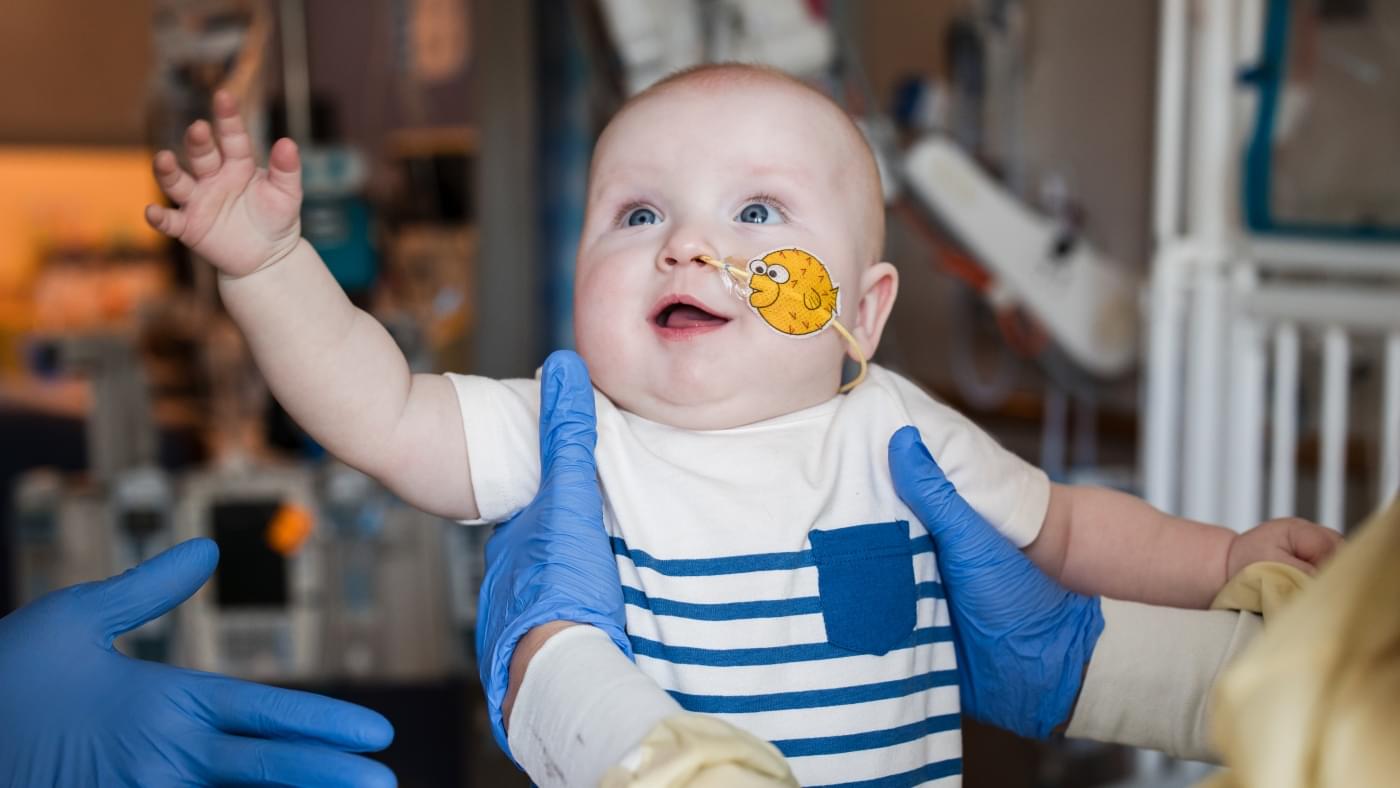
For the first time, doctors have created a customized treatment using the revolutionary gene-editing technique known as CRISPR to treat a baby with a rare, life-threatening genetic disorder.

