Large language models (LLMs) are advanced deep learning algorithms that can process written or spoken prompts and generate texts in response to these prompts. These models have recently become increasingly popular and are now helping many users to create summaries of long documents, gain inspiration for brand names, find quick answers to simple queries, and generate various other types of texts.
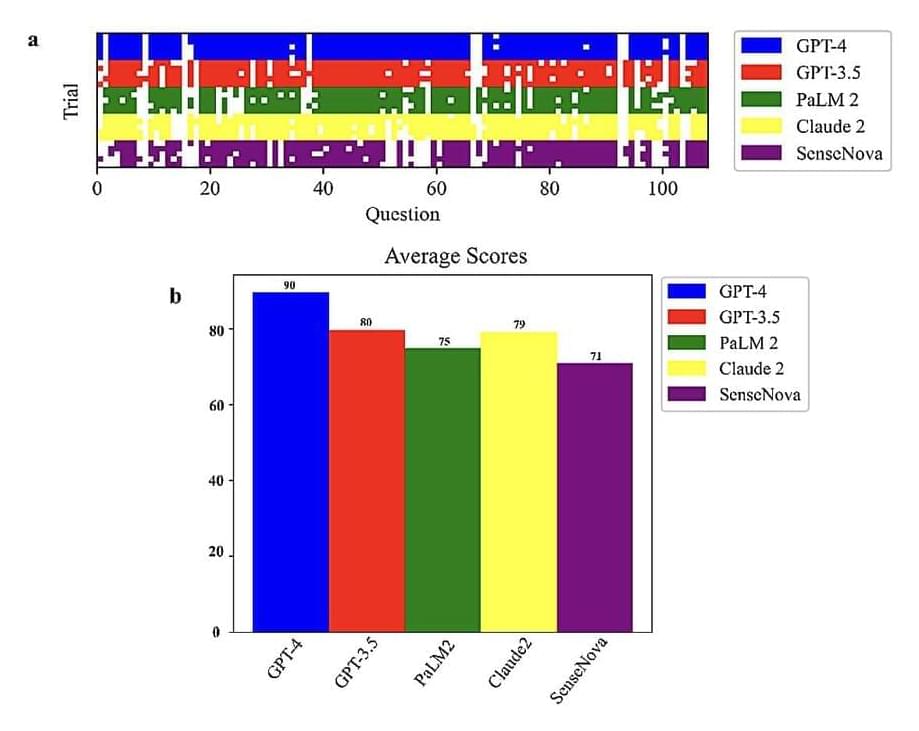
Researchers at the University of Georgia and Mayo Clinic recently set out to assess the biological knowledge and reasoning skills of different LLMs. Their paper, pre-published on the arXiv server, suggests that OpenAI’s model GPT-4 performs better than the other predominant LLMs on the market on reasoning biology problems.
“Our recent publication is a testament to the significant impact of AI on biological research,” Zhengliang Liu, co-author of the recent paper, told Tech Xplore. “This study was born out of the rapid adoption and evolution of LLMs, especially following the notable introduction of ChatGPT in November 2022. These advancements, perceived as critical steps towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), marked a shift from traditional biotechnological approaches to an AI-focused methodology in the realm of biology.”