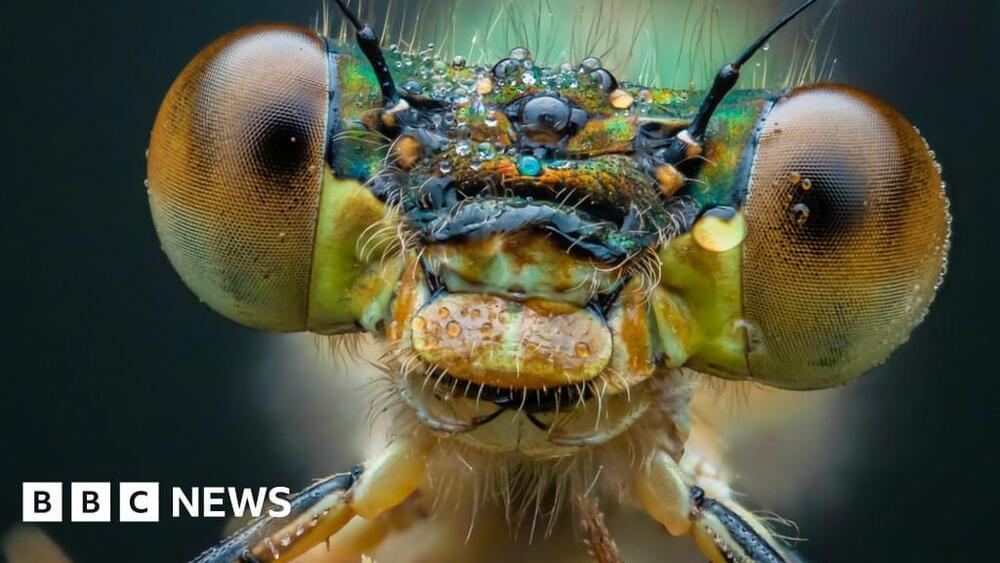
How lockdown helped David Hamilton discover his love for macro photography in a local park.
A recent estimate of NVIDIA’s profits from the AI hype shocked us all, as it was disclosed that the company earns a whopping 1000% profit on its H100 AI GPUs.
NVIDIA’s Plans to Generate $300 Billion By AI-driven Sales Seems Achievable Given The Vast Profits Being Made
Tae Kim, a senior writer from the media outlet Barron’s, estimates that NVIDIA is reaping immense benefits from its vast AI sales, potentially breaking all records.
The need for window-washing humans or robots, therefore, is only going to get bigger in 21st-century cities around the world.
Ozmo combines a flexible robotic arm, artificial intelligence, machine learning and computer vision to clean building facades. It has onboard sensors that can adjust the pressure needed based on the type and thickness of the glass. Onboard LiDAR maps the building facades it is working on in three dimensions. As it moves it calculates its cleaning path hundreds of times per second while adapting to variable external environments by using onboard machine learning. Windy conditions pose no threat. And no humans are at risk as it allows for remote control operations by a handler should Ozmo need to be shut down.
Don’t put anything into an AI tool you wouldn’t want to show up in someone else’s query or give hackers access to. While inputting every bit of information you can think of in an innovation project is tempting, you have to be careful. Oversharing proprietary information on a generative AI is a growing concern for companies. You can fall victim to inconsistent messaging and branding and potentially share information that shouldn’t be available to the public. We’re also seeing increased cyber criminals hacking into generative AI platforms.
Generative AI’s knowledge isn’t up to date. So your query results shouldn’t necessarily be taken at face value. It probably won’t know about recent competitive pivots, legislation or compliance updates. Use your expertise to research AI insight to make sure what you’re getting is accurate. And remember, AI bias is prevalent, so it’s just as essential to cross-check research for that, too. Again, this is where having smart, meticulous people on board will help to refine AI insight. They know your industry and organization better than AI and can use queries as a helpful starting point for something bigger.
The promise of AI in innovation is huge, as it unlocks unprecedented efficiency and head-turning output. We’re only seeing the tip of the iceberg as it relates to the promise the technology holds, so lean into it. But do so with governance—no one wants snake tail for dinner.
Researchers publishing in Biogerontology have tested multiple biomarkers in an effort to use them as proxies for aging, and some of their findings were surprising. A simple study with direct […].
