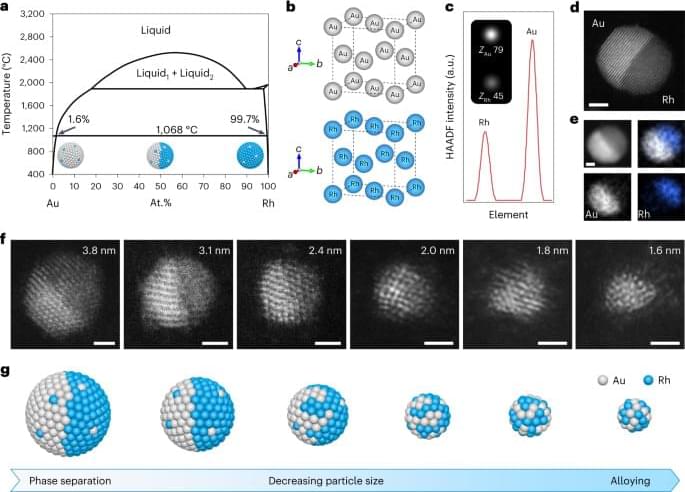
The discovery has historians…scrambling to understand old-school diets.


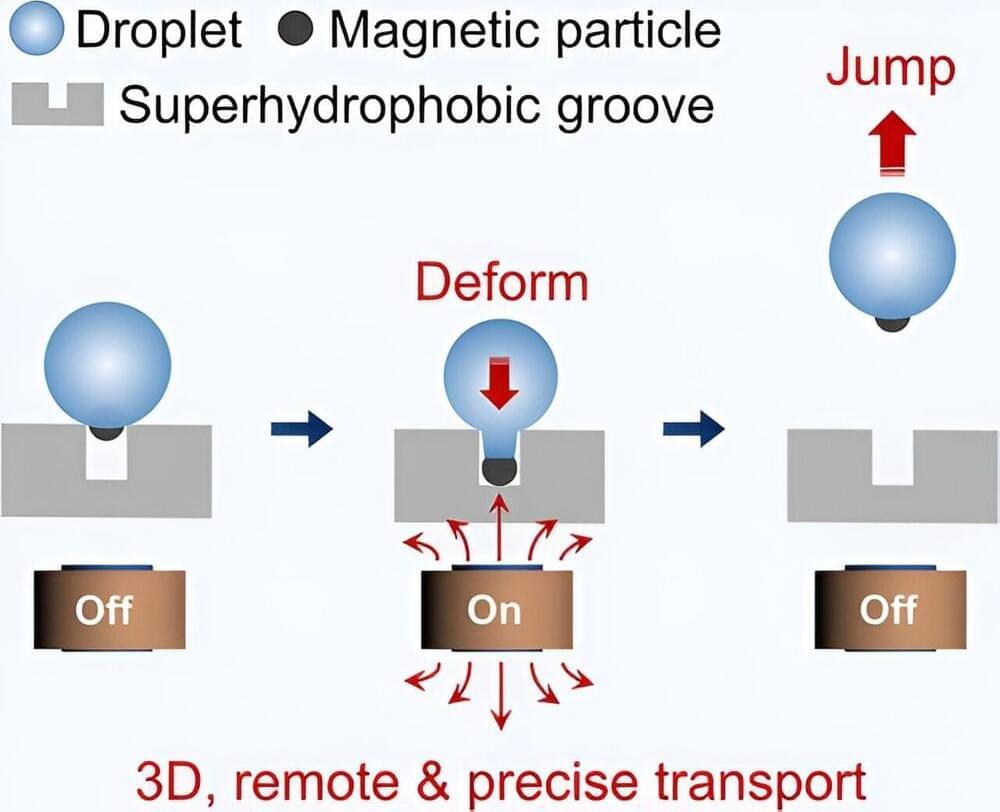
A small combined team of material scientists from Sun Yat-sen University and Dalian University of Technology, both in China, has found that it is possible to make a single drop of water hop in desired ways by putting a magnetic particle inside of it and turning an electromagnet on and off. The research published in the journal ACS Nano.
The research team was investigating on-demand droplet transportation as part of a larger effort. To learn more about the possibility of inciting drops of liquid, in this case water, to move in desired ways, they set up several structures.
The researchers carved small grooves on a flat surface. The surface was then covered with a varnish known to prevent water absorption, thereby allowing droplets to form when splashed onto the surface. Once the droplets formed, the team placed a tiny piece of metal into each drop, where it was held in place by the forces that held the bubble shape. The entire surface was then placed over a set of electromagnets.
