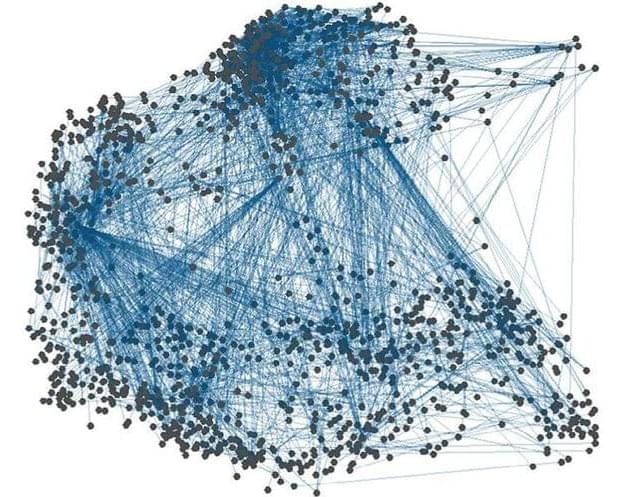
“Connectomes” among species provide chip-design inspiration.

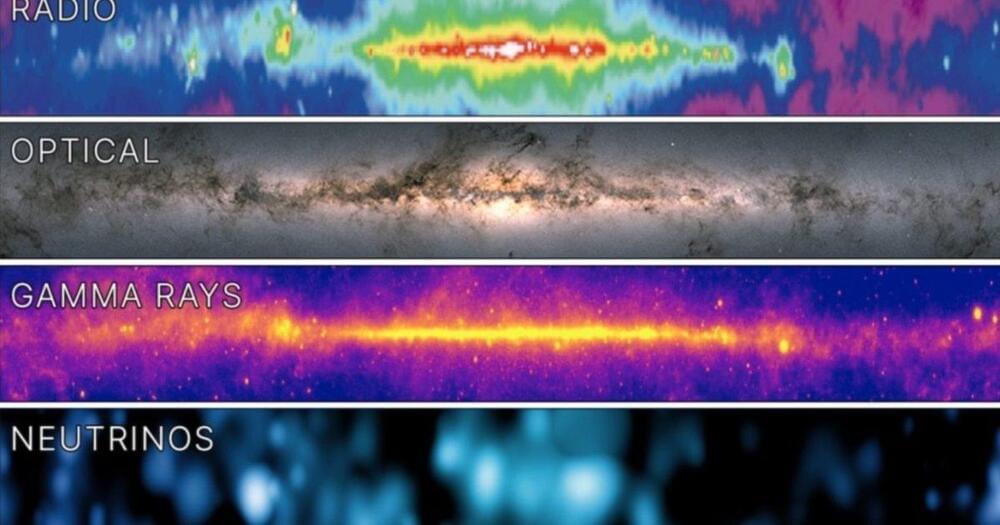
New telescope detects more sources in six months than in the 60-year history of X-ray astronomy.

New nanocavities pave the way for enhanced nanoscale lasers and LEDs that could enable faster data transmission using smaller, more energy-efficient devices.
As we transition to a new era in computing, there is a need for new devices that integrate electronic and photonic functionalities at the nanoscale while enhancing the interaction between photons and electrons. In an important step toward fulfilling this need, researchers have developed a new III-V semiconductor nanocavity that confines light at levels below the so-called diffraction limit.
“Nanocavities with ultrasmall mode volumes hold great promise for improving a wide range of photonic devices and technologies, from lasers and LEDs to quantum communication and sensing, while also opening up possibilities in emerging fields such as quantum computing,” said the leading author Meng Xiong from the Technical University of Denmark. “For example, light sources based on these nanocavities could significantly improve communication by enabling faster data transmission and strongly reduced energy consumption.


GeoMindGPT, a customized version of ChatGPT, powered by GPT-4, is p ioneering the frontier of AI-assisted understanding of complex scientific and philosophical concepts with a special focus on Global Superintelligence, Technological Singularity, Transhumanism & Posthumanism, Consciousness Studies, Quantum Gravity, Simulation Metaphysics.
Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, in addition to killing a large number of tumor cells, also result in the generation of senescent tumor cells (also called “zombie cells”). While senescent cells do not reproduce, they do, unfortunately, generate a favorable environment for the expansion of tumor cells that may have escaped the effects of the chemotherapy and eventually result in tumor regrowth.
An international team of researchers led by Dr. Manuel Serrano at IRB Barcelona has described in Nature Cancer how cancer cells that have become senescent after chemotherapy activate the PD-L2 protein to protect themselves from the immune system while recruiting immune suppressor cells. The latter creates an inhibitory environment that impairs the ability of lymphocytes to kill cancer cells.
Based on these findings, scientists wondered what would be the effect of inactivating PD-L2. Interestingly, senescent cells lacking PD-L2 are rapidly eliminated by the immune system. This intercepts the capacity of senescent cells to create an immunosuppressive environment and, as a result, lymphocytes retain their full capacity to kill those cancer cells that may have escaped the effects of chemotherapy.

Researchers have discovered an innovative approach to combat infectious viruses by leveraging a nanostructured surface. Their findings reveal that this surface successfully eradicated 96% of the viruses upon contact.
A new method using a nanostructured surface effectively kills 96% of viruses within six hours of contact.

The must-reads
I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology.
1 The world’s largest music label has yanked its artists’ music off TikTok Universal Music Group claims TikTok is unwilling to compensate musicians appropriately. (The Guardian) + Taylor Swift fans are kicking off. (Wired $) + Indie record labels don’t like the sound of Apple’s pay plans either. (FT $)

Chemotherapy can be toxic to heart cells. To help protect the hearts of cancer patients, Cedars-Sinai investigators have created a three-dimensional “heart-on-a-chip” to evaluate drug safety. In a study published in the journal Lab on a Chip, they show that the heart-on-a-chip, created using stem cells, accurately predicts the effects of drugs on human heart cells.
The investigators worked with induced pluripotent stem cells, which are blood cells that have been reprogrammed into stem cells and can be turned into any cell type in the body. They used the stem cells to create two types of heart cells, but instead of placing them all together in an unstructured cell culture dish, as is usually done in heart toxicity testing, the investigators introduced the cells into specialized chips.
The 3D chips feature two channels that are arranged to cross each other, keeping each cell type separate but allowing them to interact. The chips also allow for movement and the introduction of fluids.