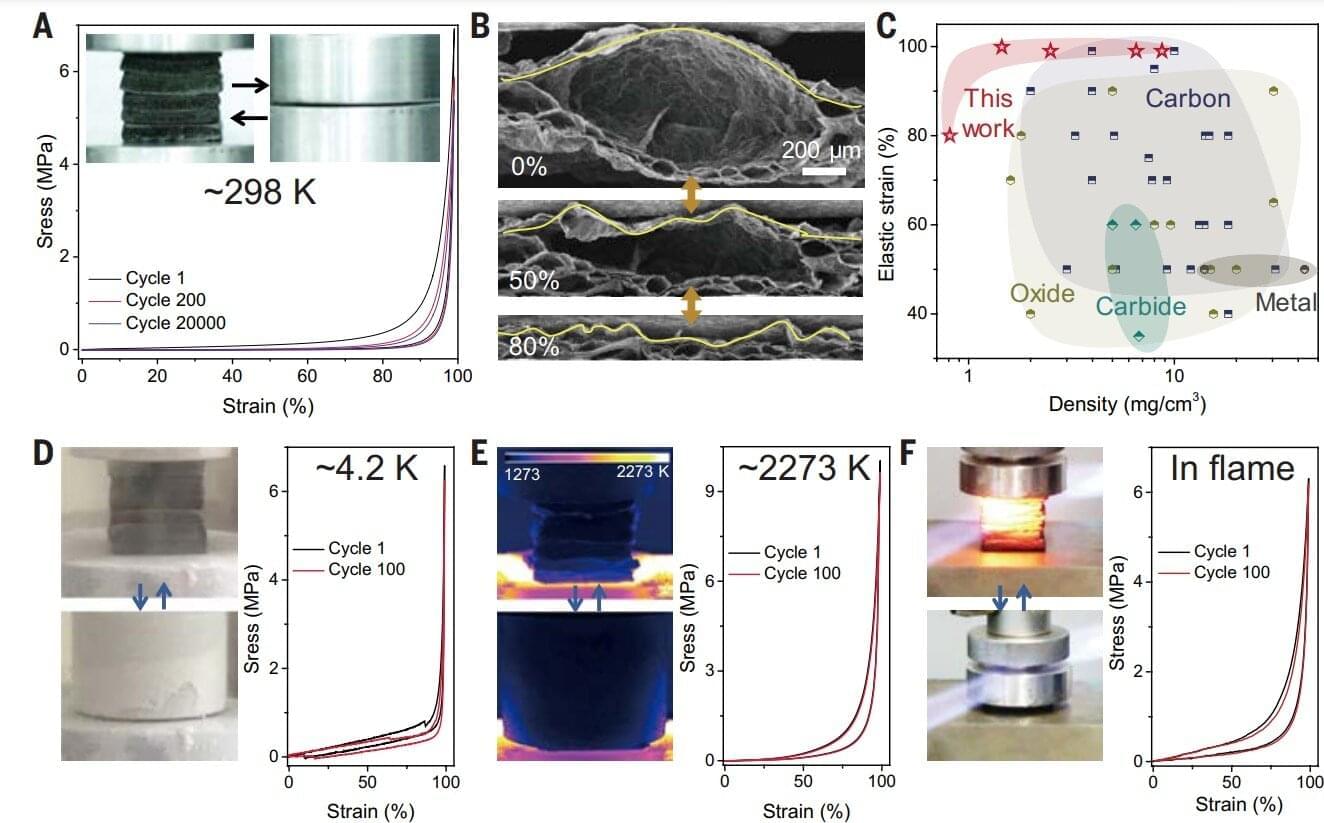
A new collection of chemically diverse dome-celled ultralight aerogels with high porosity and very low density feature elasticity and mechanical properties that remain intact even under extreme temperatures from 4.2 kelvin (K) to 2273 K.


A research team at the Politecnico di Milano has developed an innovative single-atom catalyst capable of selectively adapting its chemical activity. This is a crucial step forward in sustainable chemistry and the design of more efficient and programmable industrial processes.
