University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers are harnessing artificial intelligence and wearable tech to forecast labor, detect stress and transform how we monitor our health.
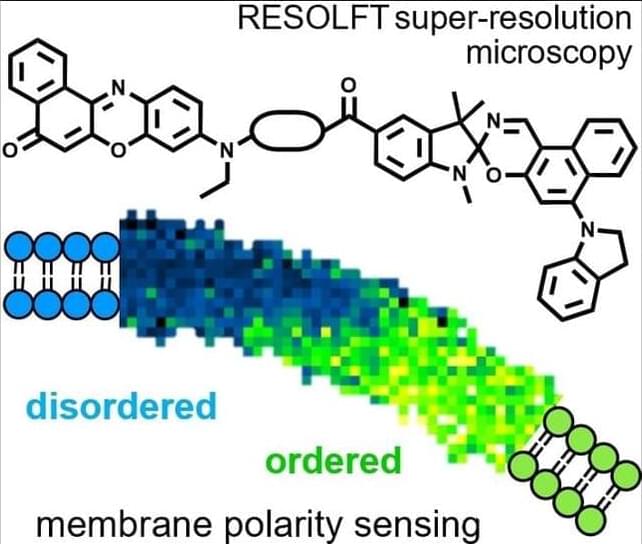
A photoswitchable solvatochromic dye has been synthesized, comprising a Nile Red fluorophore and a spironaphthoxazine photoswitch. Visible light super-resolution RESOLFT microscopy permits ordered an…
Jason Crawford
