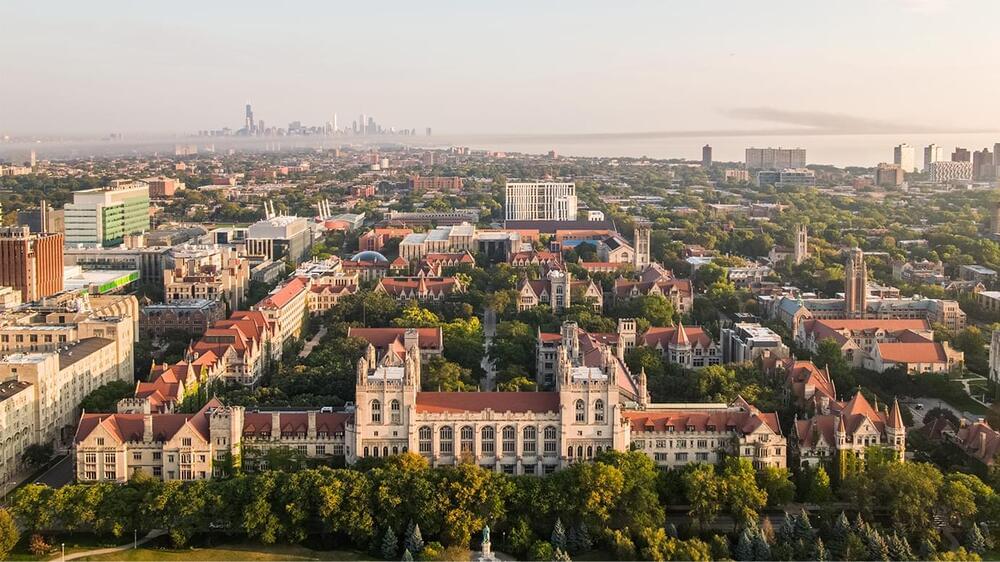
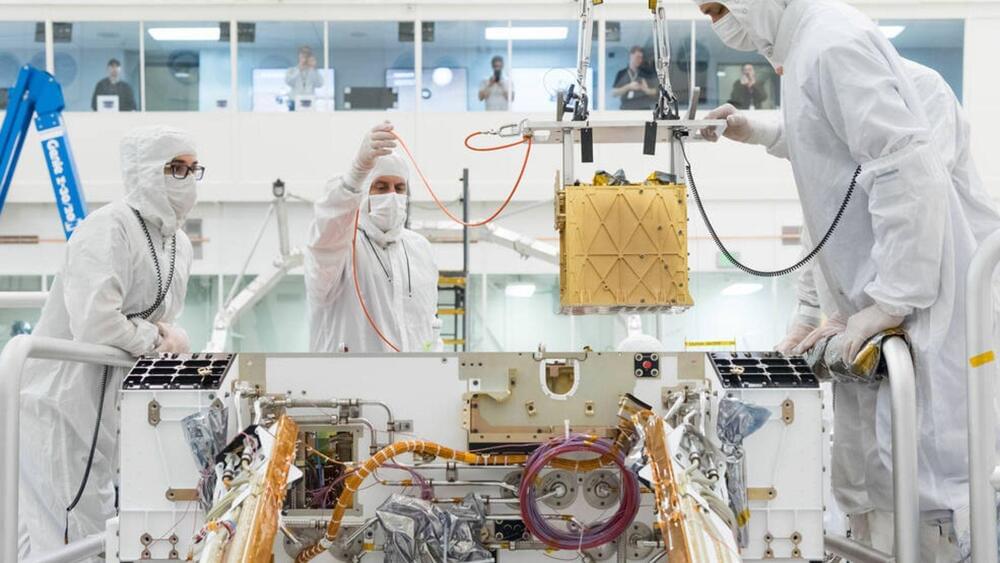
Collaboration to spur innovation in fields ranging from quantum to AI to data science.