The study was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
This achievement is novel in the field of single-atom catalysts. For the first time, scientists have demonstrated the possibility of designing a material that can selectively change its catalytic function depending on the chemical environment. It involves a sort of “molecular switch” that allows complex reactions to be performed more cleanly and efficiently, using less energy than conventional processes.
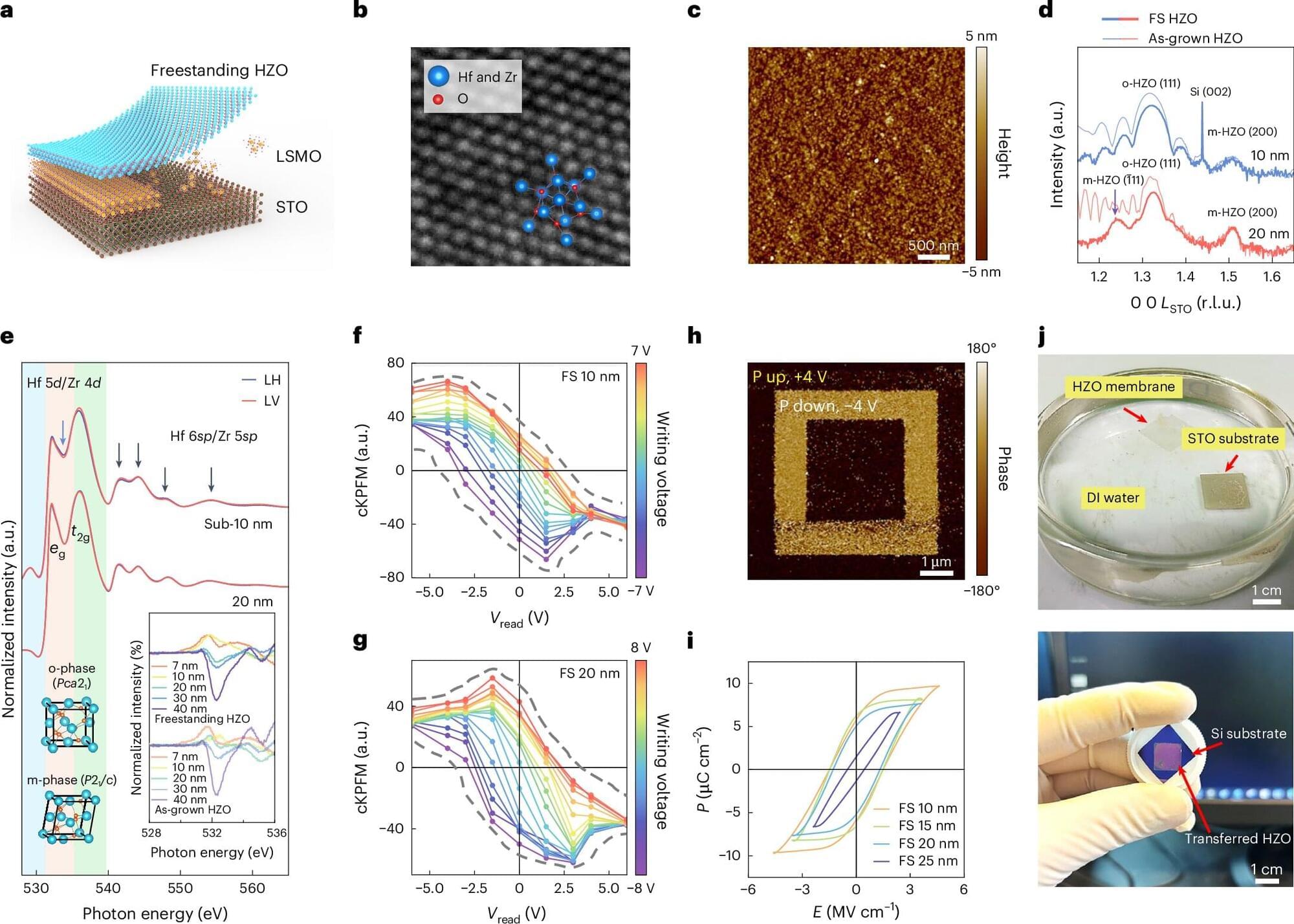
To further reduce the size of electronic devices, while also improving their performance and energy efficiency, electronics engineers have been trying to identify alternative materials that outperform silicon and other conventional semiconductors. Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors, materials that are just a few atoms thick and have a tunable electrical conductivity, are among the most promising candidates for the fabrication of smaller and better performing devices.
