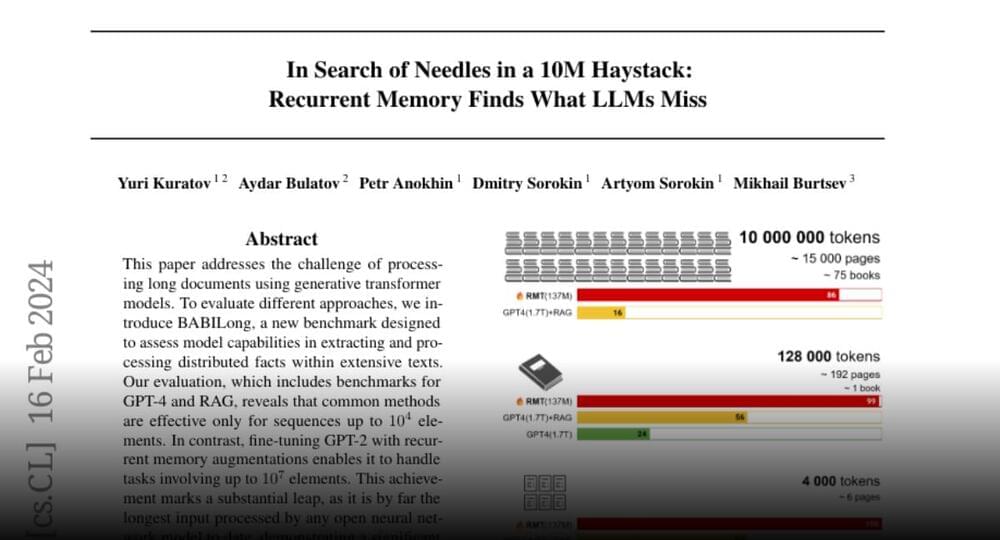
In search of needles in a 10M haystack.
Recurrent memory finds what llms miss.
Join the discussion on this paper page.
Our text-to-video model. Sora can create videos of up to 60 seconds featuring highly detailed scenes, complex camera motion, and multiple ch…

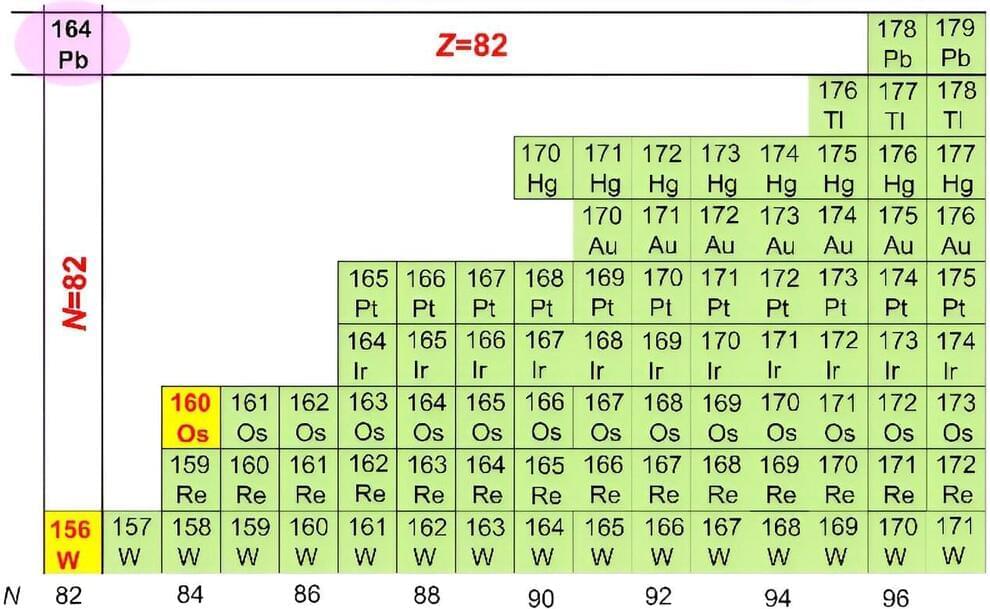
Researchers at the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their collaborators have synthesized two new isotopes—osmium-160 and tungsten-156—which sheds new light on nuclear structures and hints that lead-164 could be a doubly magic nucleus with increased stability.
The study was published in Physical Review Letters and highlighted as an Editors’ Suggestion.
“Magic numbers” of protons and neutrons can make an atomic nucleus particularly stable. The traditional magic numbers include 8, 20, 28, 50, 82 and 126. In previous studies, researchers discovered the vanishing of traditional magic numbers and the emergence of new magic numbers on the neutron-rich side of the chart of nuclides.
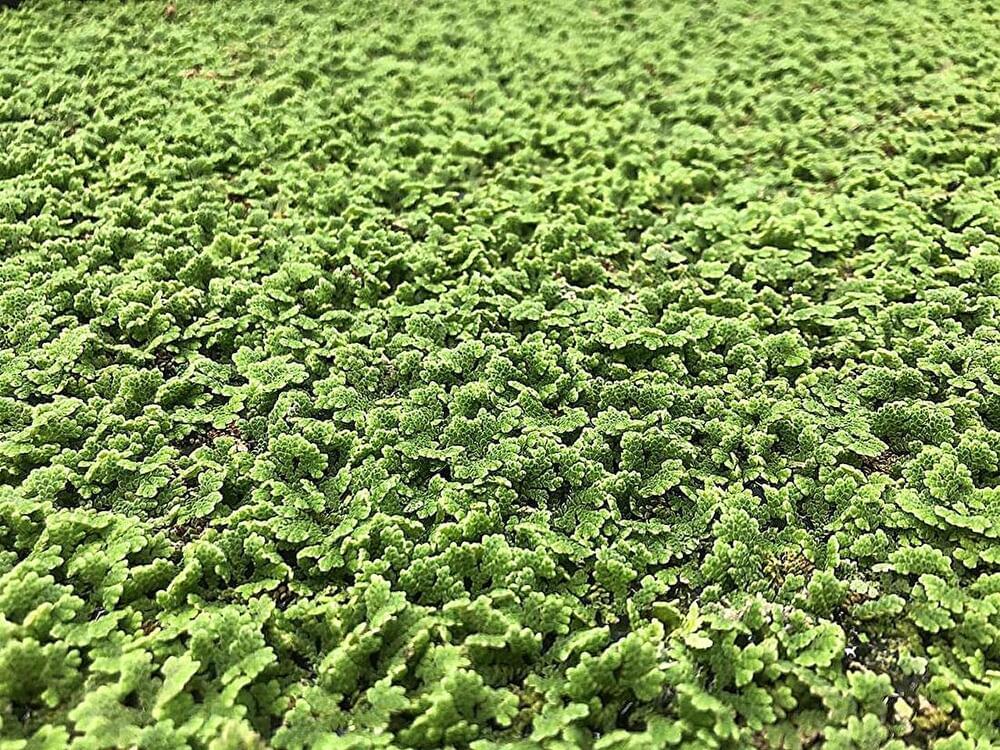


