Meta presents Proactive Detection of Voice Cloning with Localized Watermarking.
Join the discussion on this paper page.

A consensus has arisen in the astronomical community that familiar matter made of atoms is not the dominant form of matter in the Universe. Instead, an invisible form of matter, called dark matter, is thought to be far more prevalent. However, a small group of researchers deny the existence of dark matter, instead saying our understanding of how objects move is incomplete. A recent paper in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society seems to have ruled this out definitively.
Stars, planets, and galaxies move under the direction of the force of gravity, and Isaac Newton worked out the laws that govern that motion, which we now call Newtonian dynamics. However, despite the enormous success of Newtonian dynamics, this success is not universal. Indeed, when Newton’s equations are applied to certain astronomical phenomena, they do not make the correct predictions. One such example is the speed at which galaxies rotate. When astronomers measure the speed of stars in the periphery of a galaxy, they move faster than can be explained by accepted theory. Instead, the galaxies should fly apart.
The solution to this mystery favored by most scientists is that beyond the familiar stars and clouds of gas, our galaxy also hosts a large amount of invisible matter, called dark matter. This dark matter adds to the gravitational force holding the galaxy together. Thus, the evidence for dark matter is indirect. It has never been observed in the laboratory; yet its ability to explain the motion of galaxies is strong circumstantial evidence that it exists.
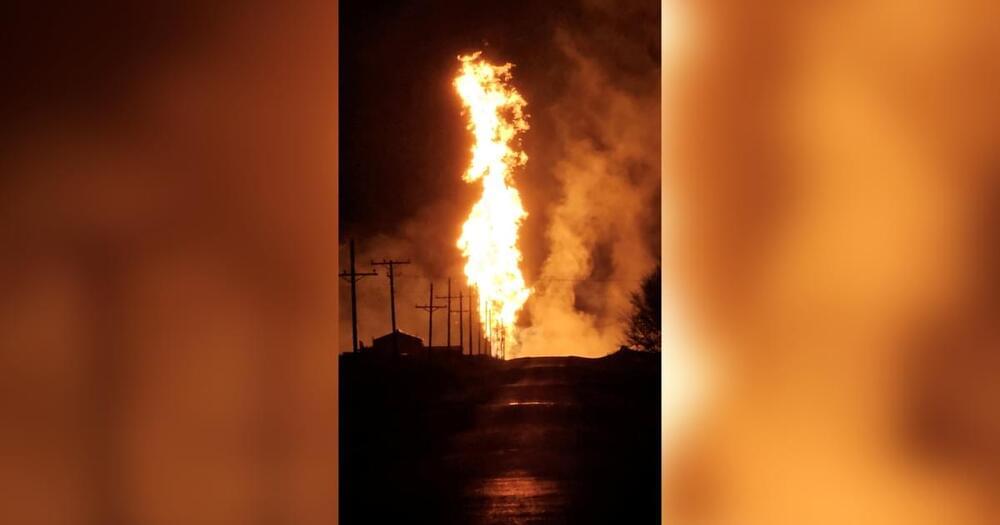

“We are 36 miles away from the fire and we can see it,” one person said, while another posted a photo of the fire’s glow from roughly 25 miles away.
The Booker Fire Department, which serves Booker, Texas, about 20 miles away from Elmwood, also responded to the fire. They posted videos of the explosion, saying it was a gas line.
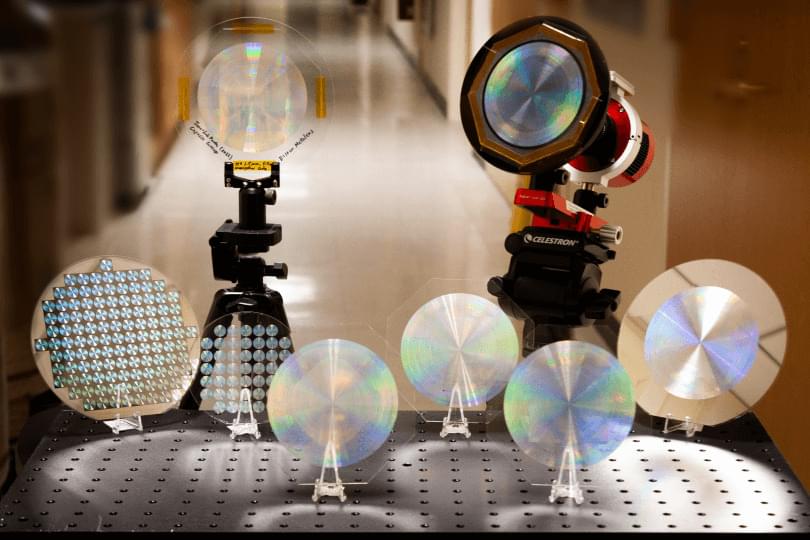

Metalenses have been used to image microscopic features of tissue and resolve details smaller than a wavelength of light. Now they are going bigger.
Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a 10-centimeter-diameter glass metalens that can image the sun, the moon and distant nebulae with high resolution.
It is the first all-glass, large-scale metalens in the visible wavelength that can be mass produced using conventional CMOS fabrication technology.
In the world of quantum computing, the spotlight often lands on the hardware: qubits, superconducting circuits, and the like. But it’s time to shift our focus to the unsung hero of this tale – the quantum software, the silent maestro orchestrating the symphony of qubits. From turning abstract quantum algorithms into executable code to optimizing circuit designs, quantum software plays a pivotal role.
Here, we’ll explore the foundations of quantum programming, draw comparisons to classical computing, delve into the role of quantum languages, and forecast the transformational impact of this nascent technology. Welcome to a beginner’s guide to quantum software – a journey to the heart of quantum computing.
Quantum vs. Classical Programming: The Core Differences.


Artificial intelligence using neural networks performs calculations digitally with the help of microelectronic chips. Physicists at Leipzig University have now created a type of neural network that works not with electricity but with so-called active colloidal particles. In their publication in Nature Communications, the researchers describe how these microparticles can be used as a physical system for artificial intelligence and the prediction of time series.
“Our neural network belongs to the field of physical reservoir computing, which uses the dynamics of physical processes, such as water surfaces, bacteria or octopus tentacle models, to make calculations,” says Professor Frank Cichos, whose research group developed the network with the support of ScaDS.AI.
“In our realization, we use synthetic self-propelled particles that are only a few micrometers in size,” explains Cichos. “We show that these can be used for calculations and at the same time present a method that suppresses the influence of disruptive effects, such as noise, in the movement of the colloidal particles.” Colloidal particles are particles that are finely dispersed in their dispersion medium (solid, gas or liquid).