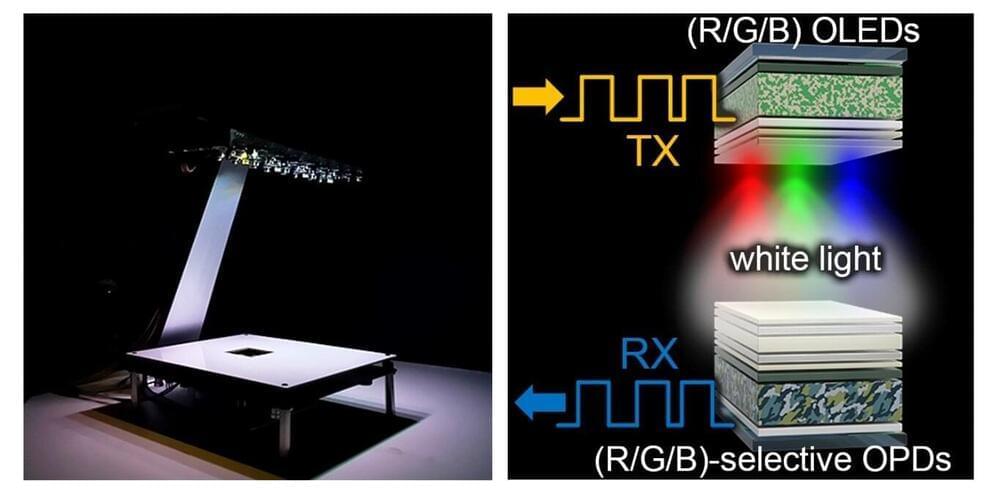
Li-fi, a communication technology harnessing visible light for data transmission, has a potential to surpass Wi-Fi’s speed by more than 100 times and boasts a high bandwidth, facilitating the simultaneous transmission of copious information. Notably, Li-fi ensures robust security by exclusively transmitting data to areas illuminated by light.
Most important, it capitalizes on existing indoor lighting infrastructure, such as LEDs, eliminating the need for separate installations. However, implementing visible light communication (VLC) in practical lighting systems poses an issue of diminished stability and accuracy in data transmission.
Recently, a collaborative team led by Professor Dae Sung Chung, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), with researcher Dowan Kim, Professor Dong-Woo Jee and Hyung-Jun Park from the Department of Intelligence Semiconductor Engineering at Ajou University, and Professor Jeong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, succeeded in utilizing indoor lighting for wireless communication by reducing light interference with a novel light source. Their findings were published in Advanced Materials.