An often-overlooked water plant that can double its biomass in two days, capture nitrogen from the air—making it a valuable green fertilizer—and be fed to poultry and livestock could serve as life-saving food for humans in the event of a catastrophe or disaster, a new study led by Penn State researchers suggests.
Native to the eastern U.S., the plant, azolla caroliniana Willd—commonly known as Carolina azolla—also could ease food insecurity in the near future, according to findings recently published in Food Science & Nutrition. The researchers found that the Carolina strain of azolla is more digestible and nutritious for humans than azolla varieties that grow in the wild and also are cultivated in Asia and Africa for livestock feed.
The study, which was led by Daniel Winstead, a research assistant in the labs of Michael Jacobson, professor of ecosystem science and management, and Francesco Di Gioia, assistant professor of vegetable crop science, is part of a larger interdisciplinary research project called Food Resilience in the Face of Catastrophic Global Events conducted in the College of Agricultural Sciences.
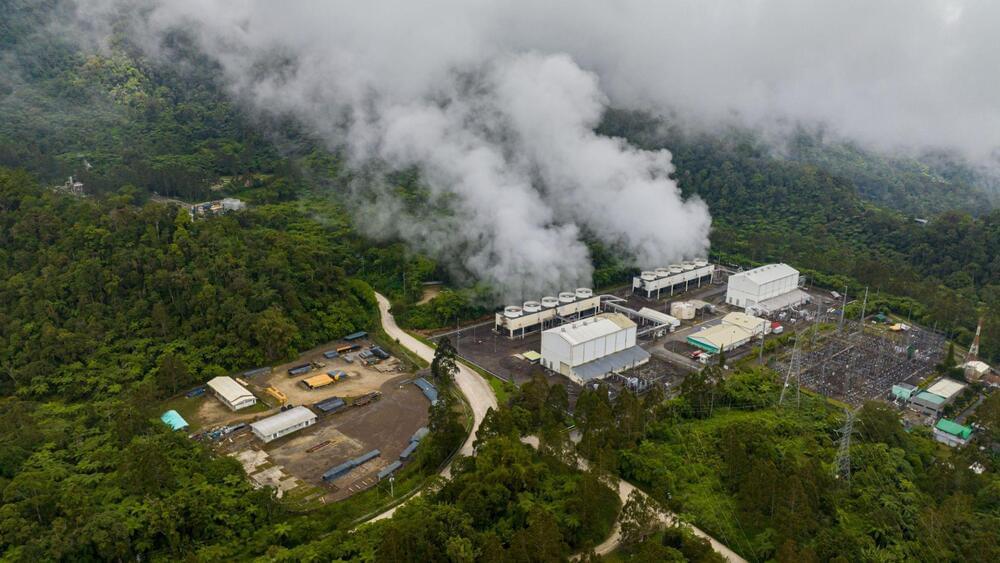

Researchers from Ohio State University have developed an innovative method to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere. Powered by geothermal energy, the team’s method poses a climate-friendly alternative to traditional carbon capture technologies. It highlights the synergy between Direct Air Carbon Dioxide Capture (DACC) technologies and renewable energies from beneath the Earth’s surface.
The approach, named Direct Air CO2 Capture with CO2 Utilization and Storage (DACCUS), promises a significant decrease in atmospheric CO2 levels, a major contributor to global warming.
Climate change primarily results from increased CO2 levels in the Earth’s atmosphere, largely due to human activities like burning fossil fuels for heat, electricity, and transportation.

Non-personalized content and ads are influenced by things like the content you’re currently viewing and your location (ad serving is based on general location). Personalized content and ads can also include things like video recommendations, a customized YouTube homepage, and tailored ads based on past activity, like the videos you watch and the things you search for on YouTube. We also use cookies and data to tailor the experience to be age-appropriate, if relevant.
Select “More options” to see additional information, including details about managing your privacy settings. You can also visit g.co/privacytools at any time.