In a recent pre-print study posted to the medRxiv* server, researchers conducted a comprehensive genome-wide association study (GWAS) to elucidate the genetic architecture of circulating retinol, identify its potential causal relationships with various clinical phenotypes, and evaluate its therapeutic or nutritional implications.
Study: Genetic influences on circulating retinol and its relationship to human health. Image Credit: SciePro/Shutterstock.com.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Elon Musk, the richest man in the world, revealed that one of the toughest choices he’s had to make in his life was when he had “$30 million dollars left.”
Musk, CEO of Tesla Inc. and SpaceX, revealed that choosing which company to invest his last $30 million in was tough.
In a conversation with screenwriter, producer and director Jonathan Nolan during a SXSW interview titled “Elon Musk Answers Your Questions!”, Musk shared his insights on topics ranging from artificial intelligence (AI) to Mars and business. He delved into his early entrepreneurial years, which ultimately led to the creation of his groundbreaking companies, including how he made $180 million from the sale of PayPal.
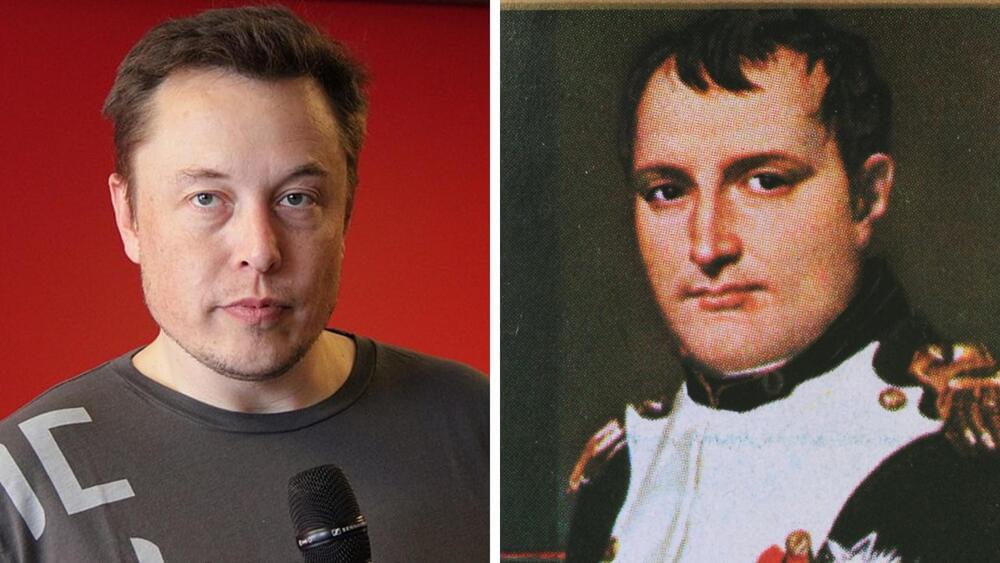
Elon Musk’s biography writer Walter Isaacson says that the billionaire has been motivated by French emperor Napoleon Bonaparte.
For these reasons, and more, it seems unlikely to me that LLM technology alone will provide a route to “true AI.” LLMs are rather strange, disembodied entities. They don’t exist in our world in any real sense and aren’t aware of it. If you leave an LLM mid-conversation, and go on holiday for a week, it won’t wonder where you are. It isn’t aware of the passing of time or indeed aware of anything at all. It’s a computer program that is literally not doing anything until you type a prompt, and then simply computing a response to that prompt, at which point it again goes back to not doing anything. Their encyclopedic knowledge of the world, such as it is, is frozen at the point they were trained. They don’t know of anything after that.
And LLMs have never experienced anything. They are just programs that have ingested unimaginable amounts of text. LLMs might do a great job at describing the sensation of being drunk, but this is only because they have read a lot of descriptions of being drunk. They have not, and cannot, experience it themselves. They have no purpose other than to produce the best response to the prompt you give them.
This doesn’t mean they aren’t impressive (they are) or that they can’t be useful (they are). And I truly believe we are at a watershed moment in technology. But let’s not confuse these genuine achievements with “true AI.” LLMs might be one ingredient in the recipe for true AI, but they are surely not the whole recipe — and I suspect we don’t yet know what some of the other ingredients are.
The Four Fundamental Forces
Posted in particle physics
Introducing the four fundamental forces of nature that describe (nearly) everything going on in our universe. This clip is taken from the Shots In The Quark T…