Bruce Burke and John Lawson III dive into the latest happenings in the world of AI

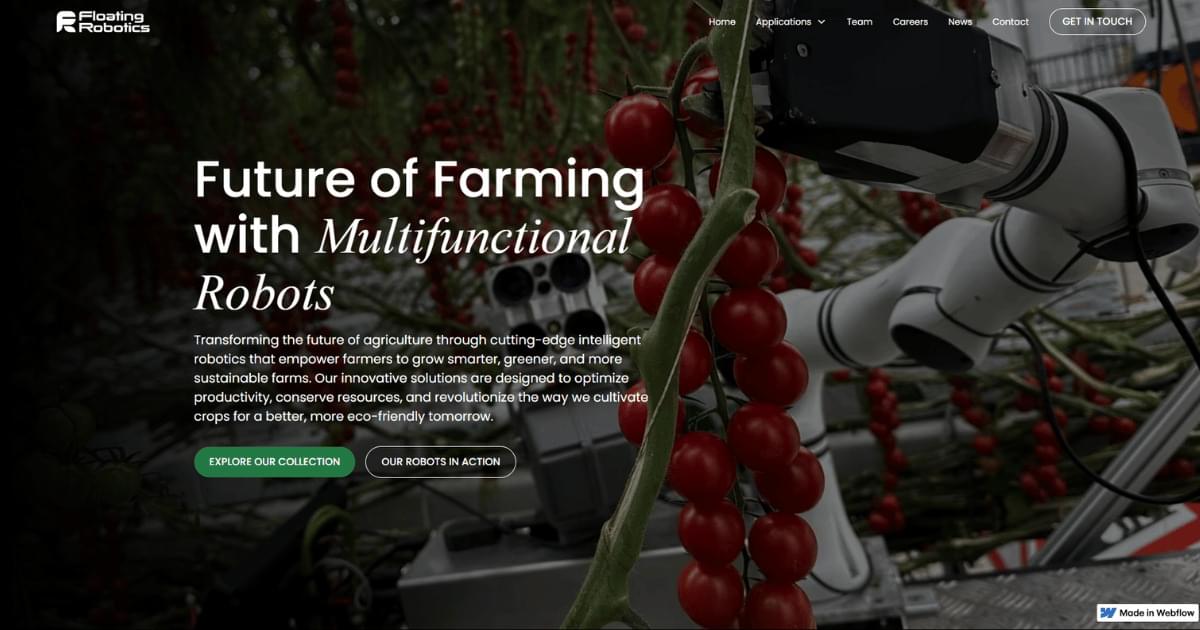
Our compact AI-driven robotic solution brings intelligence and efficiency to greenhouse automation. With 3D vision, onboard Edge Computing, and advanced AI, it detects, analyzes, and interacts with crops in real time. Mounted on a mobile platform, it can perform any of our 4 tasks and seamlessly integrates into any greenhouse to maximize yield and efficiency.
Discover Floating Robotics’ cutting-edge robotic systems designed to automate greenhouse tasks like harvesting and de-leafing, enhancing efficiency and sustainability in modern agriculture.

The deep ocean can often look like a real-life snow globe. As organic particles from plant and animal matter on the surface sink downward, they combine with dust and other material to create “marine snow,” a beautiful display of ocean weather that plays a crucial role in cycling carbon and other nutrients through the world’s oceans.
Now, researchers from Brown University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have found surprising new insights into how particles sink in stratified fluids like oceans, where the density of the fluid changes with depth. In a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, they show that the speed at which particles sink is determined not only by resistive drag forces from the fluid, but by the rate at which they can absorb salt relative to their volume.
“It basically means that smaller particles can sink faster than bigger ones,” said Robert Hunt, a postdoctoral researcher in Brown’s School of Engineering who led the work. “That’s exactly the opposite of what you’d expect in a fluid that has uniform density.”
