A personal statement from a self-confessed “doomer”
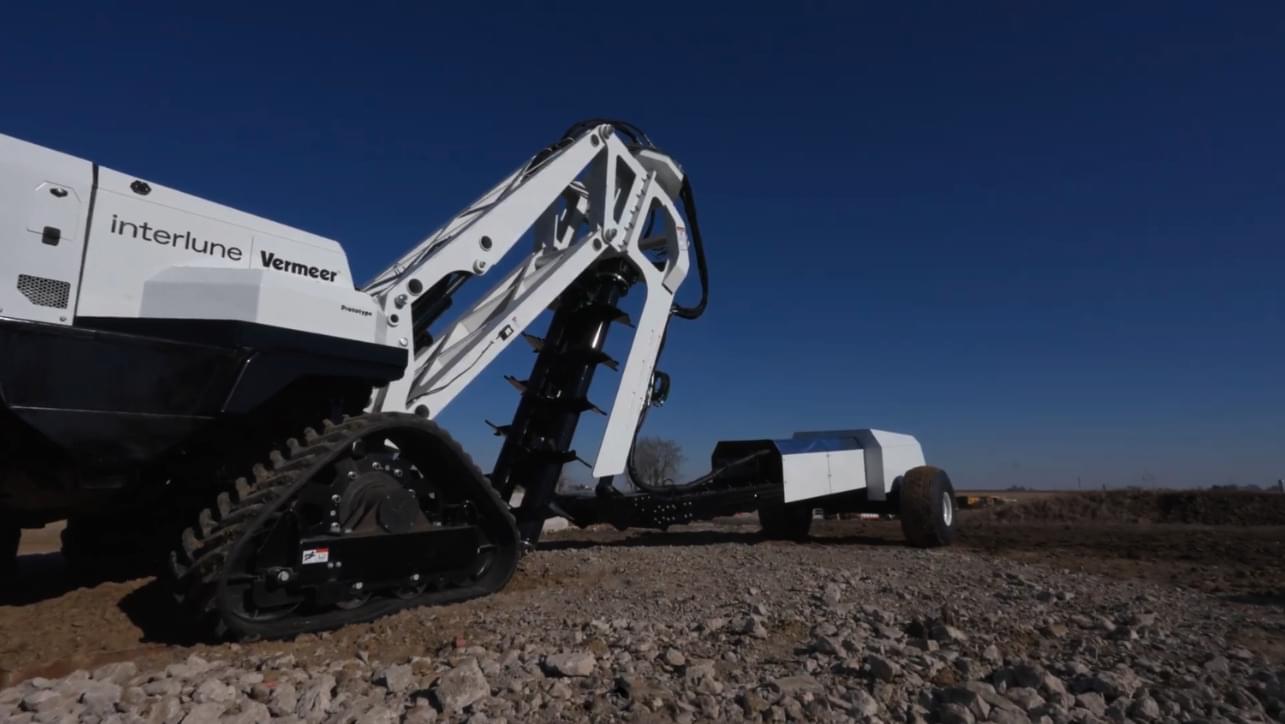





A US startup is looking to our closest satellite to fill a resources gap here on Earth. Helium-3 is rare on terra firma, but is thought to be abundant in the regolith of the Moon. Interlune has now revealed a full-scale excavator prototype that forms a key component of its lunar Harvester.
The shortage of helium-3 – a stable isotope of helium important for applications ranging from energy production to medical research – was first identified in the US toward the middle of 2008. The US government officially recognized the issue in early 2009, and mitigation efforts put in place.
“The United States supply of 3He comes from the decay of tritium (3H), which the Nation had in large quantities because of our nuclear weapons complex; however, the tritium stockpile has declined in recent years through radioactive decay and is expected to decline in the future because of reduced demand for tritium,” read the intro to a National Isotope Development Center newsletter from 2014.



A groundbreaking fuel cell could be the key to unlocking electric planes, according to a new study.
The researchers suggest that these devices could hold three times as much energy per kg compared to today’s top-performing EV batteries, providing a lightweight solution for powering not just planes, but lorries and ships too.

Neuralink did not immediately return requests for comment outside regular business hours.
Semafor’s report corroborates earlier reporting from Bloomberg, which noted in April that the startup was looking to raise $500 million at an $8.5 billion pre-money valuation.
Neuralink last year received “breakthrough device” clearance from the U.S. FDA. Three people have so far received implants made by Neuralink. Earlier this month, a nonverbal patient posted a video about how he uses a Neuralink implant to edit and narrate YouTube videos with just his brain signals.