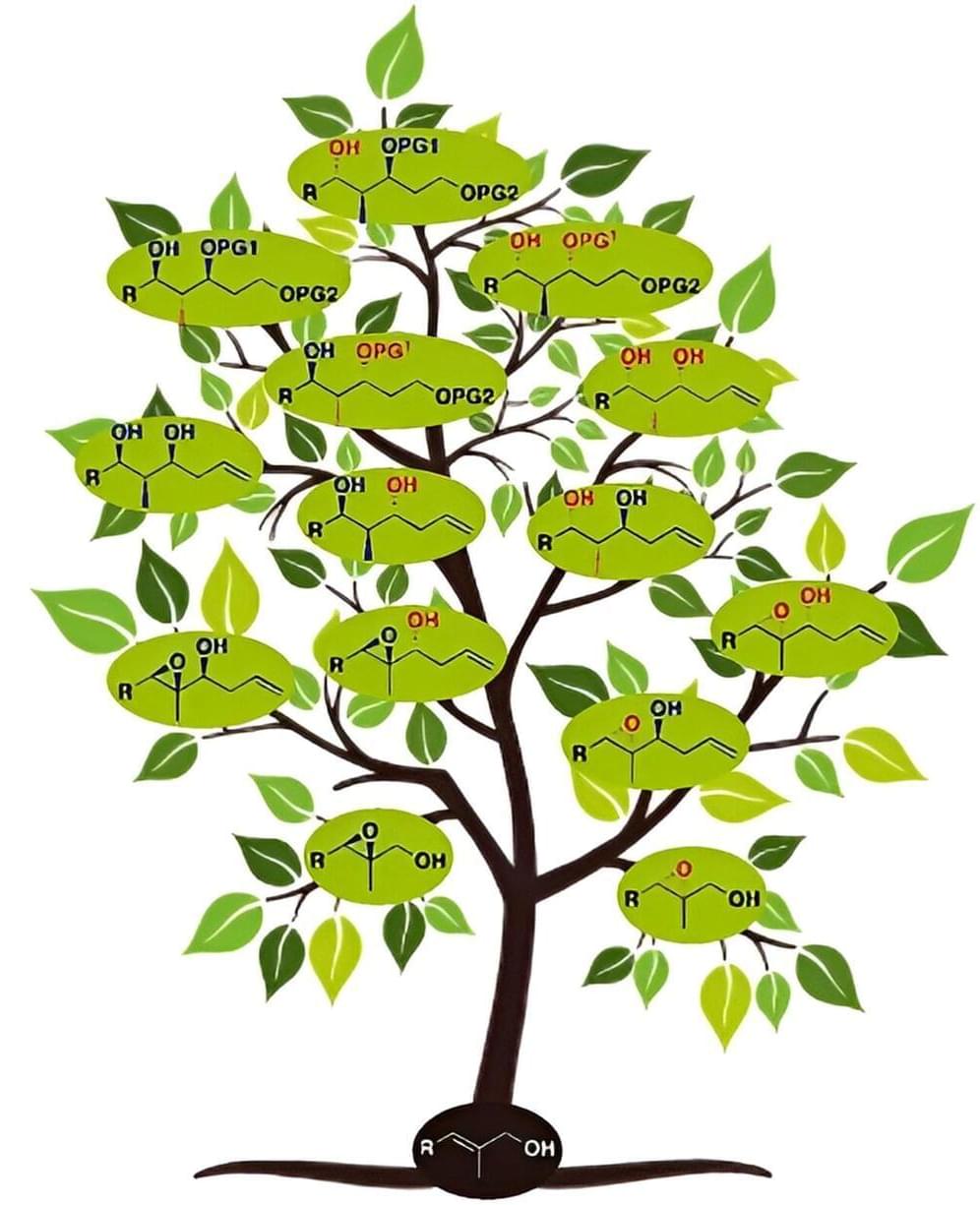
To synthesize potential drugs or natural products, you need natural substances in specific mirror-image variants and with a high degree of purity. For the first time, chemists at the University of Bonn have succeeded in producing all eight possible variants of polypropionate building blocks from a single starting material in a relatively straightforward process. Their work has now been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Polypropionates are natural products that can help save lives. They are needed to make reserve antibiotics, compounds that are only ever used to treat infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria. In nature, chiral compounds exist in two different variants that share the same molecular formula but are mirror images of each other, like a right and a left hand. Chemists call this “chirality,” which literally means “handedness.”
“What’s interesting is that the mirror-image forms can have very different properties,” explains Professor Andreas Gansäuer from the Kekulé Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of Bonn. “One well known example is undoubtedly carvone. The dextro-, or ‘right-handed,’ form of this molecule smells of caraway, while its levo-, or ‘left-handed,’ form is what gives peppermint its distinctive odor.”