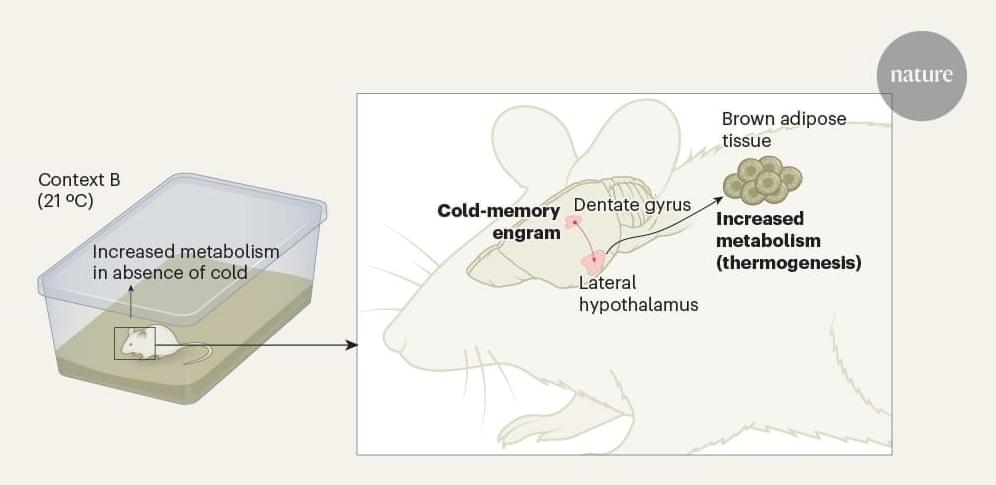
Gliner, V., Levy, I., Tsutsui, K. et al. Clinically meaningful interpretability of an AI model for ECG classification. npj Digit. Med. 8, 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01467-8
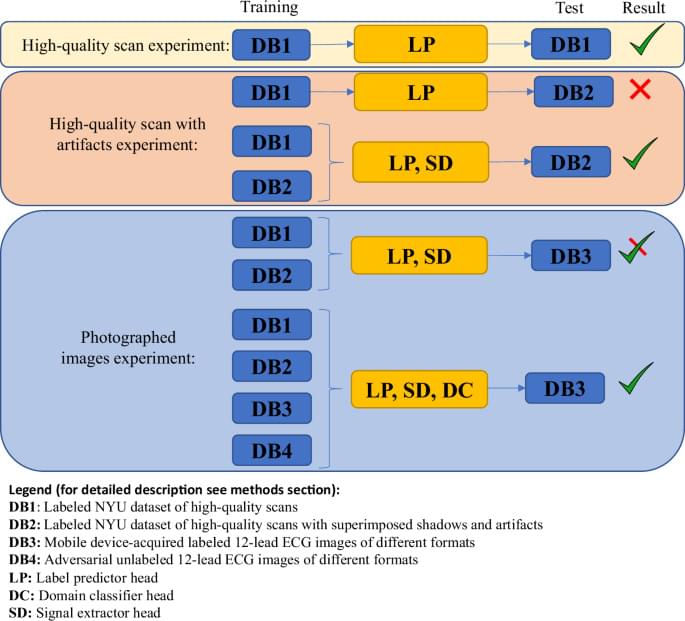

Gliner, V., Levy, I., Tsutsui, K. et al. Clinically meaningful interpretability of an AI model for ECG classification. npj Digit. Med. 8, 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01467-8

At an event in Hangzhou, China, Chinese and French guests simply donned 49-gram Rokid AR glasses and spoke in their own languages while instant subtitles appeared on the lenses, enabling seamless dialogue.
The best solar company in Australia just installed my new solar system.
Check them out here: https://www.resinc.com.au/electricviking.
I use Starlink internet to upload all of my videos, use my referral link here: https://www.starlink.com/residential?referral=RC-392400-91086-9
👇👇 Buy something and support The Electric Viking Store 👇👇
https://shop.theelectricviking.com/
Size guide and other help for the store 👇
🔔 Subscribe and hit the notification bell! ►
We are ready to unveil the world’s first real-world speeder bike.
Stay tuned for the official launch video soon.
Subscribe and check out new videos.
#speederbike #hoverbike #starwars #jetpack #ironman #futuretech #flying #airbike #teaser.
https://twitter.com/Volonaut.
https://www.tiktok.com/@volonaut.
https://www.facebook.com/volonaut.
https://www.instagram.com/volonaut.
https://www.linkedin.com/company/volonaut/

Physicists have built the first-ever lab model of a black hole bomb, a decades-old theory where spinning energy amplifies until it explodes.

Researchers from the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau), in collaboration with Sant Pau Hospital and the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute, have developed an innovative CAR-T cell therapy targeting the CD30 protein (HSP-CAR30), which has shown high efficacy in patients with refractory CD30+ lymphoma.
A Phase I clinical trial, whose results have been published in the journal Blood, reveals that this new CAR-T30 therapy promotes the expansion of memory T cells, leading to long-lasting responses and improved clinical outcomes in treated patients.
Hodgkin lymphoma and other CD30+ lymphomas have posed a significant challenge to the medical community, particularly in refractory or relapsed cases where conventional treatments have so far shown limited efficacy.