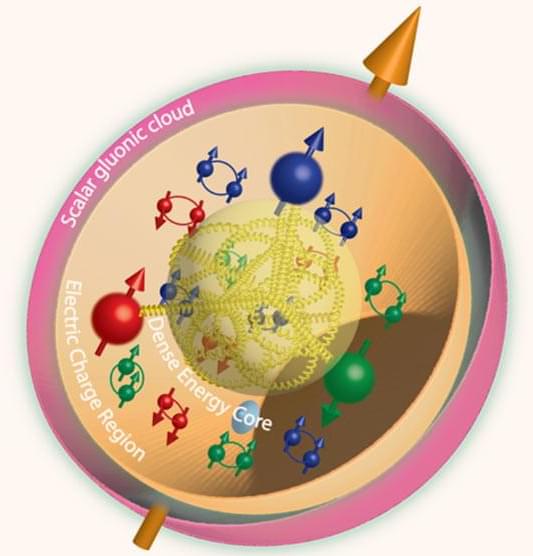
The proton is one of the main building blocks of all visible matter in the Universe.

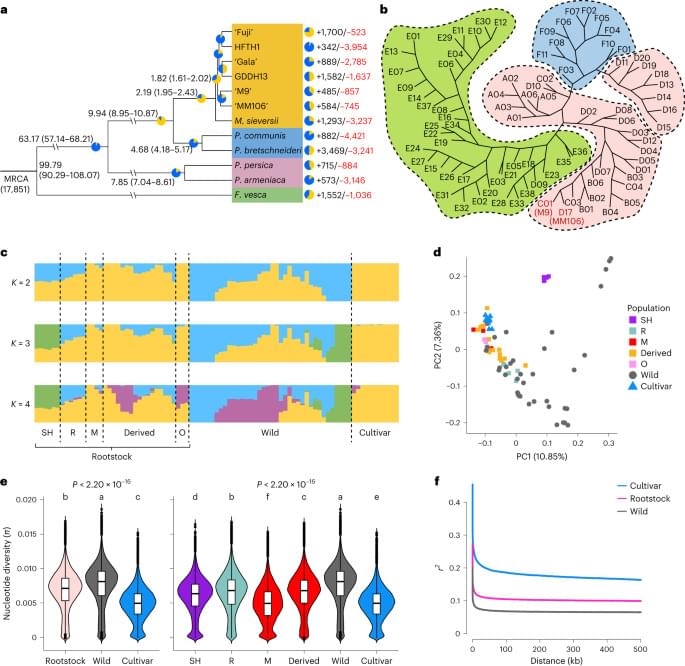
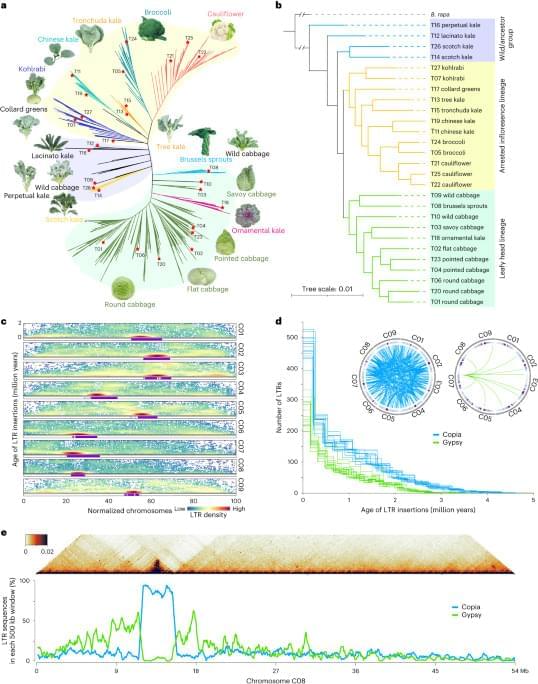
To construct a pan-genome that encompasses the full range of genetic diversity in B. ole racea, we analyzed the resequencing data of 704 globally distributed B. ole racea accessions covering all different morphotypes and their wild relatives (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). We identified 3,792,290 SNPs and 528,850 InDels in these accessions using cabbage JZS as reference genome22. A phylogenetic tree was then constructed using SNPs, which classified the 704 accessions into the following three main groups: wild B. ole racea and kales, arrested inflorescence lineage (AIL) and leafy head lineage (LHL; Fig. 1a and Supplementary Note 2). The phylogenetic relationship revealed in our study was generally consistent with those reported previously4,5,24,25. Based on the phylogeny and morphotype diversity, we selected 22 representative accessions for de novo genome assembly (Table 1).
