Apple’s Vision Pro will be released on Friday, and reviews of the VR goggle’s custom digital avatars are already pouring: unsettling and bad.



During my pursuits, I’ve come across an increasing number of exciting nontraditional routes for funding scientific research. The efforts of Adam Marblestone and Benjamin Reinhardt have been particularly instrumental in stimulating this ecosystem, but many other great people have contributed as well. These new funding routes are a welcome relief since many of the most innovative and far-reaching projects are not especially suited for receiving governmental NIH, NSF, etc. funding. If you would like to find a more comprehensive list of such alternative funding sources, you should check out https://arbesman.net/overedge/. My own list (below) consists of funding sources that stand out to me as particularly promising. I hope you find this useful and feel free to reach out if you have any questions!
Amaranthe Foundation https://amaranth.foundation/bottlenecks-of-aging “We outline initiatives which, if executed, could meaningfully accelerate the advancement of aging science and other life-extending technologies. The resulting document is a philanthropic menu, for which Amaranth is seeking both talent to execute on and co-funders. If you are a founder, researcher, or philanthropist interested in executing or co-sponsoring one or several of the projects or proposals below, please reach out to us”

The advent of advanced artificial intelligence (AI) technologies is poised to bring about a significant upheaval in societal power dynamics. One of the notable transformations on the horizon is the potential disruption of the so-called “words” class. As AI continues to advance, it has the potential to limit the status and earning potential of individuals […].
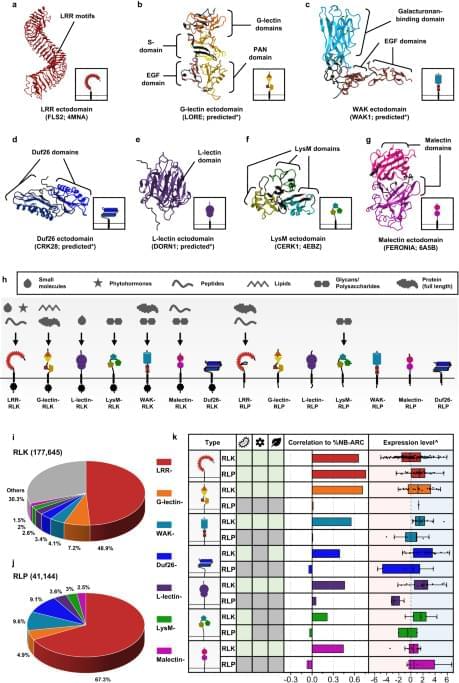
Plant cell-surface receptors that are known to participate in immunity, development, and reproductive processes include the LRR-, G-lectin-, Wall-associated kinase (WAK)-, Domain of Unknown Function 26 (Duf26)-, L-lectin-, Lysin motif (LysM)-, and Malectin-containing RLKs and RLPs (Fig. 1a–h). There are additional RLK families with different ectodomains, such as the proline-rich extensin-like receptor kinases (PERKs) and thaumatin-like protein kinases (TLPKs)9,13. However, their function in immunity is not well-characterized. Cell-surface receptors with LRR-, G-lectin-, WAK-, and LysM-ectodomains have been reported to recognise PAMPs, while others perceive self-molecules or unidentified ligands (Fig. 1h; Supplementary Fig. 1). Recognition of the diverse array of ligands is likely to be accomplished by variable structures and combinations of different ectodomains (Fig. 1a–g). To trace the origins of different receptor classes within the plant lineage, we first identified RLKs and RLPs in 350 genomes from Glaucophyta, red algae, green algae, Bryophytes, and Tracheophytes. We define here RLKs as any proteins with both 1–2 TMs and KDs, and RLPs as any protein with 1–2 TMs, but lack KDs. In total, we identified 177,645 RLKs, almost up to 70% of which possess either LRR-, G-lectin-, WAK-, Duf26-, L-lectin-, LysM-and Malectin-ectodomains (Fig. 1i). Next, we searched for proteins with these ectodomains and TMs that lack KDs and found 41,144 RLPs (Fig. 1j). We further examined which of the identified RLKs and RLPs families are likely to be involved in immunity. A previous report suggested a positive correlation between the gene family sizes of cell-surface immune receptors and intracellular immune receptors (the NB-ARC family) across the angiosperms4. We examined the correlation between the relative size (%; number of identified genes in the family/numbers of searched genes × 100; see methods) of the RLK families, the RLPs families, and the NB-ARC family in each genome. Notably, most RLK families (except for the LysM-RLKs) exhibit positive correlations with the NB-ARC family, while most RLP families (except for the LRR-RLPs) do not exhibit positive correlation with the NB-ARC family (Main Fig. 1k). Furthermore, we checked the expression level of these receptor families in Arabidopsis thaliana during immunity. Notably, the RLKs, except for LRR-and Malectin-RLKs, generally exhibit higher expression levels compared to the RLPs during immunity (Main Fig. 1k; Supplementary Fig. 2). These data collectively suggest that the RLKs are more likely to be involved in immunity than the RLPs.
Next, we examined the presence or absence of ectodomains (LRR-, G-lectin-, WAK-, Duf26-, L-lectin-, LysM-and Malectin-ectodomains lacking TM or KD; ectodomain-only proteins), RLPs (TM-bound ectodomains) and RLKs (ectodomains encompassing both TM and KD) in the plant lineage (Fig. 2; Supplementary Fig. 3; Supplementary Data 1a–c). Ectodomains exhibit an ancient heritage, with LRR-, WAK-, LysM-, Malectin-, and L-lectin-domains dating back to the era of Glaucophyta. Similarly, relatively ancient counterparts such as LRR-RLPs, WAK-RLPs, LysM-RLPs, Malectin-RLPs, and L-lectin-RLPs are found in both Glaucophyta and Rhodophyta. In contrast, RLKs emerged more recently. Green algae harbour WAK-RLKs, Malectin-RLKs, and G-lectin-RLKs, and LysM-RLKs, L-lectin-RLKs, and Duf-26-RLKs are exclusive to Embryophytes (Fig. 2). Except for LRR-RLPs, all six families of RLP are basal to the RLK families.