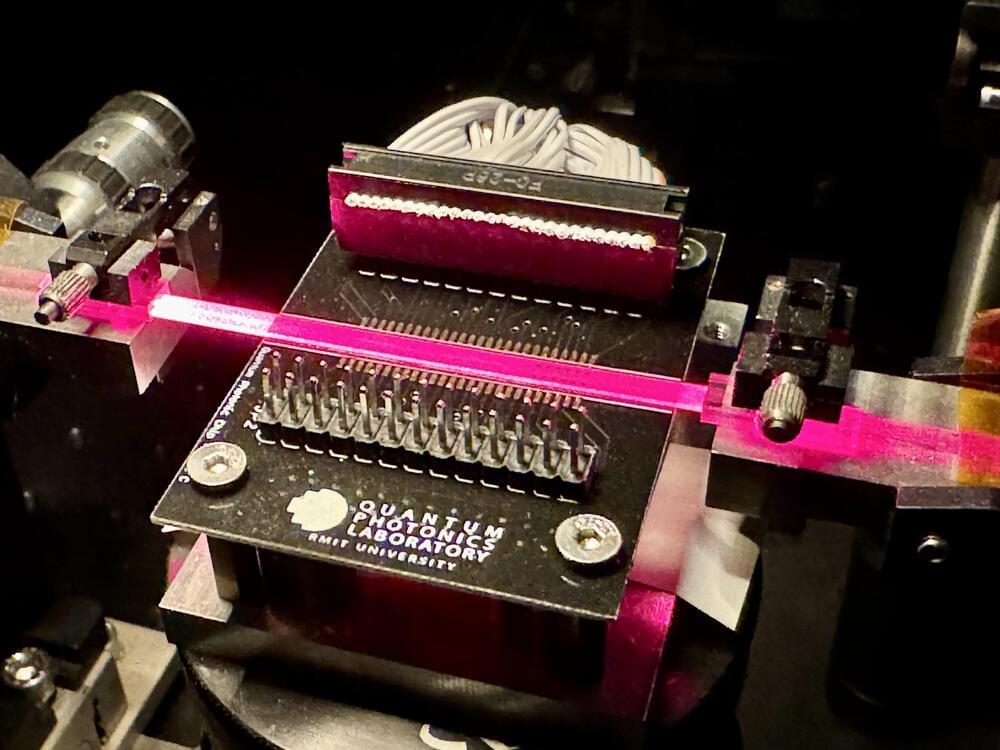
Scientists have created a reprogrammable light-based processor, a world-first, that they say could usher in a new era of quantum computing and communication.
Technologies in these emerging fields that operate at the atomic level are already realizing big benefits for drug discovery and other small-scale applications.
In the future, large-scale quantum computers promise to be able to solve complex problems that would be impossible for today’s computers.
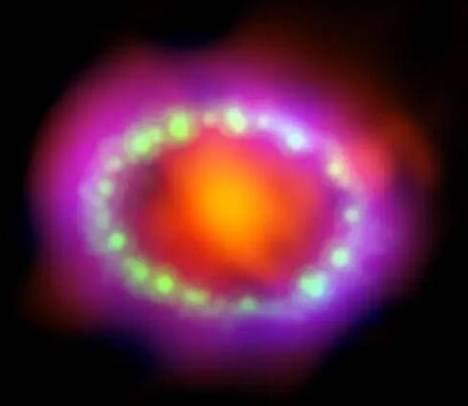
The youngest neutron star detected so far turned 37 years old last week. To celebrate, James Webb Space Telescope has finally found the most direct evidence of it, hiding among the remains of the supernova cloud it was born in.
Usually when we’re talking about the age of astronomical objects, it’s in the millions or billions of years – so finding something that’s younger than Lady Gaga feels weird. Even weirder is being able to trace its birth to a specific date – February 23, 1987, meaning it just clocked over to its 37th birthday last Friday.
The reason we can so confidently pinpoint the date is because its birth was the result of an event that only happens once every few centuries: a supernova that’s close enough to be observed from Earth with the naked eye. SN 1987A lit up the night sky for a few months in early 1987, and was quickly traced to the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way, about 168,000 light-years away. There, a blue supergiant star appeared to have collapsed and exploded, which should have left either a black hole or a neutron star.
Humanoid robot maker Figure has announced a new deal with ChatGPT-maker OpenAI.
The company recently closed a $675 million round of funding at a $2.6 billion valuation as well, with notable backers including Amazon founder Jeff Bezos, Microsoft, and AI chipmaker Nvidia.
It’s a notable agreement, especially considering Figure has yet to release a viable commercial product — which highlights just how much momentum there is in the AI space as investors hope for gargantuan growth.
The first 500 people to use my link will get a 1 month free trial of Skillshare https://skl.sh/sabinehossenfelder03241
You have probably seen headlines in the past years about lots of things out there in the cosmos that, according to astrophysicists \.