Past studies showed that these materials could be used to fabricate miniaturized transistors, electronic components that amplify or switch electrical signals, particularly field-effect transistors (FETs). These are transistors that control the flow of electrical current using an electric field.
To reliably operate, however, FETs also need to integrate an insulating layer that separates the so-called gate electrode (i.e., the terminal regulating the flow of current) from the channel (i.e., the pathway through which electrical current flows). To enable greater control over the gate, this insulating layer, known as a gate dielectric, should have a high dielectric constant (κ), or in other words, it should effectively store electrical energy.

Nematic materials are made of elongated molecules that align in a preferred direction, but, like in a fluid, are spaced out irregularly. The best-known nematic materials are liquid crystals, which are used in liquid crystal display (LCD) screens. However, nematic order has been identified in a wide range of systems, including bacterial suspensions and superconductors.
Now, a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and University of California, Santa Cruz, has discovered a nematic order in a magnetic material, in which the magnetic spins of the material are arranged into coils pointing in the same general direction.
“If we think of these magnetic helices as the objects that are aligning, the magnetism follows expectations for nematic phases,” said Zoey Tumbleson, a graduate student at Berkeley Lab and the University of California, Santa Cruz, who led this work. “These phases were not previously known and it’s very exciting to see this generalized to a wider field of study.”