We assembled genome sequences of the 22 accessions by integrating long-reads (PacBio or Nanopore sequencing), optical mapping molecules (BioNano) or high-throughput chromosome conformation capture data (Hi-C) and Illumina short-reads (Methods; Supplementary Note 2 and Supplementary Tables 3–7). The total genome size of these assemblies ranged from 539.87 to 584.16 Mb with an average contig N50 of 19.18 Mb (Table 1). An average of 98% contig sequences were anchored to the nine pseudochromosomes of B. ole racea. The completeness of these genome assemblies was assessed using benchmarking universal single-copy orthologs (BUSCO), with an average of 98.70% complete score in these genomes (Supplementary Table 8).
To minimize artifacts that could arise from different gene prediction approaches, we predicted gene models of both the 22 newly assembled genomes and the five reported high-quality genomes5,21,22,23 using the same annotation pipeline (Methods). Using an integrated strategy combining ab initio, homology-based and transcriptome-assisted prediction, we obtained a range of 50,346 to 55,003 protein-coding genes with a mean BUSCO value of 97.9% in these genomes (Table 1). After gene prediction, a phylogenetic tree constructed based on single-copy orthologous genes clustered the 27 genomes into three groups, similar to the results observed in the population (Fig. 1a and b).

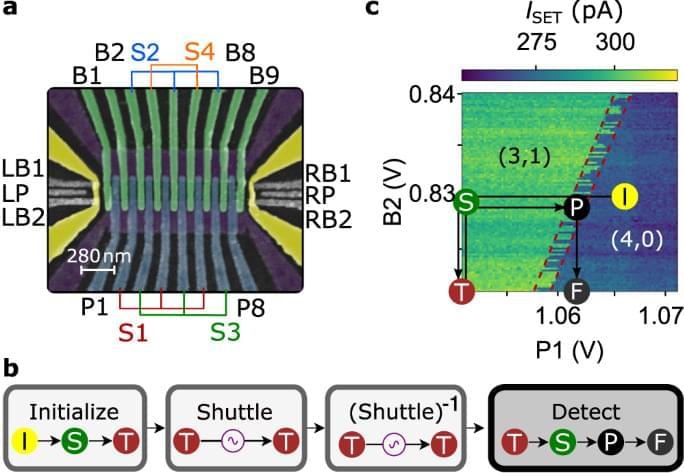
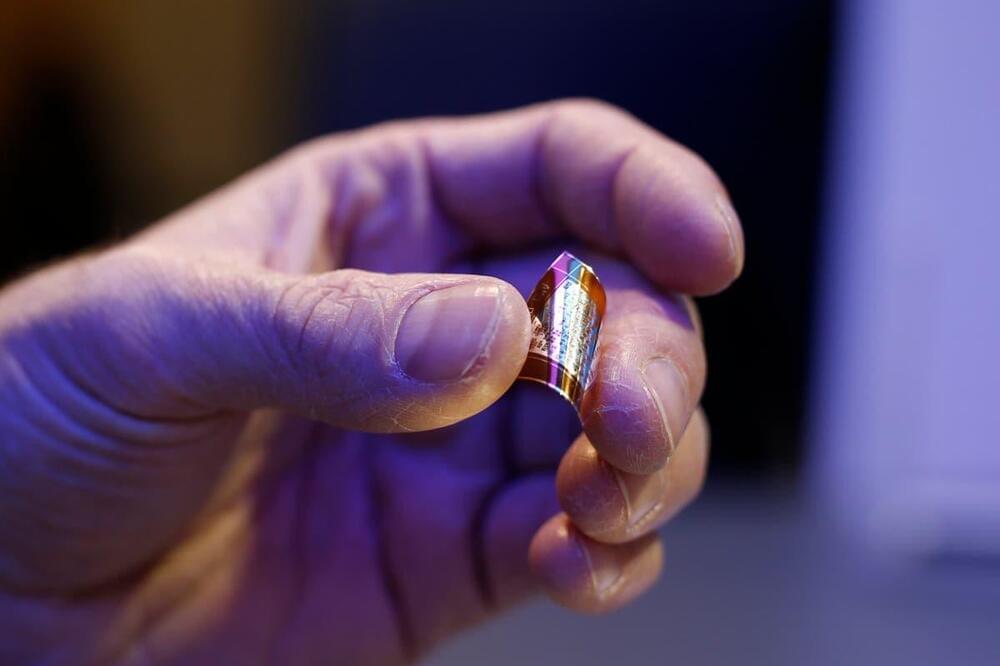
Electron charge and spin shuttling is a promising technique for connecting distant spin qubits. Here the authors use conveyor-mode shuttling to achieve high-fidelity transport of a single electron spin in Si/SiGe by separation and rejoining of two spin-entangled electrons across a shuttling distance of 560 nm.