AI surveillance, AI surveillance systems, AI surveillance technology, AI camera systems, artificial intelligence privacy, AI tracking systems, AI in public surveillance, smart city surveillance, facial recognition technology, real time surveillance ai, AI crime prediction, predictive policing, emotion detecting ai, AI facial recognition, privacy in AI era, AI and data collection, AI spying tech, surveillance capitalism, government surveillance 2025, AI monitoring tools, AI tracking devices, AI and facial data, facial emotion detection, emotion recognition ai, mass surveillance 2025, AI in smart cities, china AI surveillance, skynet china, AI scanning technology, AI crowd monitoring, AI face scanning, AI emotion scanning, AI powered cameras, smart surveillance system, AI and censorship, privacy and ai, digital surveillance, AI surveillance dangers, AI surveillance ethics, machine learning surveillance, AI powered face id, surveillance tech 2025, AI vs privacy, AI in law enforcement, AI surveillance news, smart city facial recognition, AI and security, AI privacy breach, AI threat to privacy, AI prediction tech, AI identity tracking, AI eyes everywhere, future of surveillance, AI and human rights, smart cities AI control, AI facial databases, AI surveillance control, AI emotion mapping, AI video analytics, AI data surveillance, AI scanning behavior, AI and behavior prediction, invisible surveillance, AI total control, AI police systems, AI surveillance usa, AI surveillance real time, AI security monitoring, AI surveillance 2030, AI tracking systems 2025, AI identity recognition, AI bias in surveillance, AI surveillance market growth, AI spying software, AI privacy threat, AI recognition software, AI profiling tech, AI behavior analysis, AI brain decoding, AI surveillance drones, AI privacy invasion, AI video recognition, facial recognition in cities, AI control future, AI mass monitoring, AI ethics surveillance, AI and global surveillance, AI social monitoring, surveillance without humans, AI data watch, AI neural surveillance, AI surveillance facts, AI surveillance predictions, AI smart cameras, AI surveillance networks, AI law enforcement tech, AI surveillance software 2025, AI global tracking, AI surveillance net, AI and biometric tracking, AI emotion AI detection, AI surveillance and control, real AI surveillance systems, AI surveillance internet, AI identity control, AI ethical concerns, AI powered surveillance 2025, future surveillance systems, AI surveillance in cities, AI surveillance threat, AI surveillance everywhere, AI powered recognition, AI spy systems, AI control cities, AI privacy vs safety, AI powered monitoring, AI machine surveillance, AI surveillance grid, AI digital prisons, AI digital tracking, AI surveillance videos, AI and civilian monitoring, smart surveillance future, AI and civil liberties, AI city wide tracking, AI human scanner, AI tracking with cameras, AI recognition through movement, AI awareness systems, AI cameras everywhere, AI predictive surveillance, AI spy future, AI surveillance documentary, AI urban tracking, AI public tracking, AI silent surveillance, AI surveillance myths, AI surveillance dark side, AI watching you, AI never sleeps, AI surveillance truth, AI surveillance 2025 explained, AI surveillance 2025, future of surveillance technology, smart city surveillance, emotion detecting ai, predictive AI systems, real time facial recognition, AI and privacy concerns, machine learning surveillance, AI in public safety, neural surveillance systems, AI eye tracking, surveillance without consent, AI human behavior tracking, artificial intelligence privacy threat, AI surveillance vs human rights, automated facial ID, AI security systems 2025, AI crime prediction, smart cameras ai, predictive policing technology, urban surveillance systems, AI surveillance ethics, biometric surveillance systems, AI monitoring humans, advanced AI recognition, AI watchlist systems, AI face tagging, AI emotion scanning, deep learning surveillance, AI digital footprint, surveillance capitalism, AI powered spying, next gen surveillance, AI total control, AI social monitoring, AI facial mapping, AI mind reading tech, surveillance future cities, hidden surveillance networks, AI personal data harvesting, AI truth detection, AI voice recognition monitoring, digital surveillance reality, AI spy software, AI surveillance grid, AI CCTV analysis, smart surveillance networks, AI identity tracking, AI security prediction, mass data collection ai, AI video analytics, AI security evolution, artificial intelligence surveillance tools, AI behavioral detection, AI controlled city, AI surveillance news, AI surveillance system explained, AI visual tracking, smart surveillance 2030, AI invasion of privacy, facial detection ai, AI sees you always, AI surveillance rising, future of AI spying, next level surveillance, AI technology surveillance systems, ethical issues in AI surveillance, AI surveillance future risks.

The team turned AlphaEvolve loose on Google’s Borg cluster management system for its data centers. The AI suggested a change to the scheduling heuristics, which has been implemented to save Google 0.7 percent on its computing resources globally. For a company the size of Google, that’s a significant financial benefit.
AlphaEvolve may also be able to make generative AI more efficient, which is necessary if anyone is ever going to make money on the technology. The internal workings of generative systems are based on matrix multiplication operations. The most efficient way to multiply 4×4 complex-valued matrices was devised by mathematician Volker Strassen in 1969, and that held for decades, but DeepMind says AlphaEvolve has discovered a new algorithm that’s even more efficient. DeepMind has worked on this problem before with narrowly trained AI agents like AlphaTensor. Despite being a general AI, AlphaEvolve came up with a better solution than AlphaTensor.
Google’s next-generation Tensor processing hardware will also benefit from AlphaEvolve. DeepMind reports that the AI created a change to the chip’s Verilog hardware description language that dropped unnecessary bits to increase efficiency. Google is still working to verify the change but expects this to be part of the upcoming processor.

