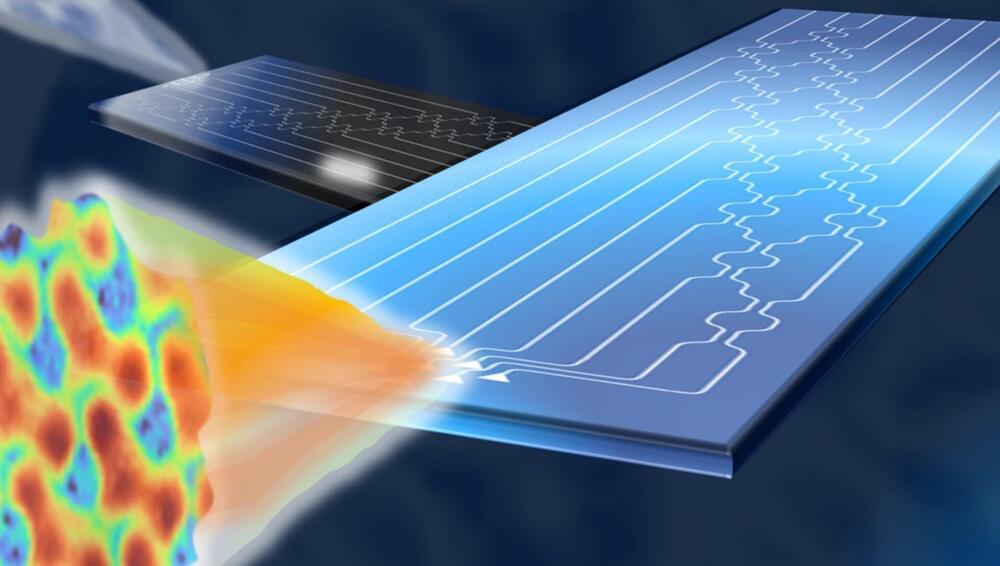
Optical wireless may no longer have any obstacles. A study by Politecnico di Milano, conducted together with Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna in Pisa, the University of Glasgow and Stanford University, and published in Nature Photonics, has made it possible to create photonic chips that mathematically calculate the optimal shape of light to best pass through any environment, even one that is unknown or changing over time.
The problem is well known: light is sensitive to any form of obstacle, even very small ones. Think, for example, of how we see objects when looking through a frosted window or simply when our glasses get foggy. The effect is quite similar on a beam of light carrying data streams in optical wireless systems: the information, while still present, is completely distorted and extremely difficult to retrieve.
The devices developed in this research are small silicon chips that serve as smart transceivers: working in pairs, they can automatically and independently ‘calculate’ what shape a beam of light needs to be in order to pass through a generic environment with maximum efficiency. And that’s not all: they can also generate multiple overlapping beams, each with its own shape, and direct them without them interfering with each other; in this way, the transmission capacity is significantly increased, just as required by next-generation wireless systems.