Add a dash of creamer to your morning coffee, and clouds of white liquid will swirl around your cup. But give it a few seconds, and those swirls will disappear, leaving you with an ordinary mug of brown liquid.
Something similar happens in quantum computer chips—devices that tap into the strange properties of the universe at its smallest scales—where information can quickly jumble up, limiting the memory capabilities of these tools.
That doesn’t have to be the case, said Rahul Nandkishore, associate professor of physics at the University of Colorado Boulder.
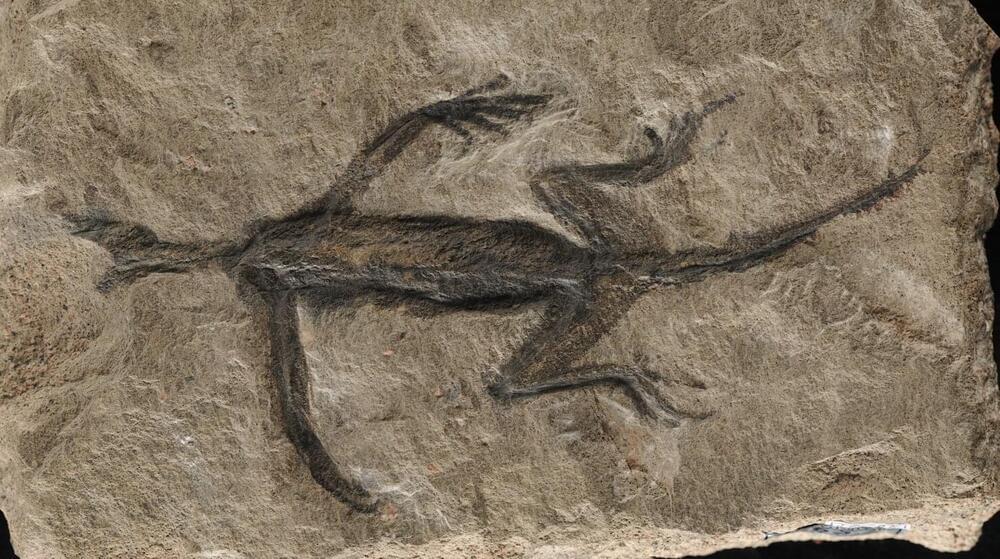


A 280-million-year-old fossil that has baffled researchers for decades has been shown to be—in part—a forgery, following new examination of the remnants.
The discovery has led the team, headed by Dr. Valentina Rossi of University College Cork, Ireland (UCC) to urge caution in how the fossil is used in future research.
Tridentinosaurus antiquus was discovered in the Italian Alps in 1931 and was thought to be an important specimen for understanding early reptile evolution. Its body outline, appearing dark against the surrounding rock, was initially interpreted as preserved soft tissues. This led to its classification as a member of the reptile group Protorosauria.
