You’ll soon be able to tell ChatGPT to forget things — or remember specific things in future conversations.
Here’s a ChatGPT guide to help understand Open AI’s viral text-generating system. We outline the most recent updates and answer your FAQs.
You’ll soon be able to tell ChatGPT to forget things — or remember specific things in future conversations.
Here’s a ChatGPT guide to help understand Open AI’s viral text-generating system. We outline the most recent updates and answer your FAQs.
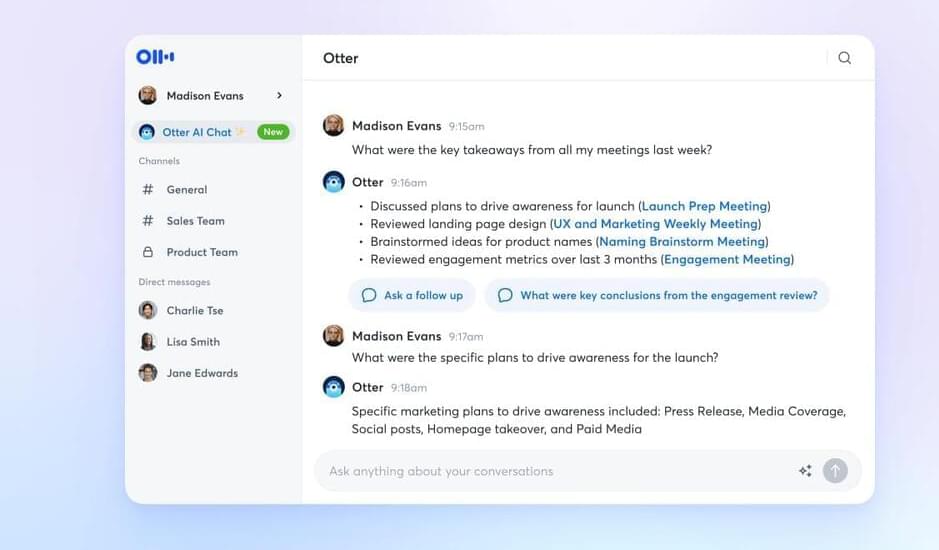
Otter, the AI-powered meeting assistant that transcribes audio in real time, is adding another layer of AI to its product with today’s introduction of Meeting GenAI, a new set of AI tools for meetings. Included with GenAI is an AI chatbot you can query to get information about past meetings you’ve recorded with Otter, an AI chat feature that can be used by teams and an AI conversation summary that provides an overview of the meeting that took place, so you don’t have to read the full transcript to catch up.
Although journalists and students may use AI to record things like interviews or lectures, Otter’s new AI features are aimed more at those who leverage the meeting helper in a corporate environment. The company envisions the new tools as a complement or replacement for the AI features offered by different services like Microsoft Copilot, Zoom AI Companion and Google Duet, for example.
Explains Otter CEO Sam Liang, the idea to introduce the new AI tools was inspired by his own busy schedule.

Nvidia, ever keen to incentivize purchases of its latest GPUs, is releasing a tool that lets owners of GeForce RTX 30 Series and 40 Series cards run an AI-powered chatbot offline on a Windows PC.
Nvidia has released a new tool, Chat with RTX, that allows users to run a GenAI model offline — and fine-tune it on their data.

This month, Google unveiled its latest attempt to dethrone ChatGPT from the position it’s held since it launched as king of the generative AI chatbots.
Bard – now renamed Gemini–was released in early 2023 following OpenAI’s groundbreaking LLM-powered chat interface.
Dive into the ultimate AI showdown between ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini to discover which platform claims the crown for superior intelligence, versatility and innovation.



Kia plans to replace the Stinger with an incredibly powerful all-electric sedan called the EV8. The high-performance EV is expected to pack over 600 hp and 500 miles range as Kia’s most powerful car yet.
The Kia EV8 will be the first electric vehicle based on Hyundai’s next-gen “eM” platform. Hyundai’s eM platform is one of two new platforms to be built under its new Integrated Modular Architecture. (IMA).
After revealing the platform last year, Hyundai claimed it would improve EV driving range by 50% compared to current models.
The short lifespan of conventional batteries means they either cannot be used or have significant drawbacks in situations where it is not feasible to charge or replace them. For example, pacemakers, satellites, high-altitude drones or even spacecraft are low-power electrical devices where long life of the energy source is needed.
What we’re doing
A team of physicists and chemists from the University of Bristol have grown a man-made diamond that, when placed in a radioactive field, is able to generate a small electrical current.