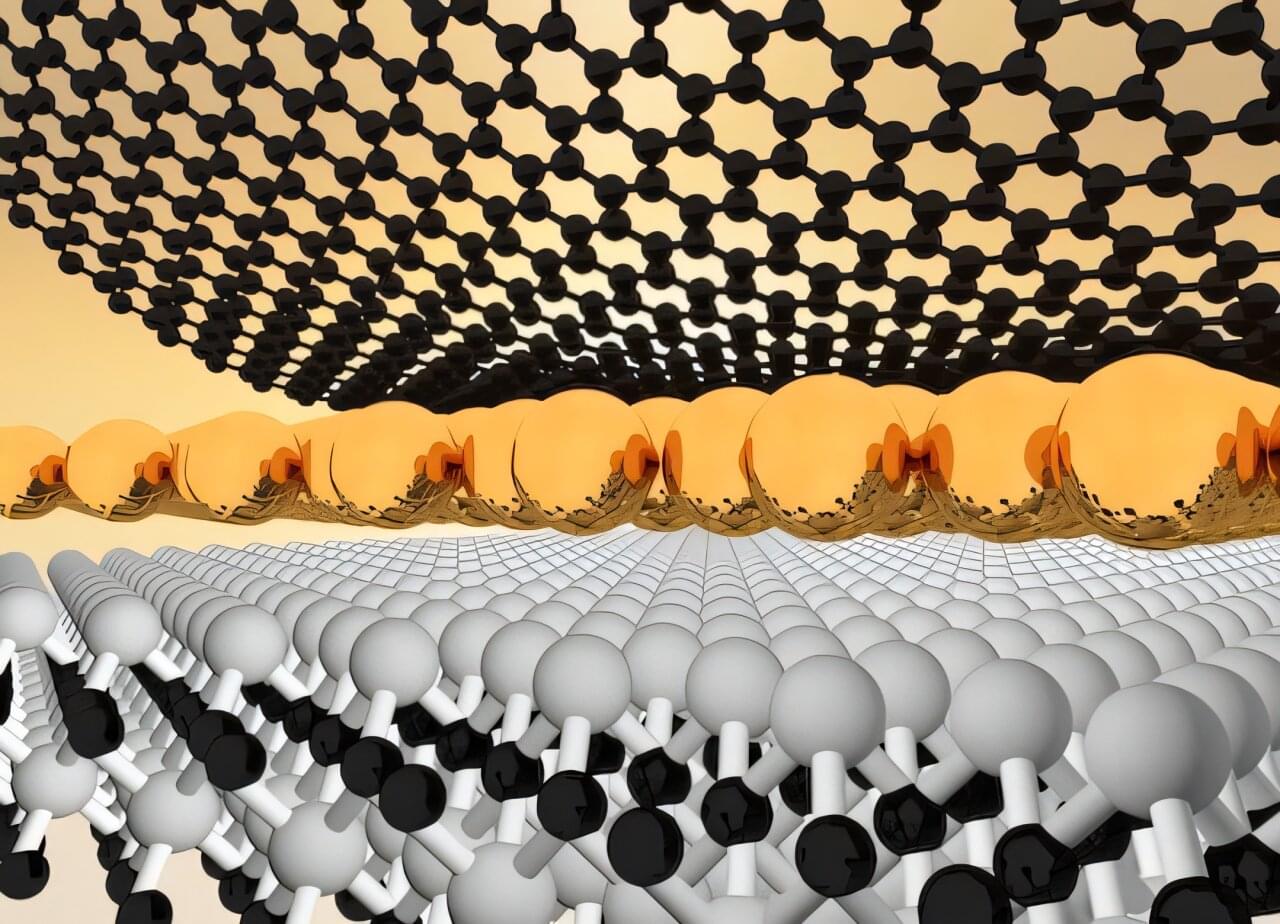
Sliding ferroelectrics are a type of two-dimensional (2D) material realized by stacking nonpolar monolayers (atom-thick layers that lack an electric dipole). When these individual layers are stacked, they produce ferroelectric materials with an intrinsic polarization (i.e., in which positive and negative charges are spontaneously separated), which can be switched using an external electric field that is perpendicular to them.
Understanding the mechanisms driving the switching of this polarization in sliding ferroelectrics has been a key goal of many studies rooted in physics and materials science. This could ultimately inform the development of new advanced nanoscale electronics and quantum technologies.
Researchers at Westlake University and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China recently uncovered a new mechanism that could drive the switching of polarization in sliding ferroelectrics. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters (PRL), suggests that polarization switching in the materials is prompted by wave-like movements of domain walls (i.e., boundaries between regions with an opposite polarization), rather than by synchronized shifts affecting entire monolayers at once, as was assumed by some earlier works.