Threads or ropes can easily be used for braiding, knotting, and weaving. In chemistry, however, processing molecular strands in this way is an almost impossible task. This is because molecules are not only tiny, they are also constantly in motion and therefore cannot be easily touched, held or precisely shaped.
A research group at the Institute of Chemistry at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) led by Dr. Michael Kathan has now succeeded in precisely winding two molecular strands around each other using an artificial, light-driven molecular motor, thereby creating a particularly complex structure: a catenane (from Latin “catena” = chain). Catenanes consist of two ring-shaped molecules that are intertwined like the links of a chain—without being chemically bonded to each other. The research results are published in the journal Science.
“What we have developed is basically a mini-machine that is powered by light and rotates in one direction,” says Kathan.
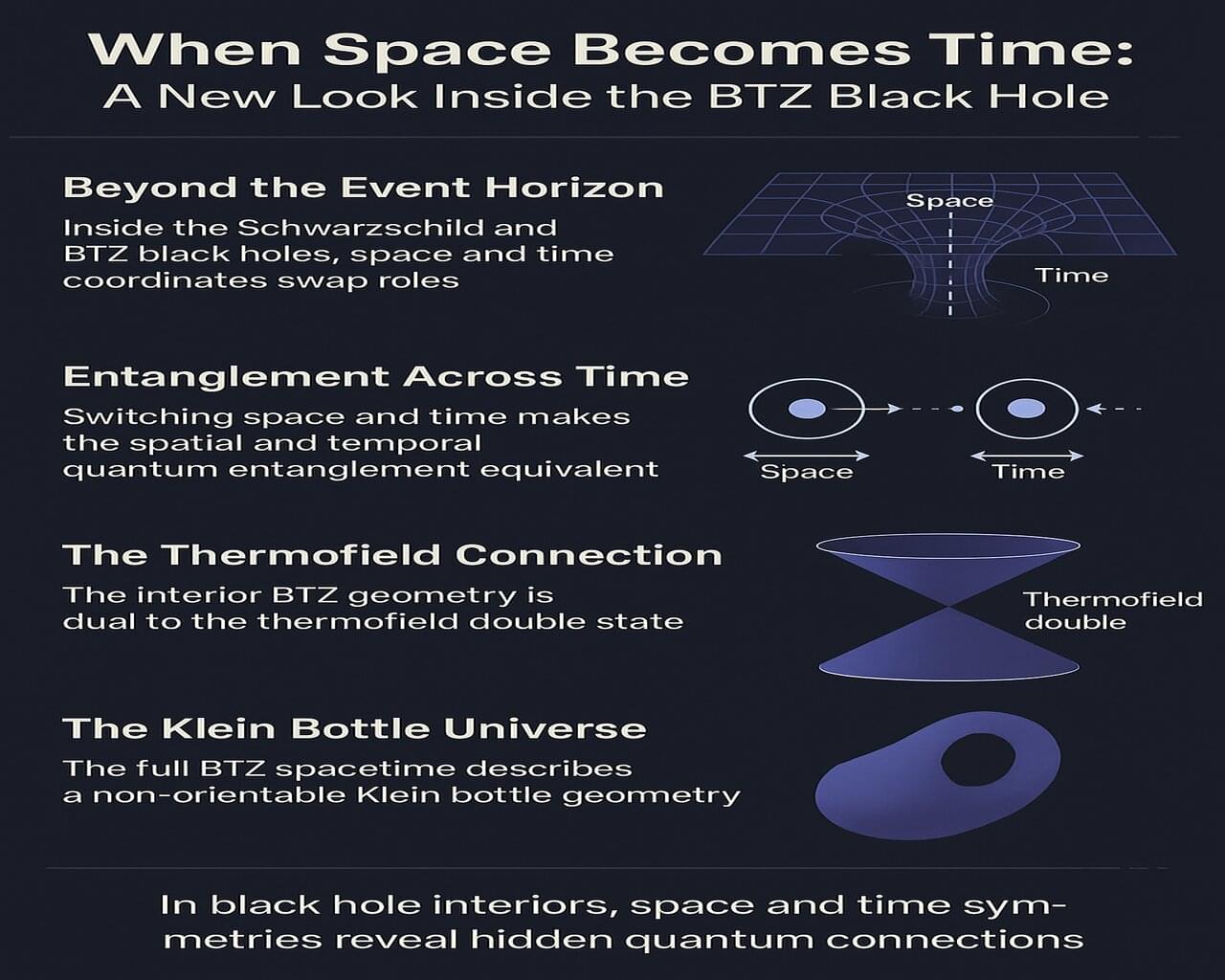
Exploring the BTZ black hole in (2+1)-dimensional gravity took me down a fascinating rabbit hole, connecting ideas I never expected—like black holes and topological phases in quantum matter! When I swapped the roles of space and time in the equations (it felt like turning my map upside down when I was lost in a new city), I discovered an interior version of the solution existing alongside the familiar exterior, each with its own thermofield double state.