Posted in futurism | Leave a Comment on Jason Crawford
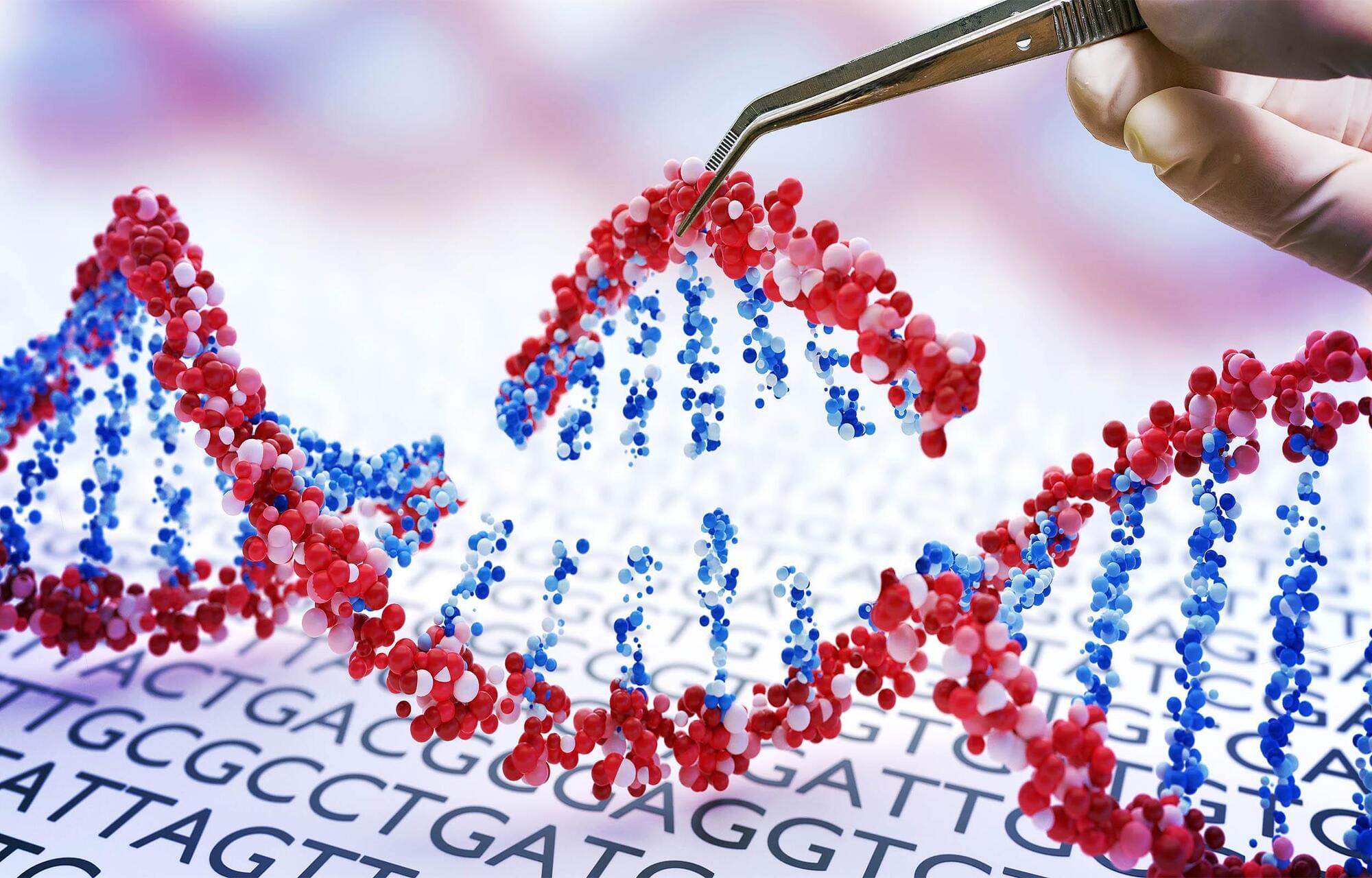
Japanese researchers have successfully eliminated the extra chromosome responsible for Down syndrome using CRISPR gene editing.
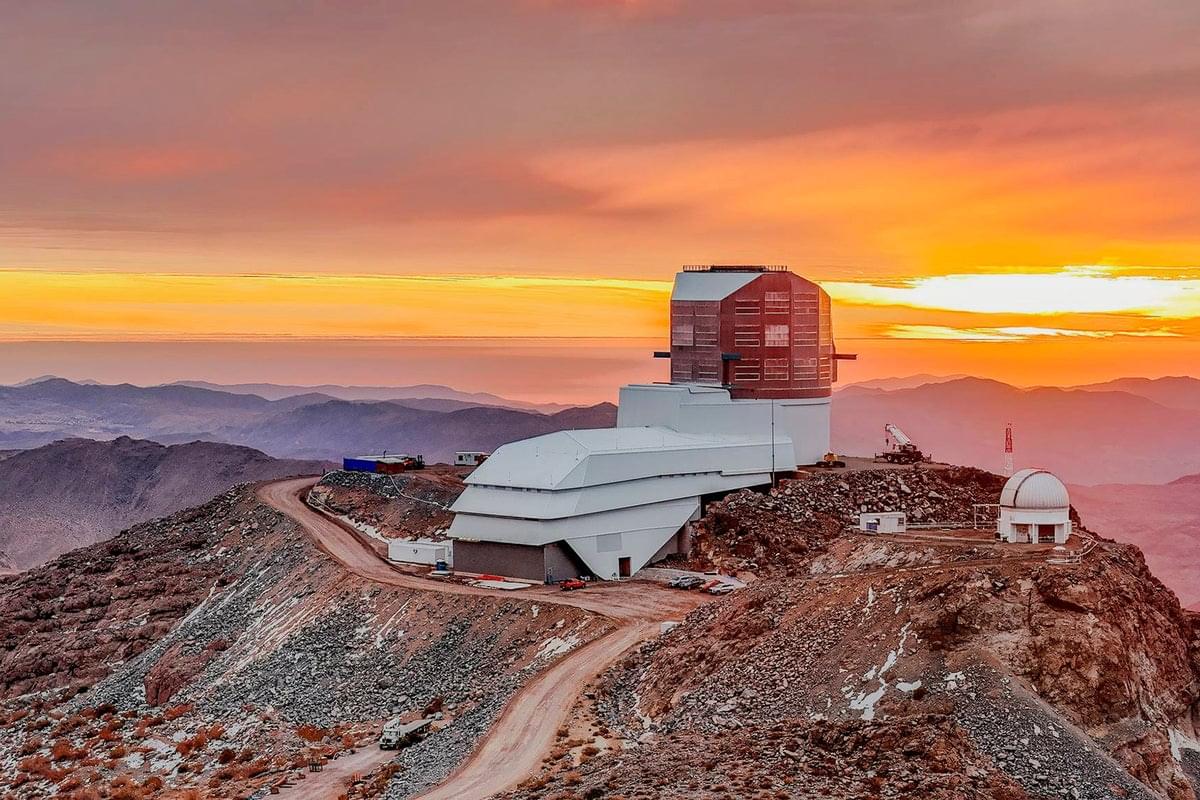
The game-changing Vera C. Rubin Observatory will collect more astronomical data in its first year than all other telescopes combined
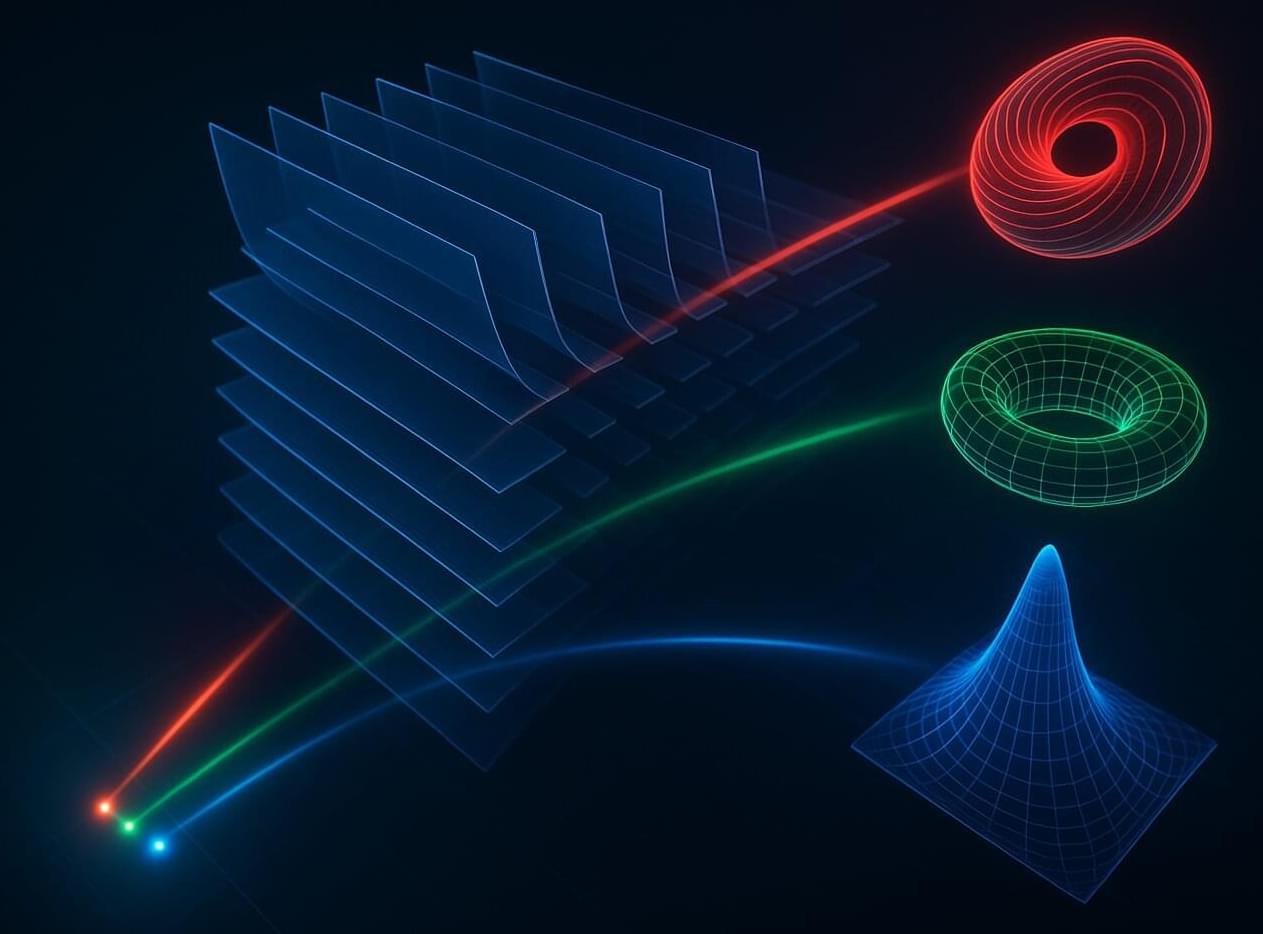
Engineers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have introduced a universal framework for point spread function (PSF) engineering, enabling the synthesis of arbitrary, spatially varying 3D PSFs using diffractive optical processors. The research is published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
This framework allows for advanced imaging capabilities—such as snapshot 3D multispectral imaging —without the need for spectral filters, axial scanning, or digital reconstruction.
