Quantum information scientists are always on the hunt for winning combinations of materials, materials that can be manipulated at the molecular level to reliably store and transmit information. Following a recent proof-of-principle demonstration, researchers are adding a new combination of compounds to the quantum materials roster.
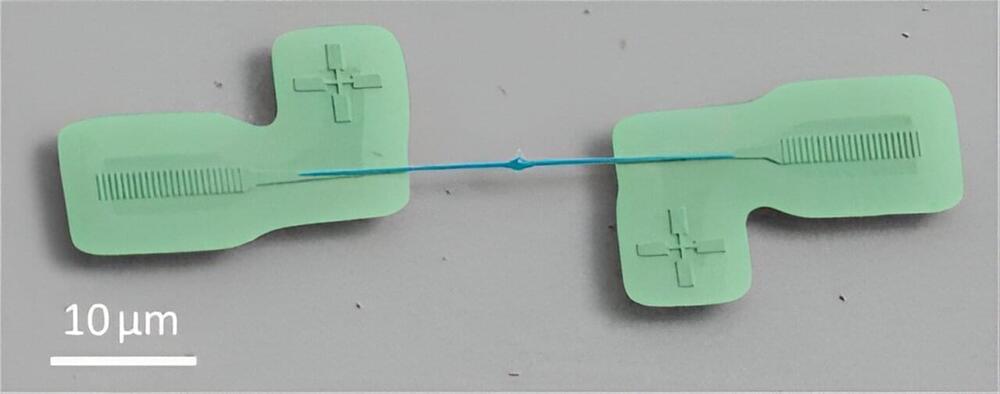
In a study reported in ACS Photonics, researchers combined two nanosized structures—one made of diamond and one of lithium niobate—onto a single chip. They then sent light from the diamond to the lithium niobate and measured the fraction of light that successfully made it across.
The greater that fraction, the more efficient the coupling of the materials, and the more promising the pairing as a component in quantum devices.