Link :
The project has secured £1.7 million.
How viewing the Sun in ultraviolet can uncover its secrets. Get a 20% discount on your next VisiSolar purchase when you use this link: https://bit.ly/49G6XhX
Astrum Podcast: https://www.buzzsprout.com/2250635/share.
Displate Posters: https://displate.com/promo/astrum?art…
Astrum Merch! https://astrum-shop.fourthwall.com/
Join us on the Astrum discord: / discord.
SUBSCRIBE for more videos about our other planets.
Subscribe! http://goo.gl/WX4iMN
Facebook! http://goo.gl/uaOlWW
Twitter! http://goo.gl/VCfejs.
Astrum Spanish: / @astrumespanol.
Astrum Portuguese: / @astrumbrasil.
Donate!
Patreon: http://goo.gl/GGA5xT
Ethereum Wallet: 0x5F8cf793962ae8Df4Cba017E7A6159a104744038
Become a Patron today and support my channel! Donate link above. I can’t do it without you. Thanks to those who have supported so far!
Image Credit: Simon and Nicolas Lefaudeux https://hdr-astrophotography.com/

“Declining winter snow cover is one of the most obvious and pronounced impacts of climate change in the Alps. Its effects on the functioning and biodiversity of alpine ecosystems are a major concern for people living in Alpine regions and beyond,” said Dr. Michael Bahn.
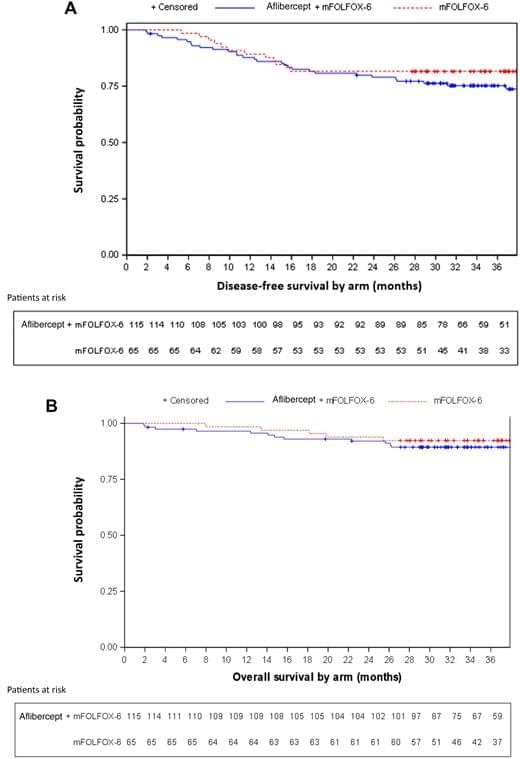
How can the impacts of climate change alter biodiversity in vast mountain ranges throughout the world? This is what a recent study published in Global Change Biology hopes to address as a team of international researchers investigated how decreased levels of vegetation and snow cover in the Alps due to climate change are having adverse effects on the region’s biodiversity. This study holds the potential to help scientists, legislators, and the public better understand the short-and long-term impacts of climate change on regions across the globe.
For the study, the researchers examined variances in soil grassland microbial nitrogen cycling within the Alps during the spring and autumn due to their warming temperatures that are exceedingly more than twice the global average. In the end, the researchers discovered that nitrogen uptake by plant organics were reduced in the spring and autumn by 70 percent and 82 percent, soil microbial biomass was reduced by 19 percent and 38 percent, and the number of harmful bacteria that could have adverse effects on nitrogen production increased 253 percent and 136 percent, respectively. Collectively, the researchers determined that climate change is having an adverse effect on nitrogen cycling within the Alps’ grasslands.
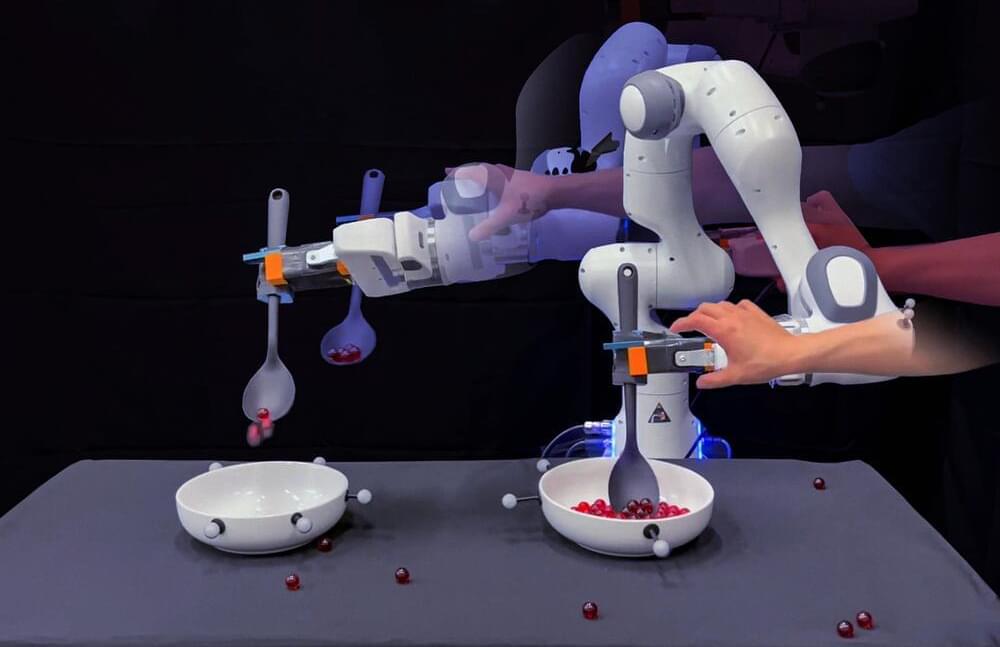
MIT engineers aim to give robots a bit of common sense when faced with situations that push them off their trained path, so they can self-correct after missteps and carry on with their chores. The team’s method connects robot motion data with the common sense knowledge of large language models, or LLMs.
Nvidia’s headquarters is now one of the most sought-after places to work. Spanning more than 1 million square feet combined, Nvidia’s space-ship-like buildings were designed with help from custom software powered by the AI chips that have made the company successful. WSJ gets a look inside. Photo: Nvidia.

