improving the health and lifespan of humans, too. In a groundbreaking endeavor, scientists at the University of Rochester have successfully transferred a longevity gene from naked mole rats to mice, leading to enhanced health and increased lifespan. Naked mole rats, noted for their resistance to age-related diseases, have a gene that produces high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA), which when introduced to mice, demonstrated potential anti-aging benefits.
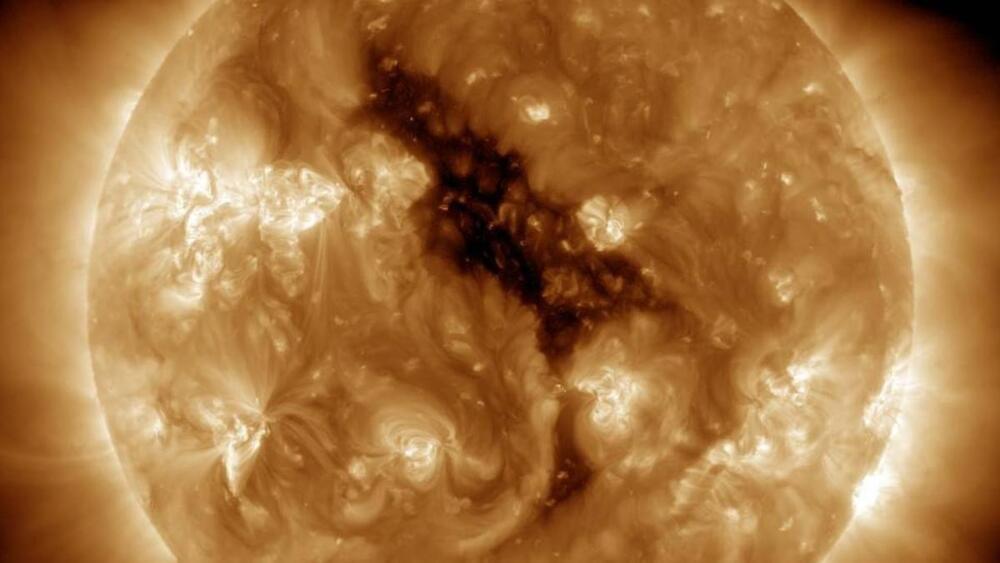
Though these picojets may be small and last no more than 60 seconds, as Chitta pointed out, they are still powerful in their own right.
“The ‘pico’ prefix refers to the energy scale of the jet. The picoflare jets that we discovered are a trillion times energetically weaker compared to large X-class flares,” he said, X-class flares being the sun’s most powerful explosive outflows.
“Still,” he continued, “the energy content of a single picoflare jet that lives for about 1 minute is equal to the average power consumed by about 10,000 households in the UK over an entire year.”

Anna Gross in London.
In June, Chanos — who won big bets on the downfall of US energy group Enron and the German payments company Wirecard — announced that his eponymous investment firm is raising several hundred million dollars for a fund that will take short positions in US-listed data centre groups.

Be one of the first 200 people to sign up with this link and get 20% off your subscription with Brilliant.org! https://brilliant.org/realscience/
Watch this video ad-free on Nebula:
https://nebula.tv/videos/realscience-intelligence-without-a-brain.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/realscience.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/stephaniesammann.
Credits:
Narrator: Stephanie Sammann.
Writer: Ashleen Knutsen.
Editor: Dylan Hennessy (https://www.behance.net/dylanhennessy1)
Editor: Leany Muñoz.
Illustrator: Jacek Ambrożewski.
Illustrator/Animator: Kirtan Patel (https://kpatart.com/illustrations)
Animator: Mike Ridolfi (https://www.moboxgraphics.com/)
Sound: Graham Haerther (https://haerther.net)
Thumbnail: Simon Buckmaster (https://twitter.com/forgottentowel)
Producer: Brian McManus (https://www.youtube.com/c/realengineering)
Imagery courtesy of Getty Images.
REFERENCES:
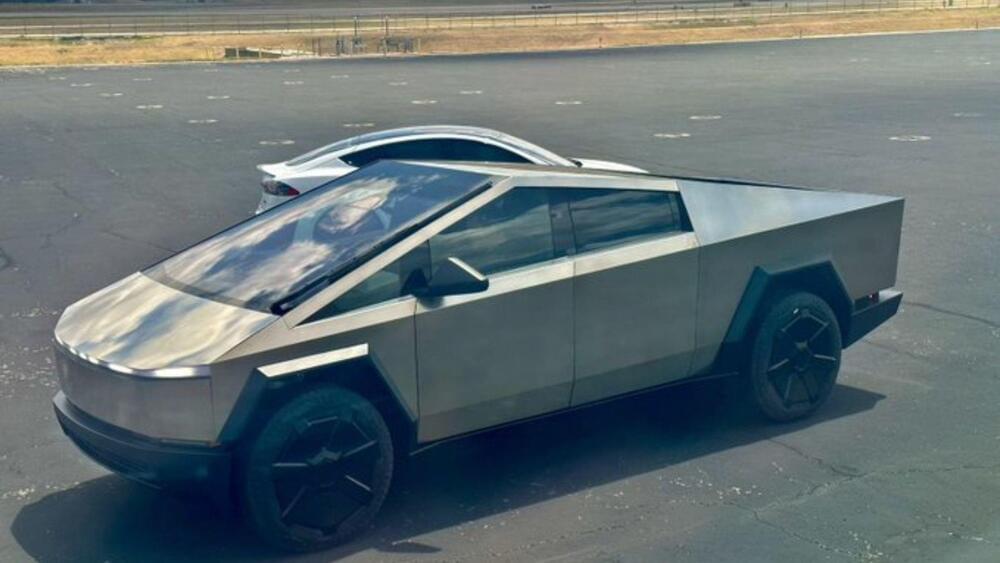

