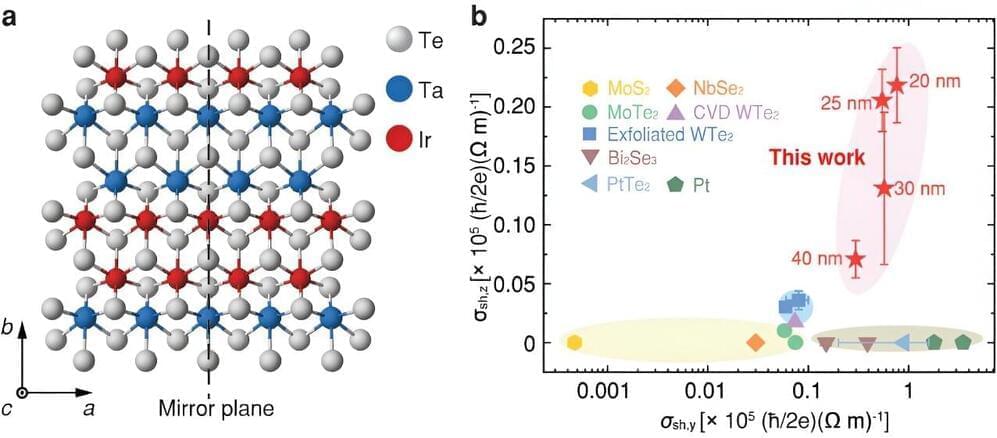
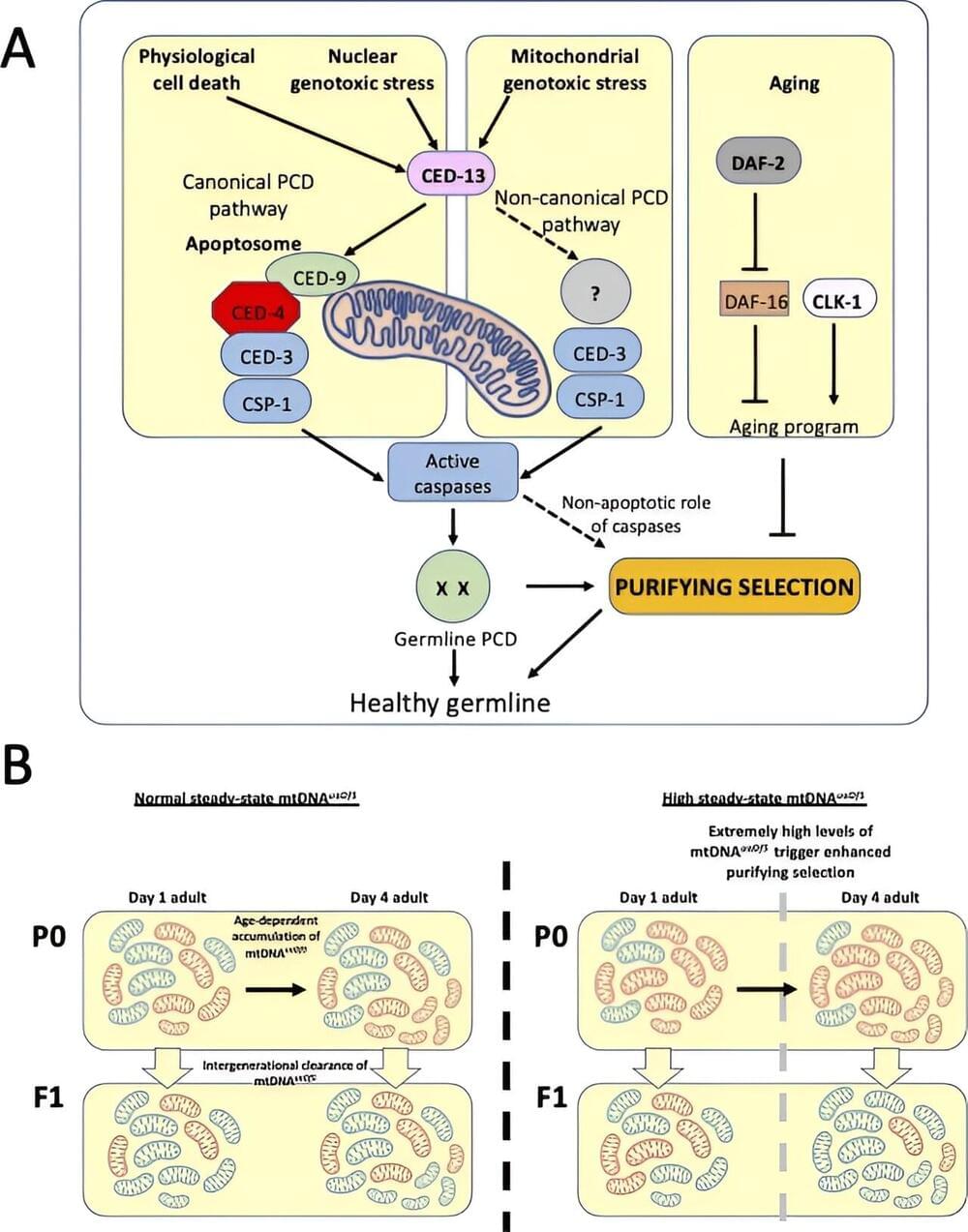
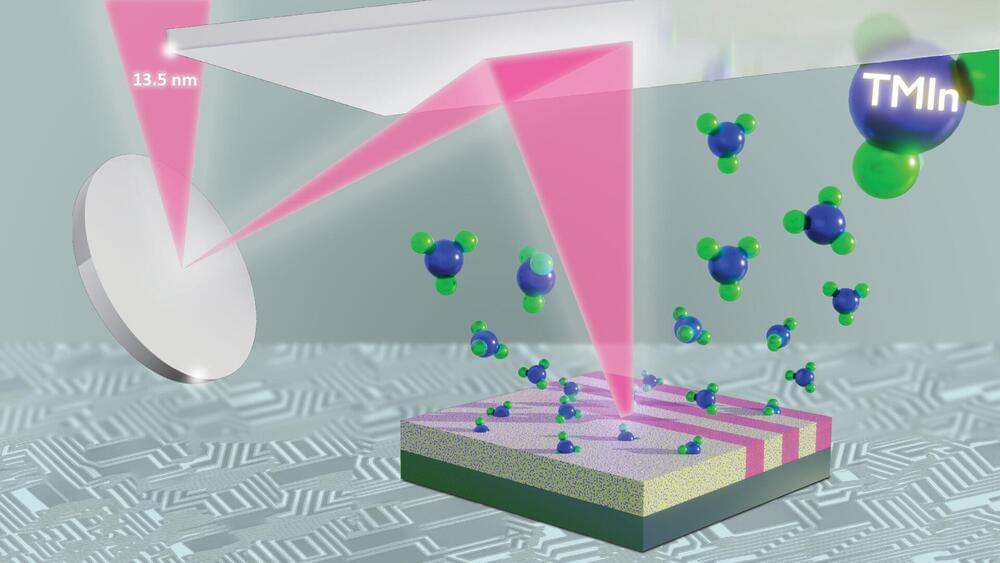
Memory, a fundamental tool for our survival, is closely linked with how we encode, recall, and respond to external stimuli. Over the past decade, extensive research has focused on memory-encoding cells, known as engram cells, and their synaptic connections. Most of this research has centered on excitatory neurons and the neurotransmitter glutamate, emphasizing their interaction between specific brain regions.
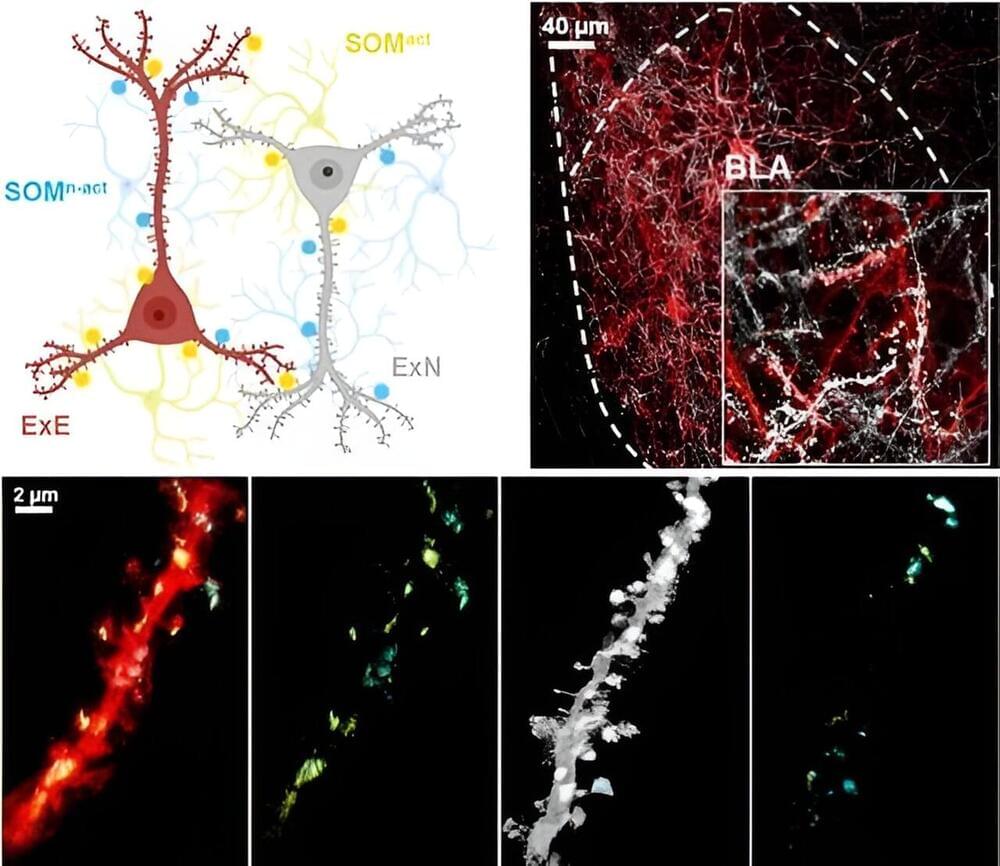
To expand the understanding of memory, a research team led by KAANG Bong-Kiun (Seoul National University, Institute of Basic Science) developed a technology called LCD-eGRASP (local circuit dual-eGRASP) that can label synapses of neural circuits within a specific brain region. The team applied this new technology to identify the local synaptic connections between inhibitory interneurons and engram cells, shedding light on the role of inhibitory interneurons in memory expression.
The researchers targeted basolateral amygdala (BLA), an evolutionarily well-preserved brain region in vertebrates known for controlling positive and negative emotions in animals, especially fear. When a fear-related event occurs, neurons activated during that specific time point become engram cells, encoding the fear memory.