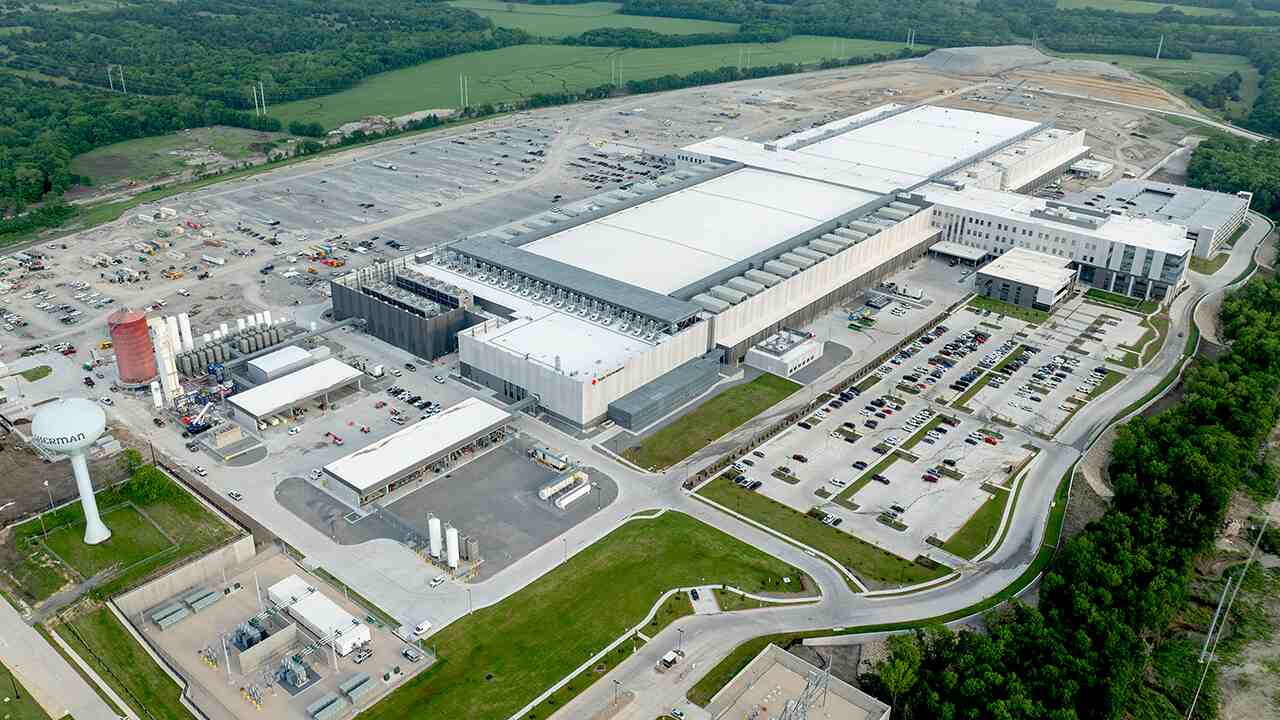

The $60 billion investment involves building or expanding seven chip-making facilities that Texas Instruments has in Sherman, Texas; Richardson, Texas; and Lehi, Utah. Notably, the North Texas city of Sherman will get two new facilities as part of Texas Instruments’ vision to manufacture hundreds of millions of chips daily.
The move comes a few years after the Biden Administration supported companies such as Texas Instruments with funding through the Chips and Science Act. Earlier this month, U.S. Secretary of Commerce Howard Lutnick said the Commerce Department is renegotiating some of its contracts.
And as President Donald Trump has been pushing for more U.S.-based manufacturing, Lutnick celebrated the Wednesday announcement from Texas Instruments.
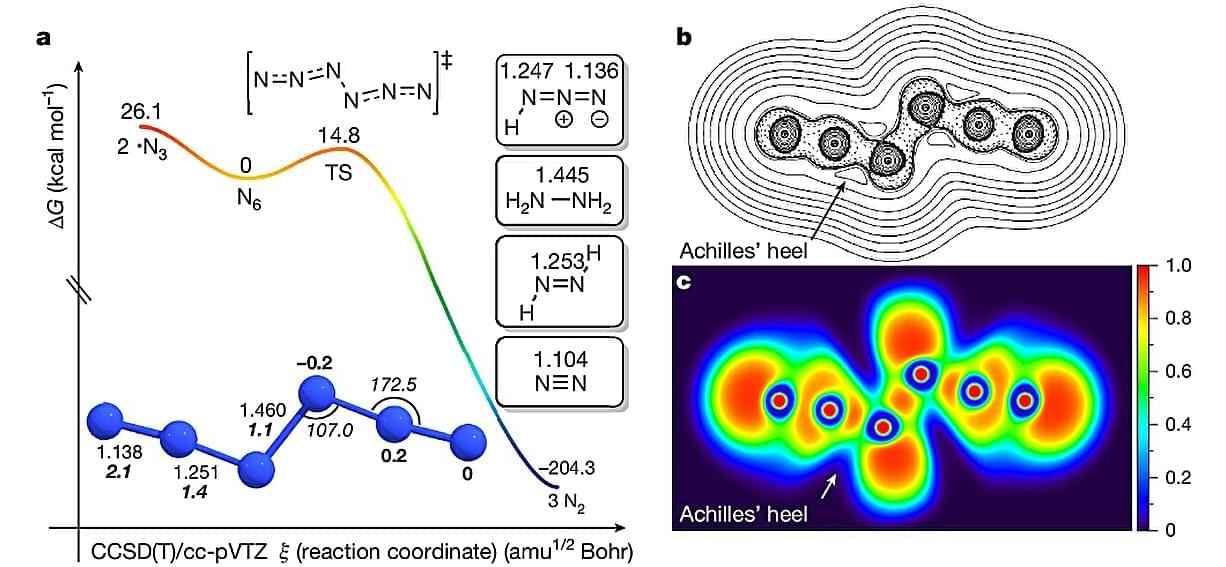
Nitrogen finally joins the elite tier of elements like carbon that can form neutral allotropes—different structural forms of a single chemical element. Researchers from Justus Liebig University, Giessen, Germany, have synthesized neutral hexanitrogen (N6)—the first neutral allotrope of nitrogen since the discovery of naturally occurring dinitrogen (N2) in the 18th century that is cryogenically stable and can be prepared at room temperature.