Dubbed ‘Luminous Fast Coolers,’ this new class of extreme cosmic explosion is incredibly rare — and unbelievably bright.
The organism fared better at converting organic waste to electricity than even some famous and exotic electricity producing microbes.
Scientists at the Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland have successfully engineered E.coli.
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E.coli, is a rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in the lower gut of organisms. However, it has become a favorite of microbial researchers worldwide for the ease with which its genetic structure can be manipulated. It has, therefore, become an indispensable part of research and industrial projects.
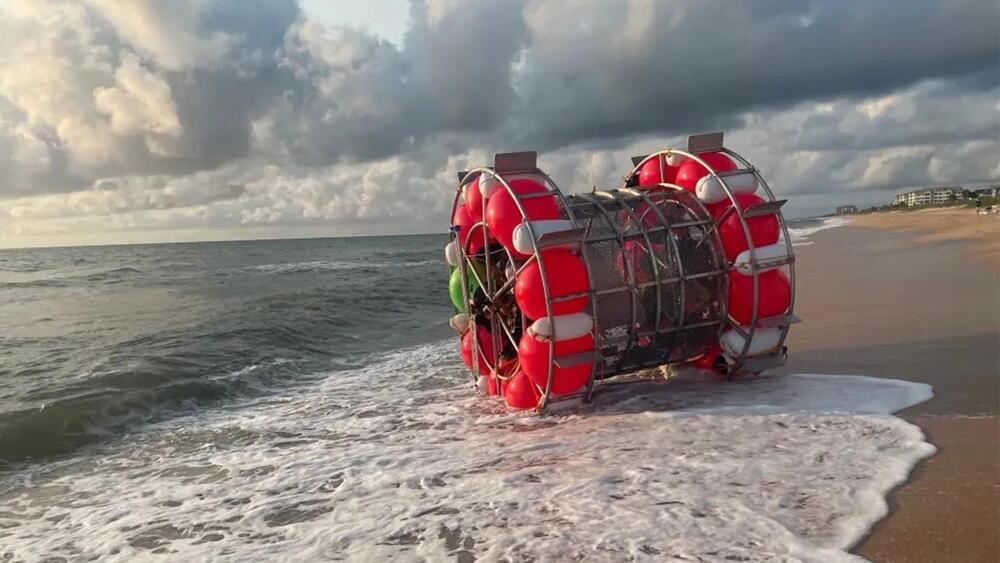
The Floridian repeat offender told the authorities that he planned on wheeling himself to London, England.
It started on August 26 when the US Coast Guard was transiting in the Atlantic Ocean in preparation for an intense hurricane when they found a weird-looking vessel in the middle of the ocean, 70 miles (110 km) off the coast of Georgia. There was a man aboard the vessel. He told the authorities that he planned on wheeling himself to London, England.
A Florida man was arrested in the middle of the ocean after he was found floating in a homemade vessel resembling a hamster wheel. But how did he get there in the first place?
Vessel has peddles to propel it
When the Coast Guard asked the man for registration papers, he assured the men that the vehicle was registered but was unable to produce papers. Looking closely at the vessel, the Coast Guard was able to identify home supplies like wires and buoys and deemed the vehicle unsafe for the voyage.
Gallium has multiple advantages but processing it has been difficult. This might be about to change after new discovery.
Researchers at the Zhejiang University in China have devised a new method that allows for easier and cost-effective production of gallium oxide, an alternative to silicon for semiconductors, South China Morning Post.
Silicon may be a significant component powering semiconductor-based applications. Still, the industry has evolved to use compounds such as gallium arsenide and indium phosphide in production processes over the years. Gallium oxide is the newest entrant in the arena.
SweetBunFactory/iStock.
This is according to a report by Reuters published on Wednesday.
