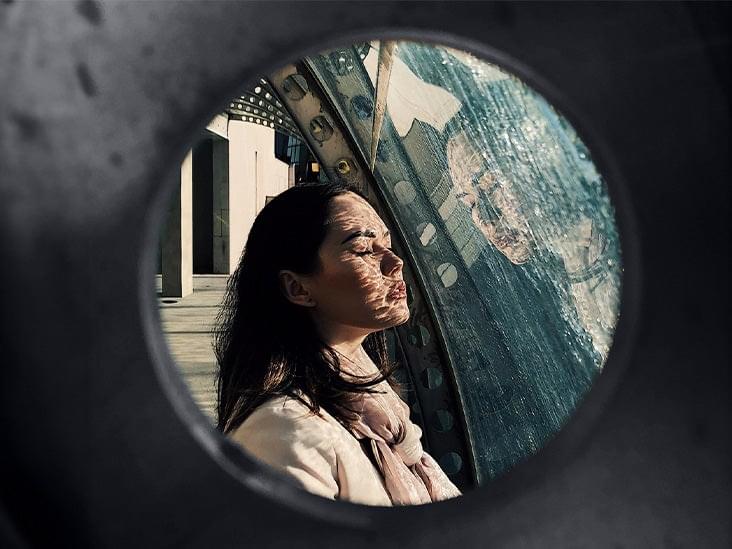
Human sensory systems are very good at recognizing objects that we see or words that we hear, even if the object is upside down or the word is spoken by a voice we’ve never heard.
Computational models known as deep neural networks can be trained to do the same thing, correctly identifying an image of a dog regardless of what color its fur is, or a word regardless of the pitch of the speaker’s voice. However, a new study from MIT neuroscientists has found that these models often also respond the same way to images or words that have no resemblance to the target.
When these neural networks were used to generate an image or a word that they responded to in the same way as a specific natural input, such as a picture of a bear, most of them generated images or sounds that were unrecognizable to human observers. This suggests that these models build up their own idiosyncratic “invariances” — meaning that they respond the same way to stimuli with very different features.