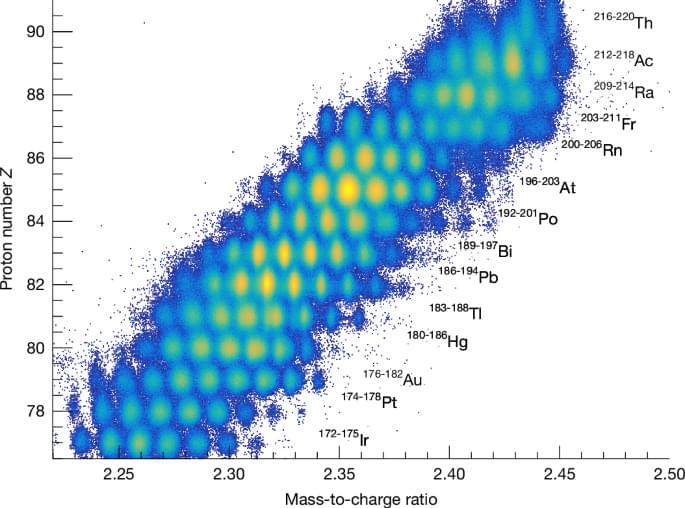
As searches for the leading dark matter candidates—weakly interacting massive particles, axions, and primordial black holes—continue to deliver null results, the door opens on the exploration of more exotic alternatives. Guanming Liang and Robert Caldwell of Dartmouth College in New Hampshire have now proposed a dark matter candidate that is analogous with a superconducting state [1]. Their proposal involves interacting fermions that could exist in a condensate similar to that formed by Cooper pairs in the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer theory of superconductivity.
The novel fermions considered by Liang and Caldwell emerge in the Nambu–Jona-Lasinio model, which can be regarded as a low-energy approximation of the quantum chromodynamics theory that describes the strong interaction. The duo considers a scenario where, in the early Universe, the fermions behave like radiation, reaching thermal equilibrium with standard photons. As the Universe expands and the temperature drops below a certain threshold, however, the fermions undergo a phase transition that leads them to pair up and form a massive condensate.
The proposed scenario has several appealing features, say Liang and Caldwell. The fermions’ behavior would be consistent with that of the cold dark matter considered by the current standard model of cosmology. Further, the scenario implies a slight imbalance between fermions with different chiralities (left-and right-handed). Such an imbalance might be related to the yet-to-be-explained matter–antimatter asymmetry seen in the Universe. What’s more, the model predicts that the fermions obey a time-dependent equation of state that would produce unique, potentially observable signatures in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation. The researchers suggest that next-generation CMB measurements—by the Simons Observatory and by so-called stage 4 CMB telescopes—might reach sufficient precision to vet their idea.

HUGE AI breakthrough: Absolute Zero Reasoner deep dive. Self-improving AI that learns with no data! #ai #aitools #ainews #llm.
Sources:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.03335
https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/Absolut… Thanks to Tavus for sponsoring this video. Try Tavus for free https://tavus.plug.dev/T4AQw5K 0:00 Absolute Zero intro 0:50 Traditional methods of training AI models 4:00 Absolute Zero algorithm 5:01 How Absolute Zero Reasoner works 7:19 Types of training tasks 9:00 How good is Absolute Zero 10:47 Tavus 12:11 Adding Absolute Zero to existing models 13:01 Interesting findings 15:43 Uhoh… 16:50 Ablation study 18:15 More interesting findings Newsletter: https://aisearch.substack.com/ Find AI tools & jobs: https://ai-search.io/ Support: https://ko-fi.com/aisearch Here’s my equipment, in case you’re wondering: Dell Precision 5690: https://www.dell.com/en-us/dt/ai-tech… Nvidia RTX 5,000 Ada https://nvda.ws/3zfqGqS Mouse/Keyboard: ALOGIC Echelon https://bit.ly/alogic-echelon Mic: Shure SM7B https://amzn.to/3DErjt1 Audio interface: Scarlett Solo https://amzn.to/3qELMeu.
Thanks to Tavus for sponsoring this video. Try Tavus for free https://tavus.plug.dev/T4AQw5K
0:00 Absolute Zero intro.
0:50 Traditional methods of training AI models.
4:00 Absolute Zero algorithm.
5:01 How Absolute Zero Reasoner works.
7:19 Types of training tasks.
9:00 How good is Absolute Zero.
10:47 Tavus.
12:11 Adding Absolute Zero to existing models.
13:01 Interesting findings.
15:43 Uhoh…
16:50 Ablation study.
18:15 More interesting findings.
Newsletter: https://aisearch.substack.com/
Find AI tools & jobs: https://ai-search.io/
Support: https://ko-fi.com/aisearch.
Here’s my equipment, in case you’re wondering:
Our first demo-type in Aachen, Germany.