PSF engineering plays a significant role in modern microscopy, spectroscopy and computational imaging. Conventional techniques typically employ phase masks at the pupil plane, which constrain the complexity and mathematical representation of the achievable PSF structures.
Dr. Mohammed Enayat has access to all sorts of experimental antiaging treatments at his clinic, but a core part of his longevity routine is pretty cheap and accessible: supplements.
Enayat told Business Insider that his most recent “biological age” tests, taken 18 months ago, said he was 24, or 17 years younger than his chronological age of 41. There’s no consensus on how to define or measure biological age, but Enayat used GlycanAge and TruAge PACE, which measure inflammation and epigenetics, respectively.
The primary care doctor, who’s also the founder of London’s Hum2n longevity clinic, has been closely tracking his health for the past seven years, using wearable tech, including an Oura ring and a Whoop strap, plus regular blood, urine, and microbiome tests.
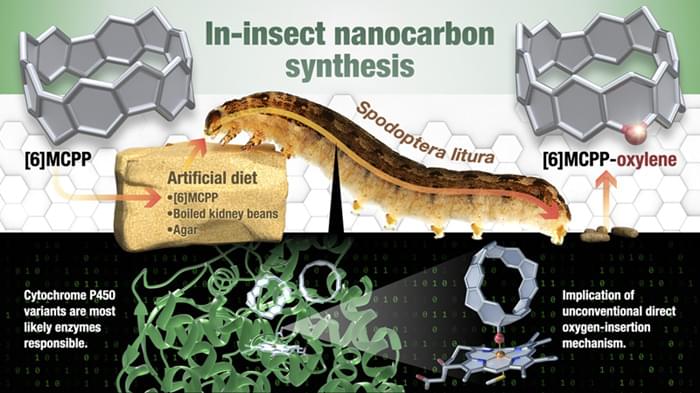
Researchers led by Kenichiro Itami at the RIKEN Pioneering Research Institute (PRI) / RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) have successfully used insects as mini molecule-making factories, marking a breakthrough in chemical engineering. Referred to as “in-insect synthesis,” this technique offers a new way to create and modify complex molecules, which will generate new opportunities for the discovery, development, and application of non-natural molecules, such as nanocarbons.
Molecular nanocarbons are super tiny structures made entirely of carbon atoms. Despite their minuscule size, they can be mechanically strong, conduct electricity, and even emit fluorescent light. These properties make them ideal for use in applications like aerospace components, lightweight batteries, and advanced electronics. However, the precision required to manufacture these tiny structures remains a major obstacle to their widespread use. Conventional laboratory techniques struggle with the fine manipulation needed to put these complex molecules together atom by atom, and their defined shapes make it especially difficult to modify them without disrupting their integrity.
“Our team has been conducting research on molecular nanocarbons, but along with that, we’ve also developed molecules that act on mammals and plants,” says Itami. “Through those experiences, we suddenly wondered — what would happen if we fed nanocarbons to insects?”