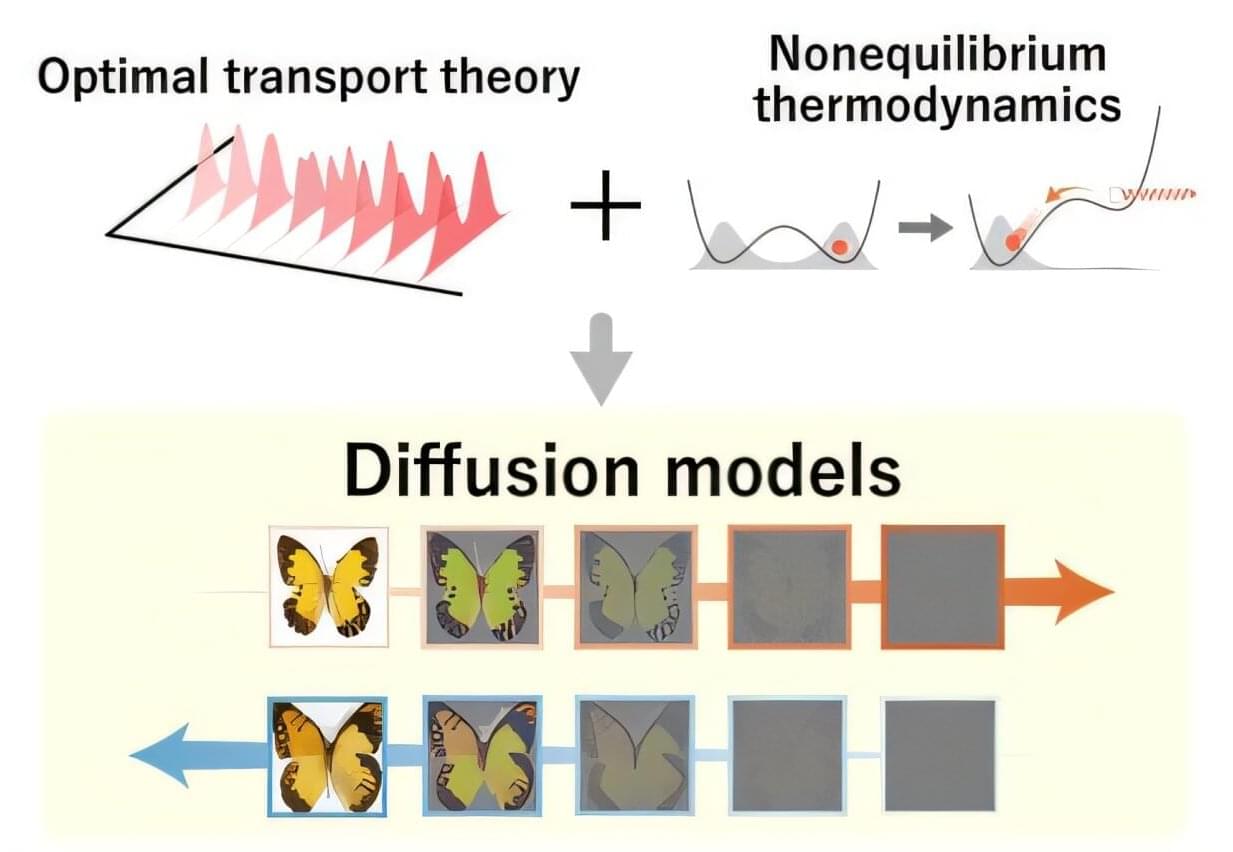
Joint research led by Sosuke Ito of the University of Tokyo has shown that nonequilibrium thermodynamics, a branch of physics that deals with constantly changing systems, explains why optimal transport theory, a mathematical framework for the optimal change of distribution to reduce cost, makes generative models optimal. As nonequilibrium thermodynamics has yet to be fully leveraged in designing generative models, the discovery offers a novel thermodynamic approach to machine learning research. The findings were published in the journal Physical Review X.
Image generation has been improving in leaps and bounds over recent years: a video of a celebrity eating a bowl of spaghetti that represented the state of the art a couple of years ago would not even qualify as good today. The algorithms that power image generation are called diffusion models, and they contain randomness called “noise.”
During the training process, noise is introduced to the original data through diffusion dynamics. During the generation process, the model must eliminate the noise to generate new content from the noisy data. This is achieved by considering the time-reversed dynamics, as if playing the video in reverse. One piece of the art and science of building a model that produces high-quality content is specifying when and how much noise is added to the data.

