The Quantum Insider (TQI) is the leading online resource dedicated exclusively to Quantum Computing.


For the first time, researchers have used sound waves to 3D print an object from a distance—even with a wall in the way.
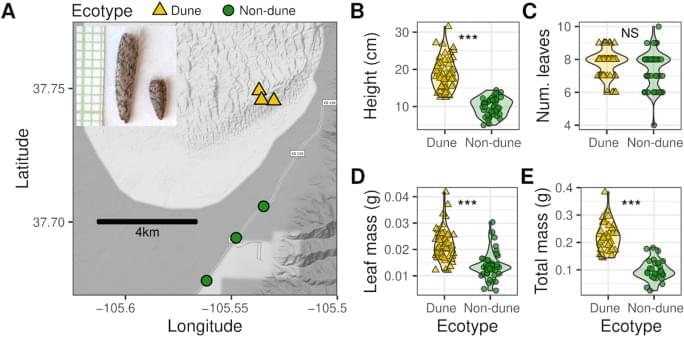
Innes, P.A., Goebl, A.M., Smith, C.C.R. et al. Gene expression and alternative splicing contribute to adaptive divergence of ecotypes. Heredity (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-023-00665-y.


This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participant:
Stephen Wolfram.
Moderator:
Brian Greene.
WSF Landing Page Link: https://www.worldsciencefestival.com/programs/coding-the-cos…putations/
- SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube Channel and “ring the bell” for all the latest videos from WSF
- VISIT our Website: http://www.worldsciencefestival.com.
- LIKE us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldsciencefestival.
- FOLLOW us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/WorldSciFest.
#briangreene #stephenwolfram #computerscience



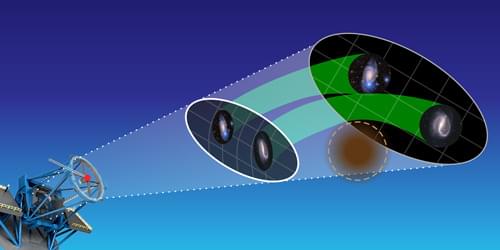
A new analysis of the distribution of matter in the Universe continues to find a discrepancy in the clumpiness of dark matter in the late and early Universe, suggesting a fundamental error in the standard cosmological model.
Cosmologists study the Universe by making a vast range of observations using a variety of modern techniques. Each observation can reveal different details about the Universe’s composition over a certain period of its history. An astronomical survey—a map of a region of the sky—is a powerful way to scan a large swath of the Universe and the objects it contains. For example, a weak-lensing survey does that by obtaining sharp images of galaxies, which can then be used to map the distribution of the Universe’s matter throughout history. The Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program (HSC-SSP) is one such weak-lensing survey, and it has the highest resolution and the deepest depth of all current weak-lensing surveys. Over the past six years, the HSC-SSP survey team has spent 330 nights scanning 3% of the entire spherical sky, capturing the light emitted by galaxies up to 10 billion years ago.