“I’m still working on being a good CEO,” Jensen Huang said in an interview at his alma mater, Stanford University.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Behavioral and neural correlates to multisensory detection of sick humans
Importantly, the superior temporal sulcus (STS), and superior temporal gyrus (STG) are considered core areas for multisensory integration (17, 38), including for olfactory–visual integration (44). The STS was significantly connected to the IPS during multisensory integration, as indicated by the PPI analysis ( Fig. 3 ) focusing on functional connectivity of IPS and whole-brain activation. Likewise, the anterior and middle cingulate cortex, precuneus, and hippocampus/amygdala were activated when testing sickness-cue integration-related whole-brain functional connectivity with the IPS but were not activated when previously testing for unisensory odor or face sickness perception. In this context, hippocampus/amygdala activation may represent the involvement of an associative neural network responding to threat (24) represented by a multisensory sickness signal. This notion supports the earlier assumption of olfactory-sickness–driven OFC and MDT activation, suggested to be part of a neural circuitry serving disease avoidance. Last, the middle cingulate cortex has recently been found to exhibit enhanced connectivity with the anterior insula during a first-hand experience of LPS-induced inflammation (26), and this enhancement has been interpreted as a potential neurophysiological mechanism involved in the brain’s sickness response. Applied to the current data, the middle cingulate cortex, in the context of multisensory-sickness–driven associations between IPS and whole-brain activations, may indicate a shared representation of an inflammatory state and associated discomfort.
In conclusion, the present study shows how subtle and early olfactory and visual sickness cues interact through cortical activation and may influence humans’ approach–avoidance tendencies. The study provides support for sensory integration of information from cues of visual and olfactory sickness in cortical multisensory convergences zones as being essential for the detection and evaluation of sick individuals. Both olfaction and vision, separately and following sensory integration, may thus be important parts of circuits handling imminent threats of contagion, motivating the avoidance of sick conspecifics (3, 5).
60 Minutes Australia
More and more people around the world are taking their chances that science will advance significantly in the future so their preserved, frozen bodies can be revived back to life.
► WATCH Full Episodes on 9NOW: https://9now.app.link/uNP4qBkmN6
► Subscribe here: http://9Soci.al/chmP50wA97J
Synopsis | Dying for Life (2024)
For as long as mankind has been capable of thought, we have known the truth about life: that it ends in death. But as our scientific knowledge increases, there are more and more believers who think humans will soon be clever enough to halt the inevitability of their mortality. Others of course will never be convinced living forever is either possible or desirable. They say the idea that death could one day be considered a curable disease is nonsense. But advocates of cryonics, including many Australians, tell Amelia Adams now is the time to start getting ready for life after life.
MORE VIDEOS like this one.
► • Extreme diets and health trends peopl…
► • Botox addicts getting younger and you…
► • Pill claiming to extend human life to…
FOLLOW 60 Minutes Australia.
► WATCH more of 60 Minutes Australia: https://www.60minutes.com.au.
► Facebook: / 60minutes9
► Twitter: / 60mins.
► Instagram: / 60minutes9
ABOUT 60 Minutes Australia.
Embodied Generalist LEO
From Beijing Institute for General Artificial Intelligence (BIGAI) 2Peking University 3Carnegie Mellon University 4Tsinghua University.
🦁 Introducing LEO: an embodied generalist agent in 3D World🌎
Everything 👉 http://embodied-generalist.github.io
Japan’s Anti-Aging Vaccine: The Future of Longevity Revealed
Welcome back to Virtual Reality James! In this exciting video, we delve into the groundbreaking topic of Japan’s Anti-Aging Vaccine and explore the future of longevity. Join us as we uncover the latest scientific advancements and reveal how this revolutionary vaccine could potentially transform the way we age.
Discover the secrets behind this cutting-edge technology that aims to slow down the aging process and enhance our quality of life. We’ll explore the science behind the vaccine, its potential benefits, and the implications it may have on society as a whole.
Throughout the video, we’ll interview leading experts in the field, providing you with valuable insights and expert opinions. Learn about the research studies conducted, the promising results obtained, and the potential challenges that lie ahead.
Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the potential impact of Japan’s Anti-Aging Vaccine on our future. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of the advancements in longevity research and the possibilities they hold.
Can algae save the world? | DW Documentary
Using algae to solve humanity’s most pressing problems — that’s the ambitious aim of a team of researchers from Germany. After all, algae are posessed of staggering superpowers: for example, the ability to bind CO2. Algae can also be used to make plastic substitutes and even medication.
For a research project called \.