As neuro-ophthalmology educators, we have sought ways to improve the teaching of pupil-related disorder, focusing on incorporating their dynamic aspects and active learning. Our solution is an app for smartphone and tablet devices. The app, Pupil Wizard, provides a digital textbook featuring a dynamic presentation of the key pupillary abnormalities. It allows the users to interact with a digital patient and explore how each condition responds to direct and indirect light stimuli, near focus, and changes in ambient light (Fig. 1). Moreover, the users can test their knowledge in quiz mode, where random pupillary abnormalities must be correctly identified and multiple-choice questions about them answered.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
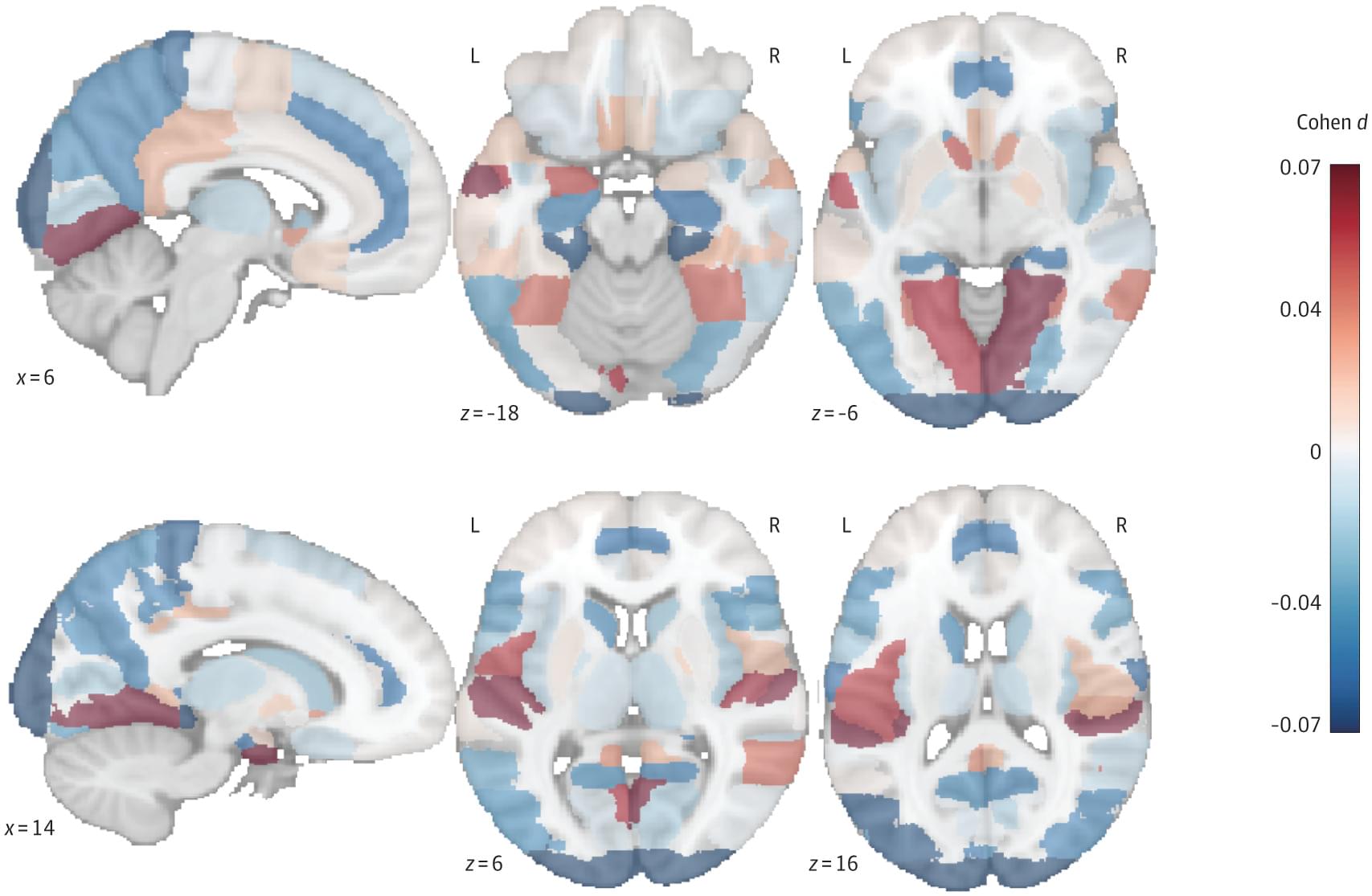
This cohort study investigates the association of active travel modes, such as walking and cycling, with dementia risk and brain structure.