The Tesla CEO keeps pushing his employees to achieve more, sometimes even the impossible.
Elon Musk allegedly asked Tesla employees to ensure that Cybertruck production achieves single-digit micron tolerance, much like Lego or even soda cans are made with. This instruction was sent to employees in an email, which was later leaked, Electrek.
The Cybertruck is Tesla’s most awaited electric vehicle, running several years behind schedule and expected to begin deliveries by the end of this quarter. The vehicle’s iconic shape piqued many potential buyers’ interest when unveiled in 2019.
Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory have successfully developed a new way to produce a specific type of photon that could prove critical for quantum data exchange, notably encryption. The specific kind of photons, called “circularly polarized light,” have thus far proved challenging to create and control, but this new technique makes the process easier and, importantly, cheaper. This was achieved, the team explains, by stacking two different, atomically thin materials to “twist” (polarize) photons in a predictable fashion.
Encoded, “twisted,” photons
“Our research shows that it is possible for a monolayer semiconductor to emit circularly polarized light without the help of an external magnetic field,” explained Han Htoon, a scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. “This effect has only been achieved before with high magnetic fields created by bulky superconducting magnets, by coupling quantum emitters to very complex nanoscale photonics structures, or by injecting spin-polarized carriers into quantum emitters. Our proximity-effect approach has the advantage of low-cost fabrication and reliability,” he added.
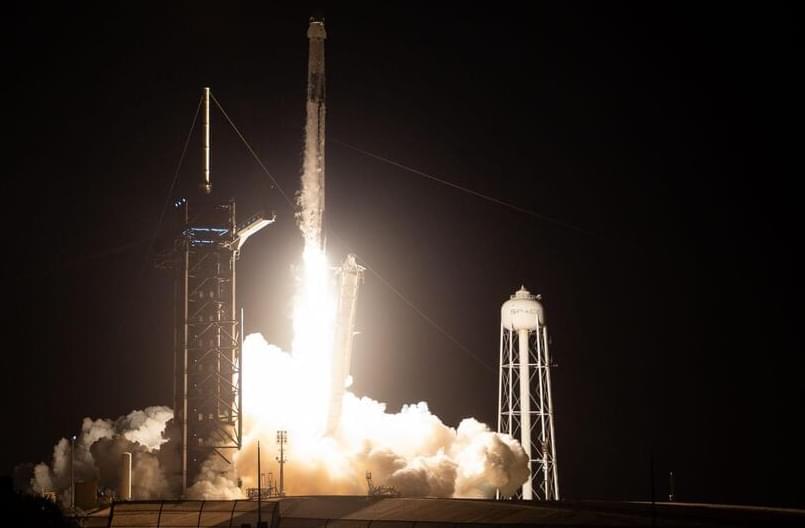

Four astronauts from four countries are on the ISS for the SpaceX Crew-7 mission.
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket successfully launched four astronauts from different space agencies to the International Space Station (ISS) on Friday, after a one-day delay due to a technical issue with the spacecraft’s life support system.
As per NASA, the rocket lifted off from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 3:27 am Eastern Time (1:57 pm IST) carrying the Crew Dragon capsule named Endurance, which separated from the rocket’s upper stage about 12 minutes later.