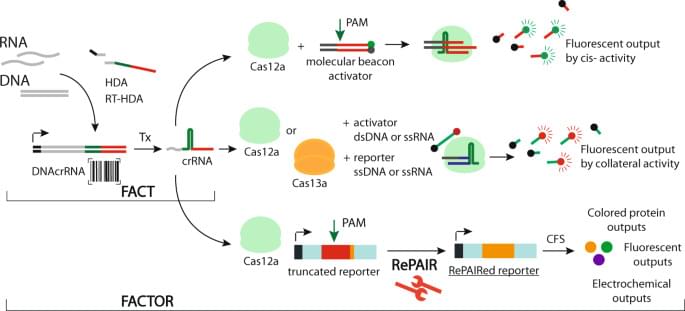
Nucleic acid sensing involving CRISPR technologies is powerful but has certain limitations, such as PAM sequence requirements and limited multiplexing. Here, authors report a CRISPR-based barcoding technology which enables multiple outputs from any target sequence, based on cis-and trans-cleavage.
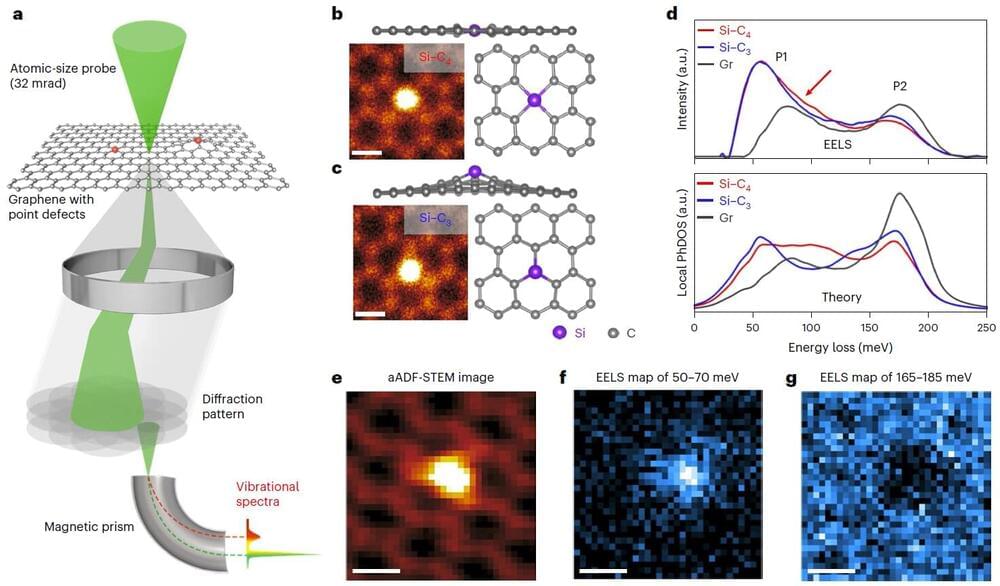
Researchers led by Prof. Zhou Wu from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS) and Prof. Sokrates T. Pantelides of Vanderbilt University have pushed the sensitivity of single-atom vibrational spectroscopy to the chemical-bonding-configuration extreme, which is critical for understanding the correlation of lattice vibrational properties with local atomic configurations in materials.
Using a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches, the researchers demonstrated the effect of chemical-bonding configurations and the atomic mass of impurity atoms on local vibrational properties at the single-atom level.
The study was published in Nature Materials.