This new study, published in Nature, synthesized hexanitrogen (N6) via gas-phase reaction, with the main ingredients being chlorine (Cl2) or bromine (Br2) and an extremely reactive and explosive solid silver azide (AgN3), under reduced pressure.
The researchers spread AgN3 on the inner surface, and a gaseous halogen (Cl2 or Br2) was passed through the solid under reduced pressure at room temperature. The reaction triggered by the process produced N6 alongside byproducts chloronitrene (ClN) and hydrazoic acid (HN3).

Avian metapneumovirus (aMPV), classified within the Pneumoviridae family, wreaks havoc on poultry health. It typically causes upper respiratory tract and reproductive tract infections, mainly in turkeys, chickens, and ducks. Four subtypes of AMPV (A, B, C, D) and two unclassified subtypes have been identified, of which subtypes A and B are widely distributed across the world. In January 2024, an outbreak of severe respiratory disease occurred on turkey and chicken farms across different states in the US. Metagenomics sequencing of selected tissue and swab samples confirmed the presence of aMPV subtype B. Subsequently, all samples were screened using an aMPV subtype A and B multiplex real-time RT-PCR kit. Of the 221 farms, 124 (56%) were found to be positive for aMPV-B. All samples were negative for subtype A.

Semiconductor quantum dots have been emerging as one of the most ideal materials for artificial photosynthesis. Here, we report the assembled ZnS-CdS hybrid heterostructure for efficient coupling cooperative redox catalysis toward the oxidation of 1-phenylethanol to acetophenone/2,3-diphenyl-2,3-butanediol (pinacol) integrated with the reduction of protons to H2. The strong interaction and typical type-I band-position alignment between CdS quantum dots and ZnS quantum dots result in efficient separation and transfer of electron-hole pairs, thus distinctly enhancing the coupled photocatalyzed-redox activity and stability. The optimal ZnS-CdS hybrid also delivers a superior performance for various aromatic alcohol coupling photoredox reaction, and the ratio of electrons and holes consumed in such redox reaction is close to 1.0, indicating a high atom economy of cooperative coupling catalysis. In addition, by recycling the scattered light in the near field of a SiO2 sphere, the SiO2-supported ZnS-CdS (denoted as ZnS-CdS/SiO2) catalyst can further achieve a 3.5-fold higher yield than ZnS-CdS hybrid. Mechanistic research clarifies that the oxidation of 1-phenylethanol proceeds through the pivotal radical intermediates of • C(CH3)(OH)Ph. This work is expected to promote the rational design of semiconductor quantum dots-based heterostructured catalysts for coupling photoredox catalysis in organic synthesis and clean fuels production.
Copyright © 2023 Lin-Xing Zhang et al.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is more common in people who experience extensive repetitive head impacts, and infrequent among individuals with isolated brain injuries or less extensive impacts, researchers from the Brain Injury Research Center of Mount Sinai have found.
The study, published in the Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, adds to knowledge of CTE, which has received extensive media attention amidst limited research in representative samples.
CTE is characterized by a neurodegenerative pathology involving abnormal accumulations of tau protein in the brain associated with head trauma, primarily identified in deceased people who sustained extensive exposure to repetitive head impacts while playing contact sports—especially American-style football. CTE has been reported more rarely in individuals who sustained repetitive head impacts through head-banging, military service, or intimate partner violence.
