The father of modern computing would have opened his arms to ChatGPT. You should too.

Tryptophan is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be produced by the body but must be included as part of our diet. People with chronic bowel inflammation consume significantly more tryptophan than healthy people, as shown by previous research that involved members of the Cluster of Excellence “Precision Medicine in Chronic Inflammation” (PMI) at Kiel University.
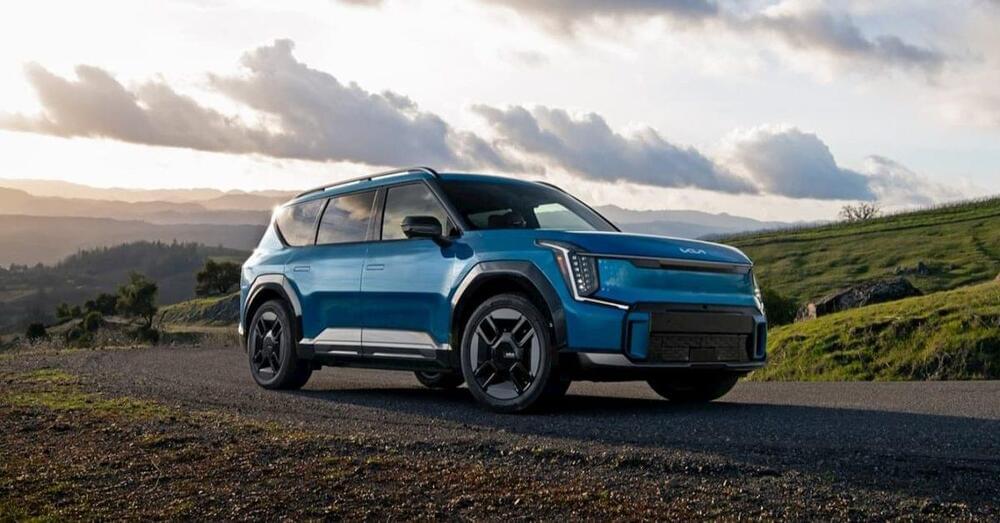

Kia’s first three-row electric SUV is off to a good start. However, Kia will accelerate EV9 momentum with plans to begin US production by May. Kia expects the EV9 will qualify for the full $7,500 EV tax credit by early next year.
After launching the EV9 in the US late last year, Kia has handed over 3,839 models in the US. Starting under $55,000, Kia calls its electric family move an “industry wake-up call.”
Despite the strong start, Kia expects the momentum to pick up. Kia currently builds the EV9 in Korea but expects to move production to the US by the end of May.

Researchers have developed a robot that can anticipate your smile and return it almost instantly. The new work, published as a study in the journal Science Robotics, is intended to help human-looking robots appear more natural. The actual expressions this one makes, however, look anything but.
Named “Emo,” the bot can predict your smile less than a second before it actually appears using cameras lodged into its pupils. Then just as the smile creeps up your face, as shown in an amusing video from New Scientist, Emo grimaces its horrific imitation of one in return, making sure to keep eye contact the entire time.
“I’m a jaded roboticist, but I smile back at this robot,” study coauthor Hod Lipson, at Columbia University, told New Scientist.

A hydrogen fuel-cell passenger train developed by Swiss rail vehicle maker Stadler Rail has achieved a new Guinness World Record, traveling for almost two days around the clock for a distance of 1,741.7 miles.
Efforts to clean up dirty trains are already well underway, with heavy investment in electrifying networks around the world as well as rolling out battery-electric locomotives such as the FLXDrive, the Blues train and the Flirt Akku.
That last example is made by Stadler Rail AG, and managed to achieve a Guinness World Record in 2021 for the longest per-charge battery-only journey of 224 km (~140 miles), on a route between Berlin and Warnemünde during a freezing local winter – not bad for a train that was designed with an operational per-charge range of 80 km.
An automated YouTube stream of an endless AI-generated “Family Guy” show called “AI Peter” has devolved into ear-bruising chaos, Kotaku reports, with some of your favorite characters of the sitcom blurting out gibberish — and screaming at the top of their lungs nonstop.
The stream, which started back in June of last year, relies on audience submissions to come up AI-generated scripts for back-t0-back “episodes” of the beloved animated series.
And, as Kotaku points out, moderation of these paid submissions doesn’t appear to be front of mind. Some users are misusing the generative AI tech to break the unsettling, 3D-animated characters in unusual ways.