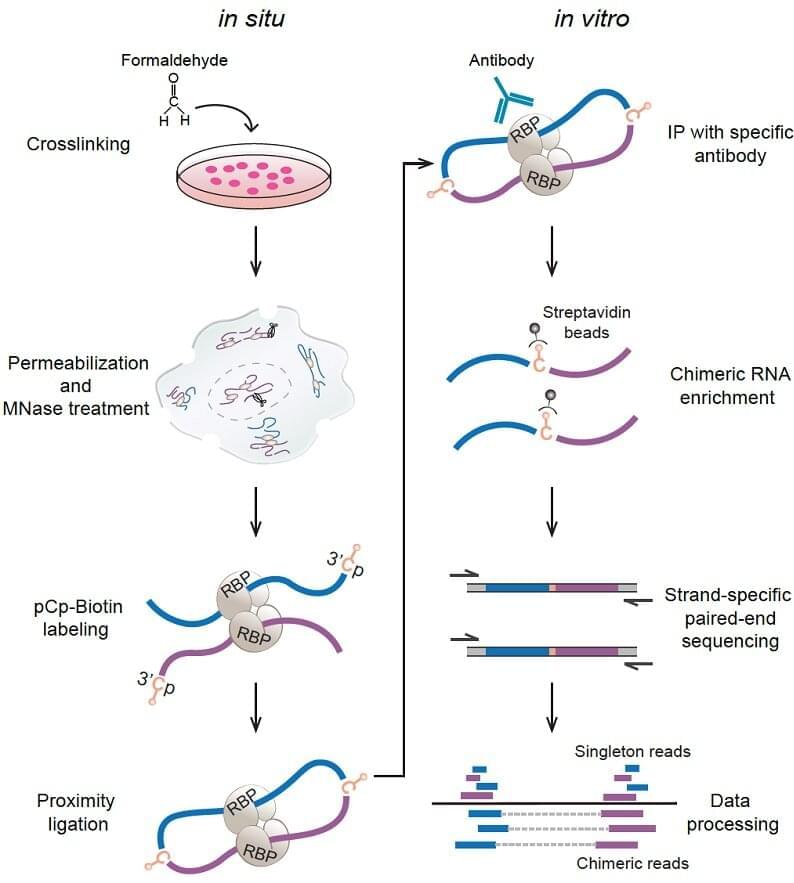
A research team led by Prof. Xue Yuanchao from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new method for global profiling of in-situ RNA–RNA contacts associated with a specific RNA-binding protein (RBP) and revealed positional mechanisms by which PTBP1-associated RNA loops regulate cassette exon splicing.
This study was published online in Molecular Cell on March 22.
In eukaryotes, the same pre-mRNA can produce multiple protein isoforms to execute similar or different biological functions through alternative splicing. Several longstanding models proposed that RBPs may regulate alternative splicing by modulating long-range RNA–RNA interactions (RRI). However, direct experimental evidence was lacking.
The secret to a perfect croissant is the layers—as many as possible, each one interspersed with butter. Similarly, a new material with promise for new applications is made of many extremely thin layers of metal, between which scientists can slip different ions for various purposes. This makes them potentially very useful for future high-tech electronics or energy storage.
Until recently, these materials—known as MXenes, pronounced “max-eens”—were as labor-intensive as good croissants made in a French bakery.
But a new breakthrough by scientists with the University of Chicago shows how to make these MXenes far more quickly and easily, with fewer toxic byproducts.
The “iPhone moment for A.I.” hype takes many hues, but Nvidia is about the future of computing itself. NVIDIA DGX supercomputers, originally used as an AI research instrument, are now running 24/7 at businesses across the world to refine data and process AI.
While OpenAI gets a lot of the glory, I believe the credit should go to Nvidia. Launched late last year, ChatGPT went mainstream almost instantaneously, attracting over 100 million users, making it the fastest-growing application in history. “We are at the iPhone moment of AI,” Huang said. Nvidia makes about $6 to $7 Billion a fiscal quarter in revenue.
Nvidia said it’s offering a new set of cloud services that will allow businesses to create and use their own AI models based on their proprietary data and specific needs. The new services, called Nvidia AI Foundations, include three major components and are meant to accelerate enterprise adoption of generative AI: Enterprises can use Nvidia NeMo language service or Nvidia Picasso image, video and 3D service to gain access to foundation models that can generate text or images based on user inputs.
The Iron Fist Unleashed!
Posted in life extension
Senescent cells accumulate with age when one senescent cell turns another cell senescent through SASP secretion. New research is offering new hope for fighting this.
In a ground-breaking experiment, scientists have successfully created the fifth form of matter, known as the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), for a remarkable duration of six minutes.
This major accomplishment has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of quantum mechanics and open the door to new technological advancements. In this article, we will explore the significance of this achievement, the nature of BECs, and the potential applications of this newfound knowledge.
Scientists had a hard time reconstructing how complex molecular parts are being held together. However, that was before SISSA’s Cristian Micheletti and his team studied how the DNA double helix unzips when translocated at high velocity through a nanopore.
DNA Double Helix’s Unzipping
DNA has a double helix structure because it consists of two spiral chains of deoxyribonucleic acid. Its shape is reminiscent of a spiral staircase.