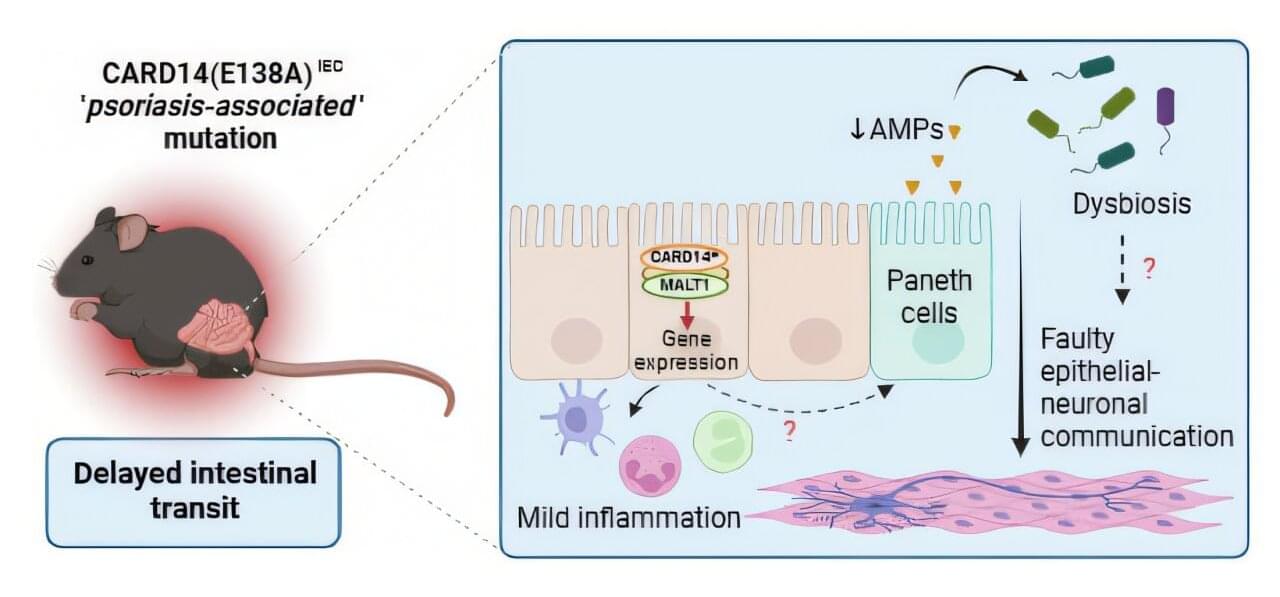
A mutation previously linked to skin disorders like psoriasis may also play a surprising role in gut health, according to new research published by scientists at VIB-UGent and colleagues from UGent, the University of Barcelona, and University College London. This mutation activates skin immune responses but also affects the intestine.
This finding, published in EMBO Molecular Medicine, reveals a new connection between genetics, the immune system, and the gut, which may have therapeutic implications.
Scientists under the leadership of Dr. Inna Afonina and Prof. Rudi Beyaert (VIB-UGent Center for Inflammation Research) have found that a mutation in the gene CARD14, known for activating skin immune responses in psoriasis patients, also affects the intestine. This mutation reduces gut motility, promotes mild inflammation, and increases vulnerability to bacterial infections.
The immune system works to identify and target invading pathogens. Specifically, our bodies work to get rid of any harmful infections by employing a two-part immune response. The first wave of immunity is the innate immune system. This initial reaction is broad and non-specific with innate cells circulating throughout the body to detect foreign pathogens. These cells that are involved include neutrophils, macrophages, eosinophils, basophils, and dendritic cells. Once cells detect an issue, they alert the rest of the body to completely filter out the infection. Importantly, the second wave of immunity, or the adaptive immune system, elicits a strong, specific response that target pathogens the innate immune system cannot neutralize.
Adaptive immunity builds to generate robust protection against aggressive diseases. The cells that make up this response include B and T cells. B cells are mainly responsible for generating antibodies to neutralize and signal infections throughout the body. T cells are the drivers that get rid of disease. T cell activity destroys infected cells and other pathogens lingering throughout the body or site of infection. The adaptive immune response is also critical for immune memory. Once someone experiences a disease and recovers, adaptive immune cells will remember that pathogen next time it enters the body — this is how vaccines work. A patient is injected with a non-harmful virus to expose the immune system. Immediately, the body will respond and destroy the virus. However, a few T cells will also be generated to targeted similar viruses in the future. As a result, when a patient is exposed to the infection again, they will be protected and not experience symptoms.
T cells are critical for any disease or infection, including cancer. Many immunotherapies currently being develop involve activating and directing T cells to the site of the tumor. However, immunotherapies have limited efficacy due to various mechanisms around the tumor that suppress immunity. Scientists are working to understand T cell biology to develop better immunotherapies and more accurately predict treatment outcomes in patients.