A physicist’s wild romp through the multiverse probes space-time, string theory, and everything in between.
Melanie Frappier [email protected] Authors Info & Affiliations
Science.
There has been significant progress in the field of quantum computing. Big global players, such as Google and IBM, are already offering cloud-based quantum computing services. However, quantum computers cannot yet help with problems that occur when standard computers reach the limits of their capacities because the availability of qubits or quantum bits, i.e., the basic units of quantum information, is still insufficient.
One of the reasons for this is that bare qubits are not of immediate use for running a quantum algorithm. While the binary bits of customary computers store information in the form of fixed values of either 0 or 1, qubits can represent 0 and 1 at one and the same time, bringing probability as to their value into play. This is known as quantum superposition.
This makes them very susceptible to external influences, which means that the information they store can readily be lost. In order to ensure that quantum computers supply reliable results, it is necessary to generate a genuine entanglement to join together several physical qubits to form a logical qubit. Should one of these physical qubits fail, the other qubits will retain the information. However, one of the main difficulties preventing the development of functional quantum computers is the large number of physical qubits required.

We are in the middle of a data-driven science boom. Huge, complex data sets, often with large numbers of individually measured and annotated ‘features’, are fodder for voracious artificial intelligence (AI) and machine-learning systems, with details of new applications being published almost daily.
But publication in itself is not synonymous with factuality. Just because a paper, method or data set is published does not mean that it is correct and free from mistakes. Without checking for accuracy and validity before using these resources, scientists will surely encounter errors. In fact, they already have.
In the past few months, members of our bioinformatics and systems-biology laboratory have reviewed state-of-the-art machine-learning methods for predicting the metabolic pathways that metabolites belong to, on the basis of the molecules’ chemical structures1. We wanted to find, implement and potentially improve the best methods for identifying how metabolic pathways are perturbed under different conditions: for instance, in diseased versus normal tissues.
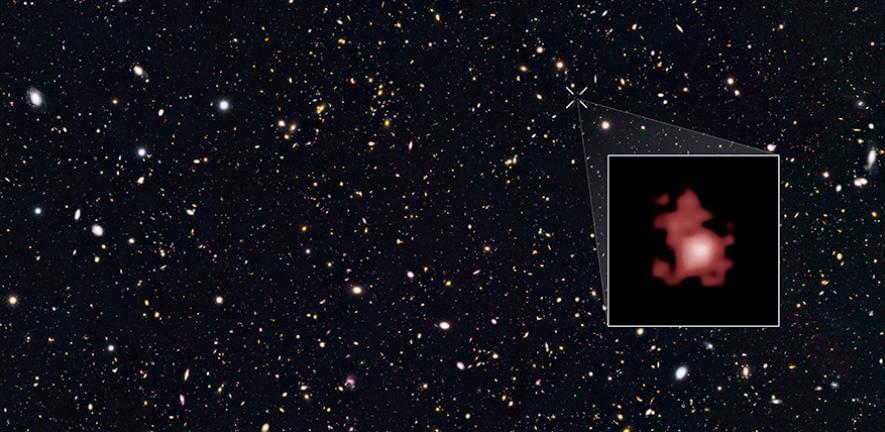