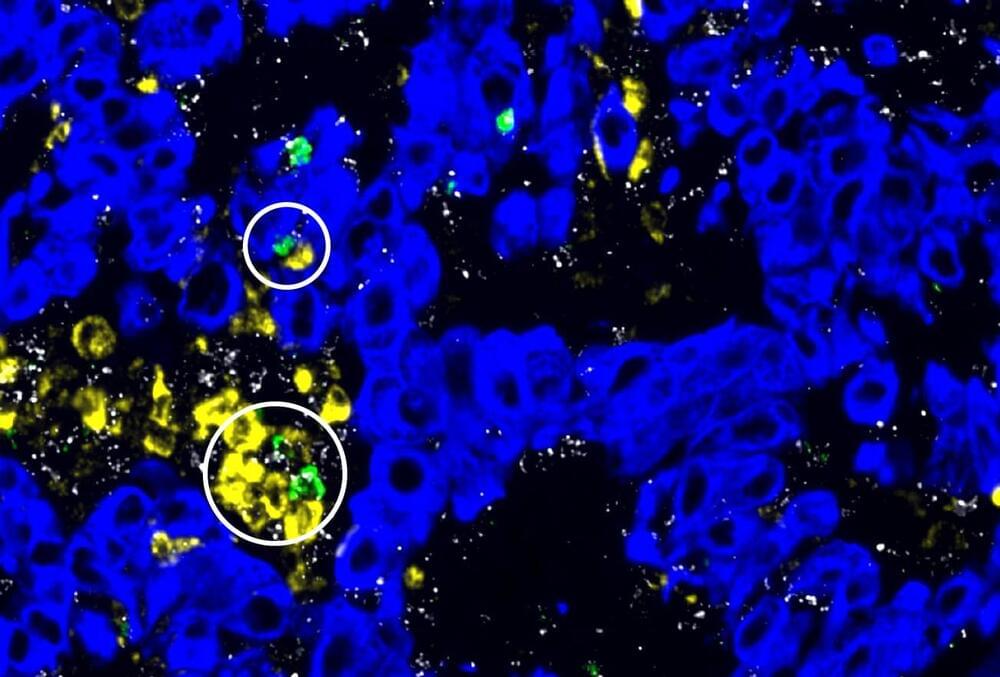
Spatial study of lung cancer reveals immune markers of response to immunotherapy
Through Broad’s Scientists in the Classroom program, Broad researchers visit every 8th grade classroom in Cambridge each year to talk about genetics and evolution.
Every summer, 18 high school students spend six weeks at Broad working side-by-side with mentors on cutting-edge research.
In November 2022, Broad’s Genomics Platform sequenced its 500,000th whole human genome, a mere four years after sequencing its 100,000th.

Elon Musk Predicts A ‘Universal High Income’ As Jobs Are Phased Out And Employment Becomes Obsolete — It’ll Be ‘Somewhat Of An Equalizer’
Elon Musk made some striking predictions about the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on jobs and income at the inaugural AI Safety Summit in the U.K. in November.
The serial entrepreneur and CEO painted a utopian vision where AI renders traditional employment obsolete but provides an “age of abundance” through a system of “universal high income.”
“It’s hard to say exactly what that moment is, but there will come a point where no job is needed,” Musk told U.K. Prime Minister Rishi Sunak. “You can have a job if you want to have a job or sort of personal satisfaction, but the AI will be able to do everything.”
19.5y Younger Biological Age: Supplements, Diet (Test #2 in 2024)
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7x…

Nvidia’s Jensen Huang says AI hallucinations are solvable, artificial general intelligence is 5 years away
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) — often referred to as “strong AI,” “full AI,” “human-level AI” or “general intelligent action” — represents a significant future leap in the field of artificial intelligence. Unlike narrow AI, which is tailored for specific tasks, such as detecting product flaws, summarizing the news, or building you a website, AGI will be able to perform a broad spectrum of cognitive tasks at or above human levels. Addressing the press this week at Nvidia’s annual GTC developer conference, CEO Jensen Huang appeared to be getting really bored of discussing the subject — not least because he finds himself misquoted a lot, he says.
The frequency of the question makes sense: The concept raises existential questions about humanity’s role in and control of a future where machines can outthink, outlearn and outperform humans in virtually every domain. The core of this concern lies in the unpredictability of AGI’s decision-making processes and objectives, which might not align with human values or priorities (a concept explored in-depth in science fiction since at least the 1940s). There’s concern that once AGI reaches a certain level of autonomy and capability, it might become impossible to contain or control, leading to scenarios where its actions cannot be predicted or reversed.
When sensationalist press asks for a timeframe, it is often baiting AI professionals into putting a timeline on the end of humanity — or at least the current status quo. Needless to say, AI CEOs aren’t always eager to tackle the subject.