With more code created by AI, there is more surface area to troubleshoot. There is a need for AI to autonomously troubleshoot, mediate and even prevent complex incidents at scale—self-healing codegen.




A gene-editing delivery system developed by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers simultaneously targeted the liver and lungs of a preclinical model of a rare genetic disease known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), significantly improving symptoms for months after a single treatment, a new study shows.

A gene-editing delivery system developed by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers simultaneously targeted the liver and lungs of a preclinical model of a rare genetic disease known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), significantly improving symptoms for months after a single treatment, a new study shows. The findings, published in Nature Biotechnology, could lead to new therapies for a variety of genetic diseases that affect multiple organs.
“Multi-organ diseases may need to be treated in more than one place. The development of multi-organ-targeted therapeutics opens the door to realizing those opportunities for this and other diseases,” said study leader Daniel Siegwart, Ph.D., Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Biochemistry, and in the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UT Southwestern.
Gene editing—a group of technologies designed to correct disease-causing mutations in the genome—has the potential to revolutionize medicine, Dr. Siegwart explained. Targeting these technologies to specific organs, tissues, or cell populations will be necessary to effectively and safely treat patients.

The brains of humans and other primates are known to execute various sophisticated functions, one of which is the representation of the space immediately surrounding the body. This area, also sometimes referred to as “peripersonal space,” is where most interactions between people and their surrounding environment typically take place.
Researchers at Chinese Academy of Sciences, Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) and other institutes recently investigated the neural processes through which the brain represents the area around the body, using brain-inspired computational models. Their findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggest that receptive fields surrounding different parts of the body contribute to building a modular model of the space immediately surrounding a person or artificial intelligence (AI) agent.
