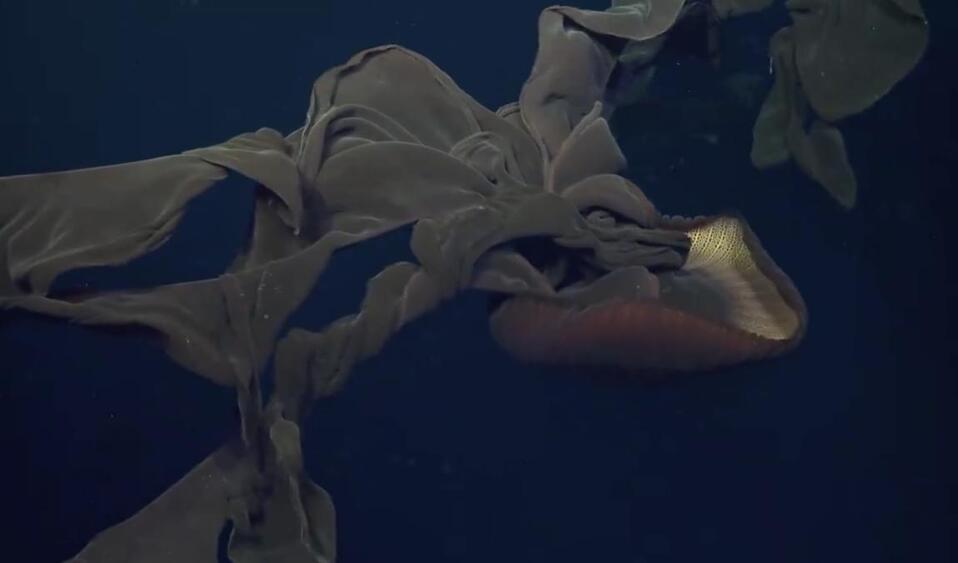
An elusive creature of the deep sea.


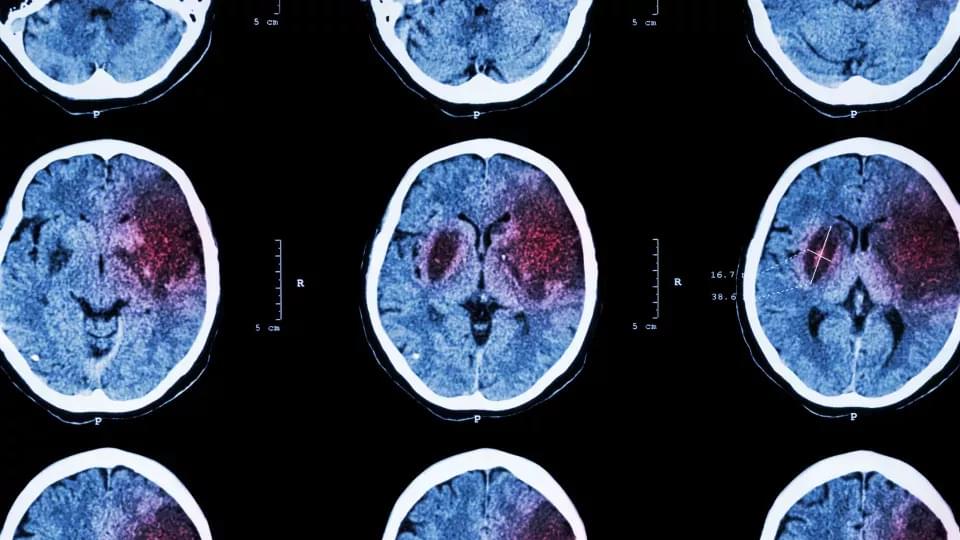
Researchers have succeeded in restoring lost brain function in mouse models of stroke using small molecules that in the future could potentially be developed into a stroke recovery therapy. “Communication between nerve cells in large parts of the brain changes after a stroke and we show that it can be partially restored with the treatment,” says Tadeusz Wieloch, senior professor of neurobiology at Lund University in Sweden.
“Concomitantly, the rodents regain lost somatosensory functions, something that around 60 per cent of all stroke patients experience today. The most remarkable result is that the treatment began several days after a stroke,” Wieloch continues.
In an ischemic stroke, lack of blood flow to the brain causes damage, which rapidly leads to nerve cell loss that affects large parts of the vast network of nerve cells in the brain.

The asteroid that causes the Geminid shooting star swarm has also puzzled researchers with its comet-like tail. The infrared spectrum of rare meteorites helped to determine the composition of the asteroid.
Asteroid Phaethon, which is five kilometers in diameter, has been puzzling researchers for a long time. A comet-like tail is visible for a few days when the asteroid passes closest to the Sun during its orbit.
However, the tails of comets are usually formed by vaporizing ice and carbon dioxide, which cannot explain this tail. The tail should be visible already at Jupiter’s distance from the Sun.
An exploration of the merging of biology, AI and quantum computing and the spooky implications of it. My Patreon Page: https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodi…
An exploration of a recent paper that suggests that there may not have been a single big bang, but two at the beginning of the universe.
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
Papers:
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7x…
Tesla’s success and potential for “Total Domination” in the automotive industry is driven by their advanced technology and their ability to revolutionize vehicle production.
Questions to inspire discussion.
What is the analyst’s best idea for 2024 regarding Tesla’s stock?
—The analyst’s best idea for 2024 is to short Tesla’s stock, despite the risky and historically unsuccessful nature of such a bet.


In just one year, artificial intelligence has gone from being the stuff of science fiction movies to being used as a tool to help us polish our resumes and plan European getaways.
Although generative AI models may be capable of writing emails and reviewing code, these tech experts don’t see them replacing humans any time soon. Here’s why.