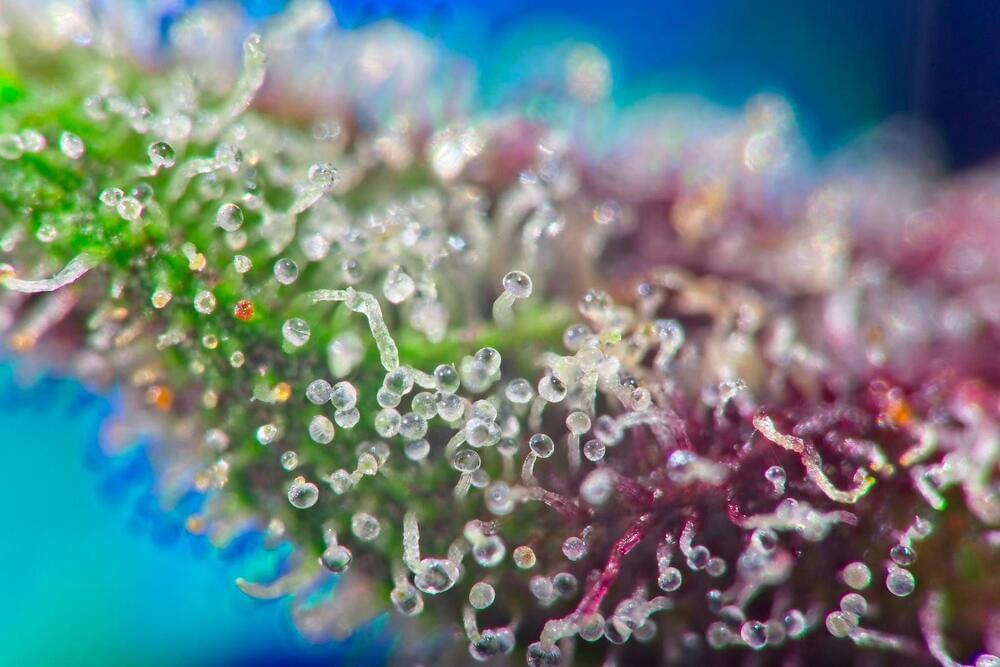

The cultivation of triploid genetics could be the game changer for the cannabis industry, as it promises to deliver higher THC levels, larger yields, faster growth, and seedless flowers.
The application of triploids is not a new concept in agriculture. Consuming seedless fruit generally enhances the eating experience for most people.
Consider bananas, for instance. Bananas lack seeds because the parent banana tree is triploid, even though pollination normally occurs.

Infleqtion is unique amongst quantum companies due its participation in so many different segments of the quantum computing industry including quantum components, quantum computers, quantum software, and quantum sensors. This strategy of a broad product portfolio provides both advantages and disadvantages for a company. The potential advantages include achieving synergy between different product areas with the neutral atom, atomic prism, photonic, software, and other technologies they have developed over the years. It also brings some diversity in the revenue streams because some products will provide early revenue while others might take a few years of development before they can make a revenue contribution. The potential disadvantages could include execution risks if the engineering resources are spread too thin. Also, there may be different sets of customers and sales channels for the different product lines which can increase the complexities of managing a sales force, calling on customers, and generating new business.
Nonetheless, Infleqtion has made some interesting announcements in the past few months. In 2023 alone, the Quantum Computing Report by GQI ran 17 different stories that included Infleqtion. This week they hosted a webinar to discuss their product roadmaps for sensors, software, and computing. The highlight of the webinar was the announcement of their quantum computing roadmap. In this article, we will cover their plans for quantum computing, but first we will start with the progress they talked about in quantum sensors and quantum software and then discuss quantum computing afterwards.
Infleqtion’s discussion of sensor products included ones named Tiqker, Sqywire, and eXaqt. Tiqker is a small form factor ultra-accurate clock intended for use in navigation, data centers, and communication networks. The company asserts that this clock is 100X more accurate than cesium beam atomic clocks and 100,000X more accurate than a crystal oscillator. In navigation applications it can be used in GPS-denied environments and in communication networks it can help increase bandwidth and reduce latencies due to the more precise clocking of the data signals. The company mentioned that they are partnering with a large company for use of Tiqker in data center applications and that Tiqker is now available for pre-order. Sqywire is an ultra-sensitive radio frequency (RF) receiver that senses RF signals with Rydberg state atom-based sensing. It can be used installed of a classical antenna and provides high sensitivity, lower power, and ultra-wide bandwidth in a form factor.