“Our journey into this field began truly serendipitously, during unfunded experiments done purely out of curiosity,” Giandomenico Iannetti, senior author of the paper, told Medical Xpress. “We discovered that the hand-blink reflex, which is evoked by electrically shocking the hand, was strongly modulated by the position of the hand with respect to the eye.
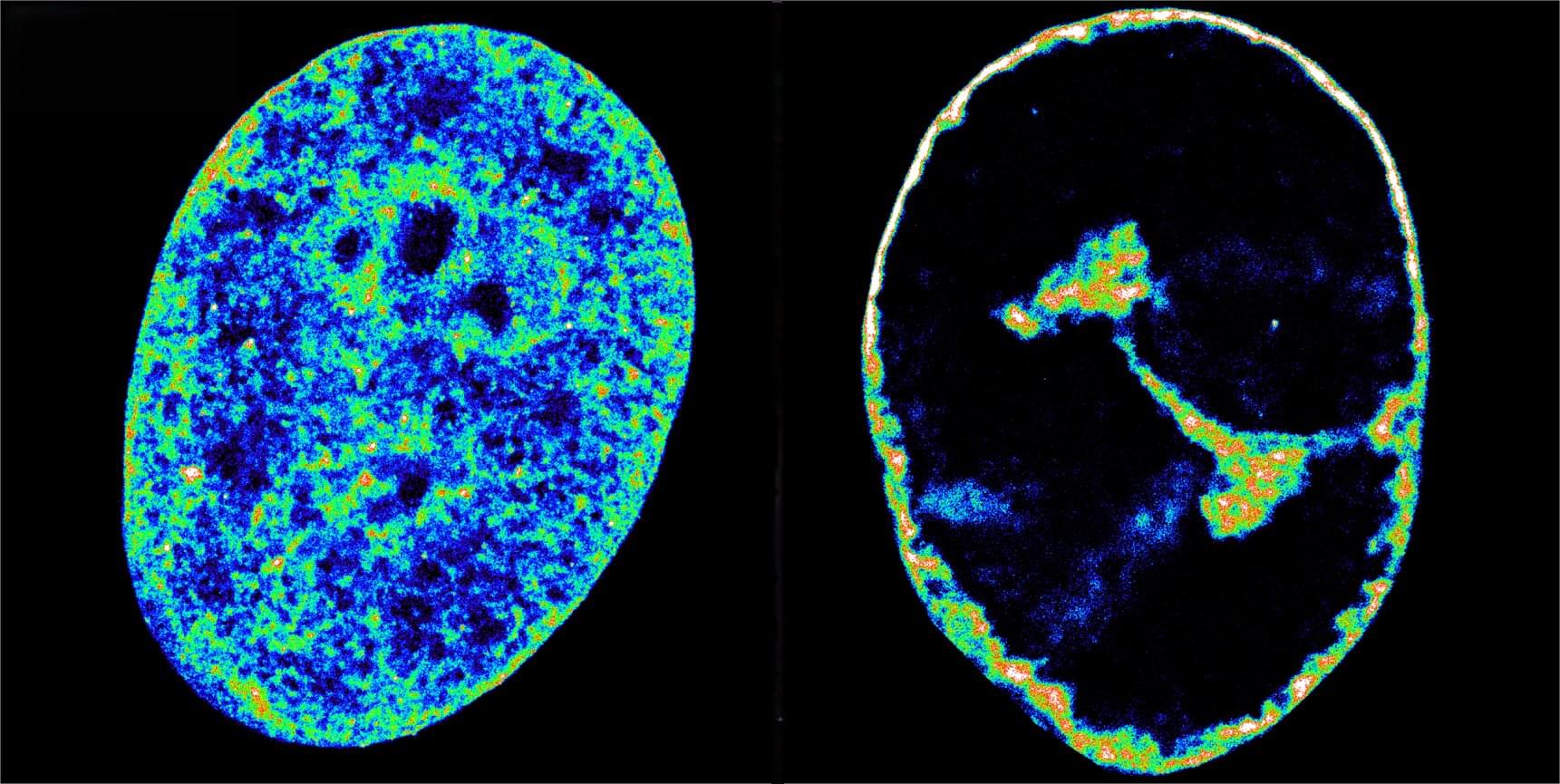
Viruses are entirely dependent on their hosts to reproduce. They ransack living cells for parts and energy and hijack the host’s cellular machinery to make new copies of themselves. Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), it turns out, also redecorates, according to a study in Nature Communications.
Researchers at the Center for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona have discovered the cold sore virus reshapes the human genome’s architecture, rearranging its shape in three-dimensional space so that HSV-1 can access host genes most useful for its ability to reproduce.
“HSV-1 is an opportunistic interior designer, reshaping the human genome with great precision and choosing which bits it comes into contact with. It’s a novel mechanism of manipulation we didn’t know the virus had to exploit host resources,” says Dr. Esther González Almela, first author of the study.
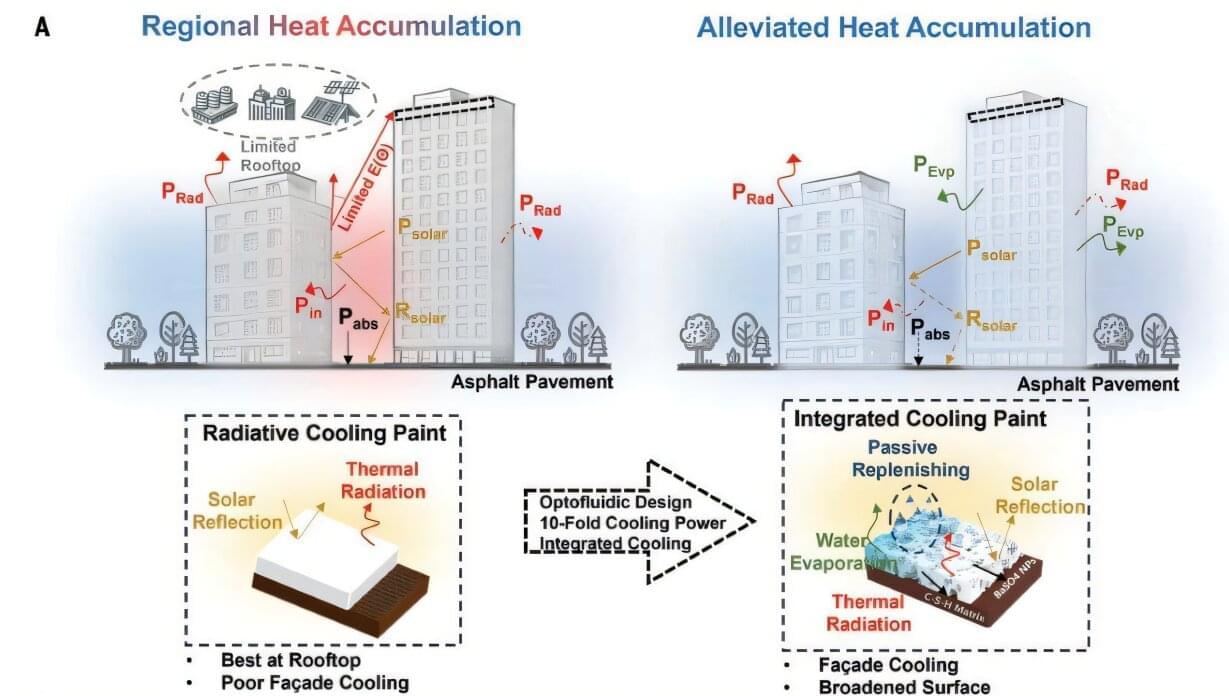
A new cement-based paint can cool down the building by sweating off the heat. The cooling paint, named CCP-30, was designed by an international team of researchers and features a nanoparticle-modified porous structure composed of a calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel network.
This design enabled it to achieve superior cooling by combining both radiative, evaporative and reflective cooling mechanisms, which allowed it to reflect 88–92% of sunlight, emit 95% of the heat as infrared radiation, and hold about 30% of its weight in water, making it a paint ideal for keeping spaces cool throughout the day and across seasons.
As per the findings published in Science, the paint provides 10 times the cooling power of commercial cooling paints in tropical climates, resulting in electricity savings of 30 to 40%.