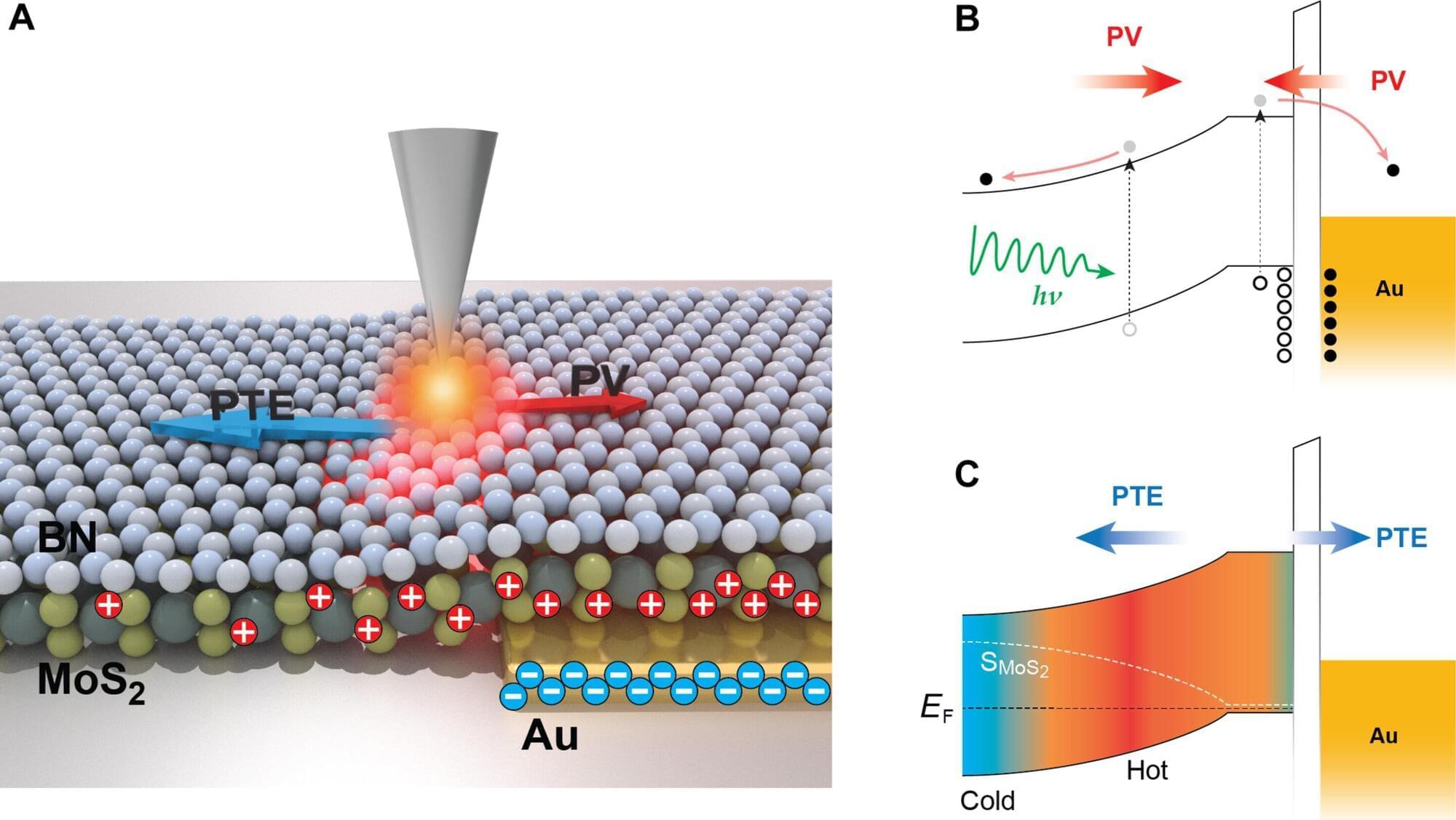
UC Riverside researchers have unveiled a powerful new imaging technique that exposes how cutting-edge materials used in solar panels and light sensors convert light into electricity—offering a path to better, faster, and more efficient devices.
The breakthrough, published in the journal Science Advances, could lead to improvements in solar energy systems and optical communications technology. The study title is “Deciphering photocurrent mechanisms at the nanoscale in van der Waals interfaces for enhanced optoelectronic applications.”
The research team, led by associate professors Ming Liu and Ruoxue Yan of UCR’s Bourns College of Engineering, developed a three-dimensional imaging method that distinguishes between two fundamental processes by which light is transformed into electric current in quantum materials.