Update added to the bottom of the article.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT is down for many people worldwide, with users facing multiple problems, including being unable to access their accounts, having their chat history come up empty, and the chat screens not loading properly.
When accessing ChatGPT, users may see a blank screen with “How can I help you today?” and, in some cases, a missing chat history.

During cell division, a ring forms around the cell equator, which contracts to divide the cell into two daughter cells. Together with researchers from Heidelberg, Dresden, Tübingen and Harvard, Professor Jan Kierfeld and Lukas Weise from the Department of Physics at TU Dortmund University have succeeded for the first time in synthesizing such a contractile ring with the help of DNA nanotechnology and to uncover its contraction mechanism.
The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications (“Triggered contraction of self-assembled micron-scale DNA nanotube rings”).
In synthetic biology, researchers try to recreate crucial mechanisms of life in vitro, such as cell division. The aim is to be able to synthesize minimal cells. The research team led by Professor Kerstin Göpfrich from Heidelberg University has now synthetically reproduced contractile rings for cell division using polymer rings composed of DNA nanotubes.


In support of a major collaborative project to store massive amounts of data in DNA molecules, a Los Alamos National Laboratory–led team has developed a key enabling technology that translates digital binary files into the four-letter genetic alphabet needed for molecular storage.
“Our software, the Adaptive DNA Storage Codec (ADS Codex), translates data files from what a computer understands into what biology understands,” said Latchesar Ionkov, a computer scientist at Los Alamos and principal investigator on the project. “It’s like translating from English to Chinese, only harder.”
DNA offers a compact way to store huge amounts of data cost-effectively. Los Alamos National Laboratory has developed ADS Codex to translate the 0s and 1s of digital computer files into the four-letter code of DNA.