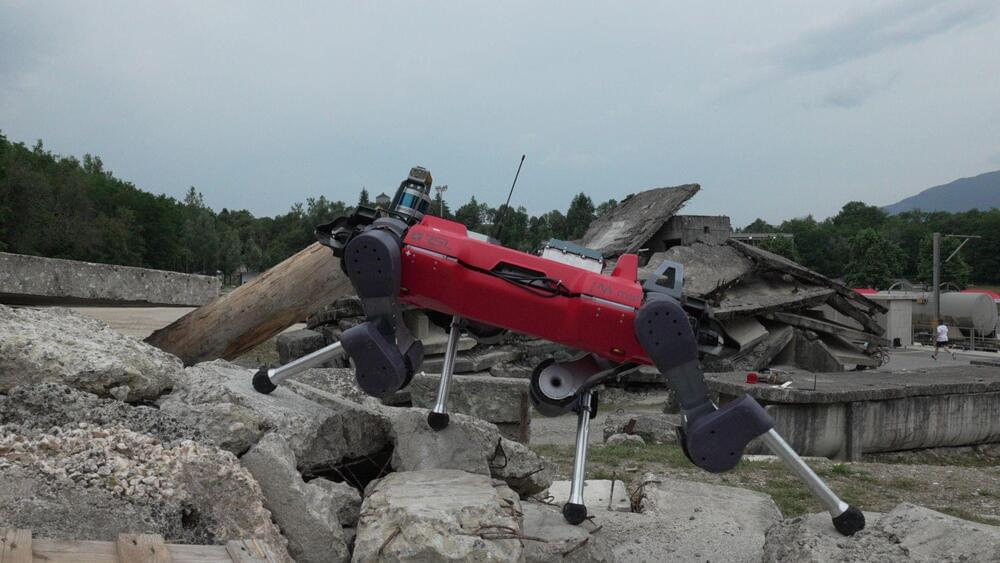
The system combines trajectory optimization and enhanced reinforcement learning to improve how ANYmal chooses its leg positions and footholds.
In the field of robotics, the development of legged robots stands as a formidable challenge. The dynamic and agile movements observed in animals prove difficult to replicate through conventional human-made methods.
Researchers at ETH Zurich have now used an innovative control framework that has helped an autonomous robot, ANYmal, to traverse challenging terrains seamlessly.
Negotiating surfaces ranging from staircases to foam blocks and rugged terrain, this robotic quadruped demonstrates a newfound agility and adaptability, showcasing the effectiveness of its upgraded control system.