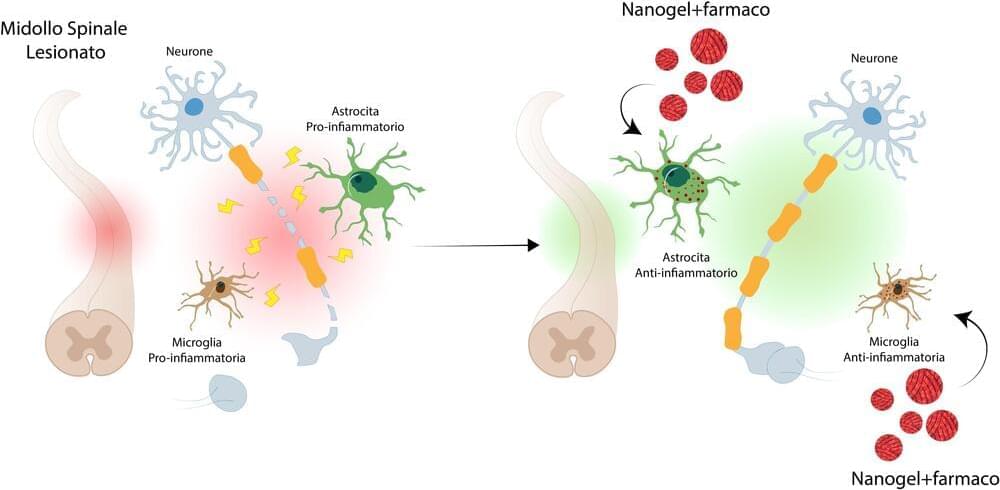
In a study published in Advanced Materials, researchers have demonstrated that an innovative nano-vector (nanogel), which they developed, is able to deliver anti-inflammatory drugs in a targeted manner into glial cells actively involved in the evolution of spinal cord injury, a condition that leads to paraplegia or quadriplegia.
Treatments currently available to modulate the inflammatory response mediated by the component that controls the brain’s internal environment after acute spinal cord injury showed limited efficacy. This is also due to the lack of a therapeutic approach that can selectively act on microglial and astrocytic cells.
The nanovectors developed by Politecnico di Milano, called nanogels, consist of polymers that can bind to specific target molecules. In this case, the nanogels were designed to bind to glial cells, which are crucial in the inflammatory response following acute spinal cord injury. The collaboration between Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS and Politecnico di Milano showed that nanogels, loaded with a drug with anti-inflammatory action (rolipram), were able to convert glial cells from a damaging to a protective state, actively contributing to the recovery of injured tissue.