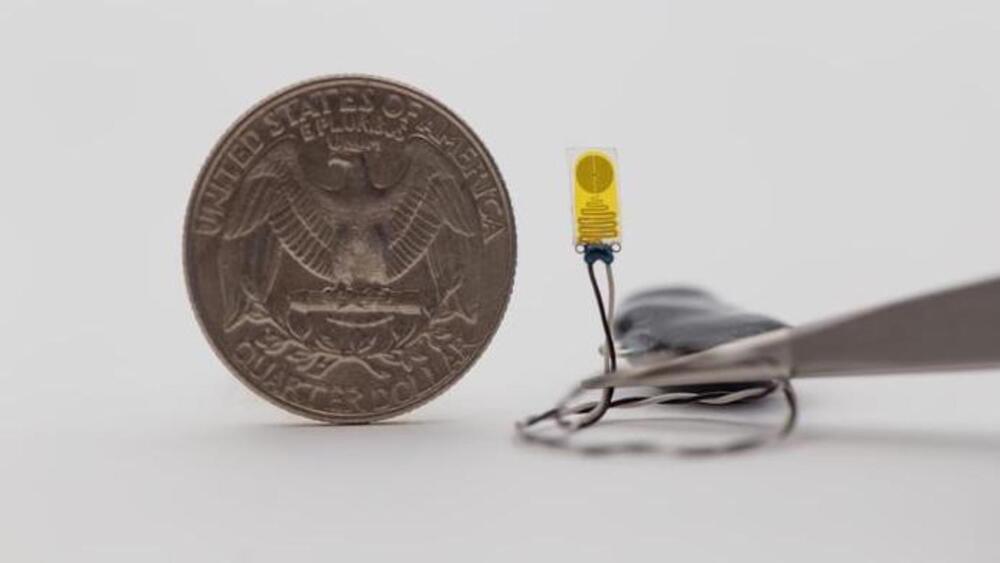
The device is the size of a fingernail, is Bluetooth-enabled, and has a coin battery.
After an organ transplant, the body either accepts the organ or rejects it. All patients have some amount of acute rejection, but hyperacute rejection is when the body vehemently rejects the organ and it must be removed immediately to save the life of the patient. And then there’s chronic rejection, which can take many years as the body’s immune response towards the new organ slowly damages the transplanted tissues or organ.
So, how do we detect early on that an organ transplant has failed? The gold standard is currently via a biopsy, performed periodically to detect rejection early before symptoms develop.
This microbot has the adeptness to navigate precisely within clusters of cells.
In recent years, introducing tiny robots into biological studies and therapeutic delivery has generated significant excitement and is poised to revolutionize the medical field.
These mini robotic systems, often measuring just a few millimeters or even smaller, bring various capabilities and advantages, transforming multiple aspects of medicine, including targeting precise tumor sites to deliver drugs, cellular simulation, and even performing microsurgery.
Since the Perseverance rover’s landing in 2021, MOXIE has produced a cumulative 122 grams of oxygen.
NASA’s Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) successfully concluded its mission by producing oxygen on the Red Planet for the 16th and final time. Developed by a team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the machine exceeded the initial expectations of its creators and has set a strong precedent for future missions aimed at human exploration of Mars.
“MOXIE’s outstanding results validate the viability of extracting oxygen from the Martian atmosphere—a crucial resource for both life-support and propellant for return missions,” stated NASA Deputy Administrator… More.
Source: NASA
New details of Musk’s involvement in the Ukraine-Russia war revealed in his biography.
Elon Musk holds many titles. He is the CEO of Tesla SpaceX and owns the social media company X, which was recently rebranded from Twitter. Going by an excerpt of his biography, published in the Washington Post.
According to the excerpt from Walter Isaacson’s book, Musk disabled his company Starlink’s satellite communication networks, which were being used by the Ukrainian military to attack the Russian naval fleet in Sevastopol, Crimea, sneakily. The Ukrainian army was using Starlink as a guide to target Russian ships and attack them with six small… More.
Musk’s biographer alleges he prevented nuclear war between Ukraine and Russia by turning off Starlink satellite network near Crimea, but Musk says, ‘SpaceX did not deactivate anything’.