The young host galaxy, called GN-z11, glows from such an energetic black hole at its centre. Black holes cannot be directly observed, but instead they are detected by the tell-tale glow of a swirling accretion disc, which forms near the edges of a black hole. The gas in the accretion disc becomes extremely hot and starts to glow and radiate energy in the ultraviolet range. This strong glow is how astronomers are able to detect black holes.
GN-z11 is a compact galaxy, about one hundred times smaller than the Milky Way, but the black hole is likely harming its development. When black holes consume too much gas, it pushes the gas away like an ultra-fast wind. This ‘wind’ could stop the process of star formation, slowly killing the galaxy, but it will also kill the black hole itself, as it would also cut off the black hole’s source of ‘food’
Maiolino says that the gigantic leap forward provided by JWST makes this the most exciting time in his career. “It’s a new era: the giant leap in sensitivity, especially in the infrared, is like upgrading from Galileo’s telescope to a modern telescope overnight,” he said. “Before Webb came online, I thought maybe the universe isn’t so interesting when you go beyond what we could see with the Hubble Space Telescope. But that hasn’t been the case at all: the universe has been quite generous in what it’s showing us, and this is just the beginning.”
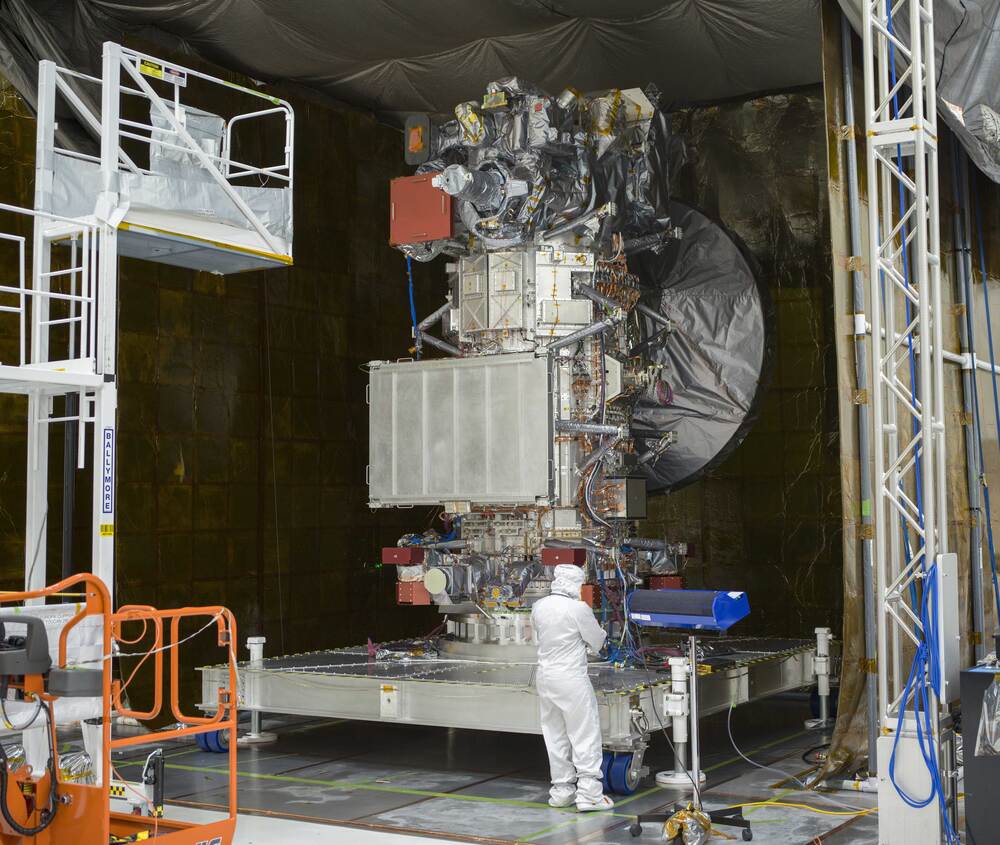

A mission more than a decade in the making, NASA’s Europa Clipper is slated to greatly expand our understanding of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, including whether it could support life. These findings will be conducted by a suite of powerful instruments contributed by a myriad of academic and research institutions across the United States. Recently, NASA JPL finished installing all these instruments on the pioneering spacecraft, bringing it one major step closer to its launch, which is currently scheduled for October of this year.
“The instruments work together hand in hand to answer our most pressing questions about Europa,” said Dr. Robert Pappalardo, who is the project scientist on Europa Clipper. “We will learn what makes Europa tick, from its core and rocky interior to its ocean and ice shell to its very thin atmosphere and the surrounding space environment.”
The nine instruments that will be responsible for accomplishing the fantastic science during the mission include the Europa Imaging System (EIS), Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS), Europa Ultraviolet Spectrograph (Europa-UVS), Mapping Imaging Spectrometer for Europa (MISE), Europa Clipper Magnetometer (ECM), Plasma Instrument for Magnetic Sounding (PIMS), Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface (REASON), MAss Spectrometer for Planetary EXploration/Europa (MASPEX), SUrface Dust Analyzer (SUDA).