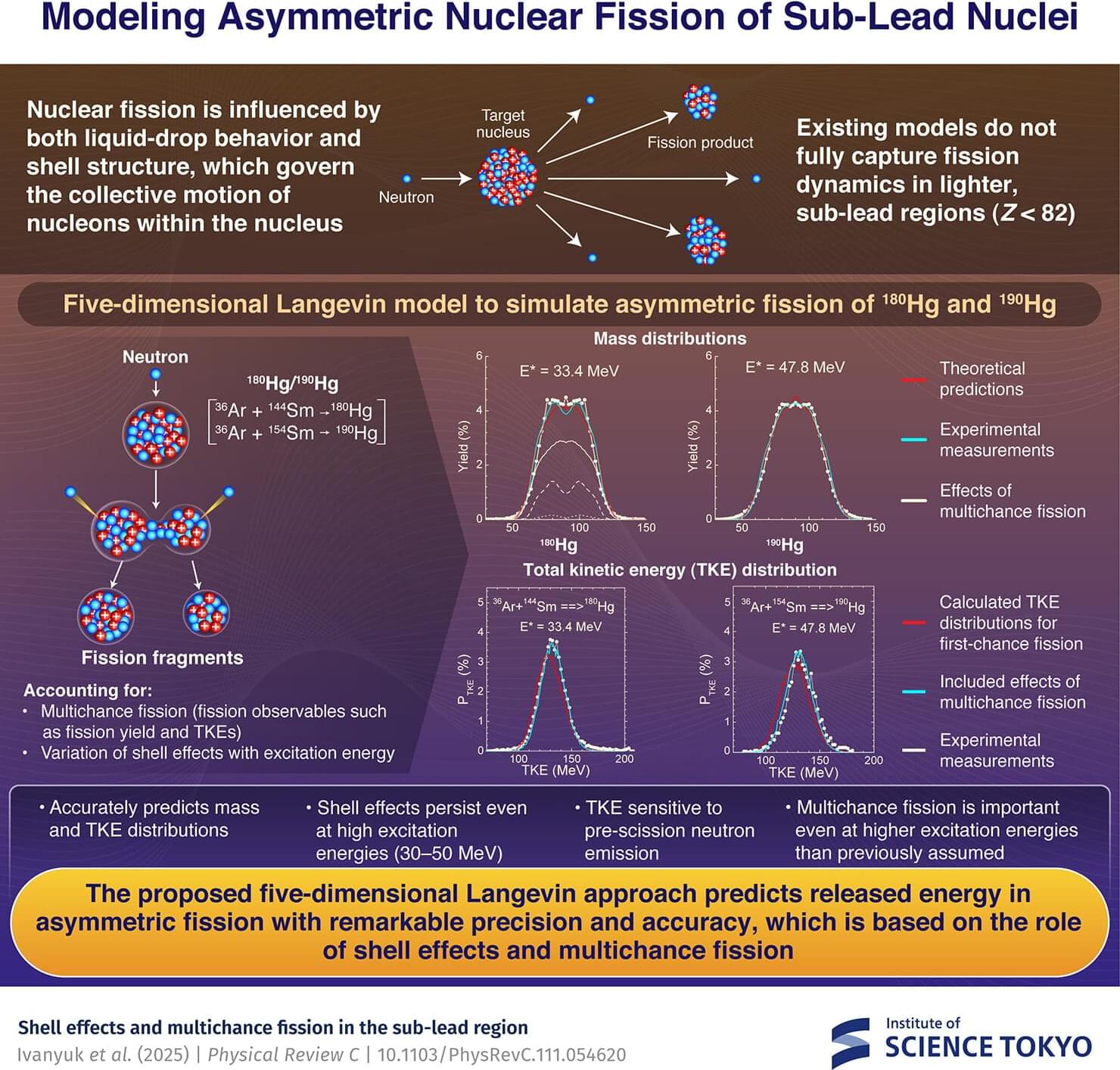
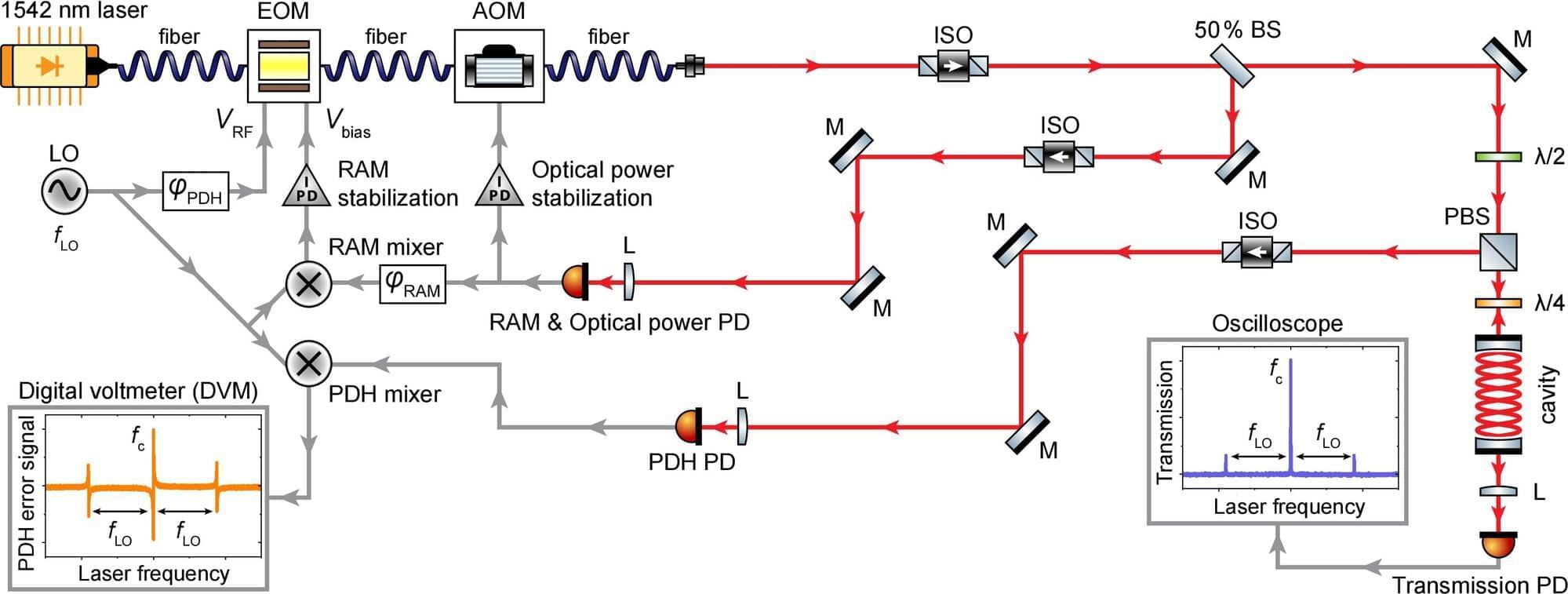
A five-dimensional (5D) Langevin approach developed by an international team of researchers, including members from Science Tokyo, accurately reproduces complex fission fragment distributions and kinetic energies in medium-mass mercury isotopes (180 Hg and 190 Hg). The model successfully captures the unusual “double-humped” fragment mass distribution observed in mercury-180 and offers new insights into how nuclear shell effects influence fission dynamics—even at higher excitation energies than previously thought—advancing our understanding of fission in the sub-lead region.
Nuclear fission, the process by which an atomic nucleus splits into smaller parts, is a fundamental process in nuclear physics. While the fission of heavy elements like uranium and plutonium is well studied, lighter nuclei such as mercury (Hg) behave in unexpected ways.
Experiments have shown that 180 Hg undergoes an unexpected form of asymmetric fission, producing fragments of very different sizes. These findings challenge existing models and highlight the need to better understand how nuclear structure affects fission in the sub-lead region, which includes elements with atomic numbers below 82.