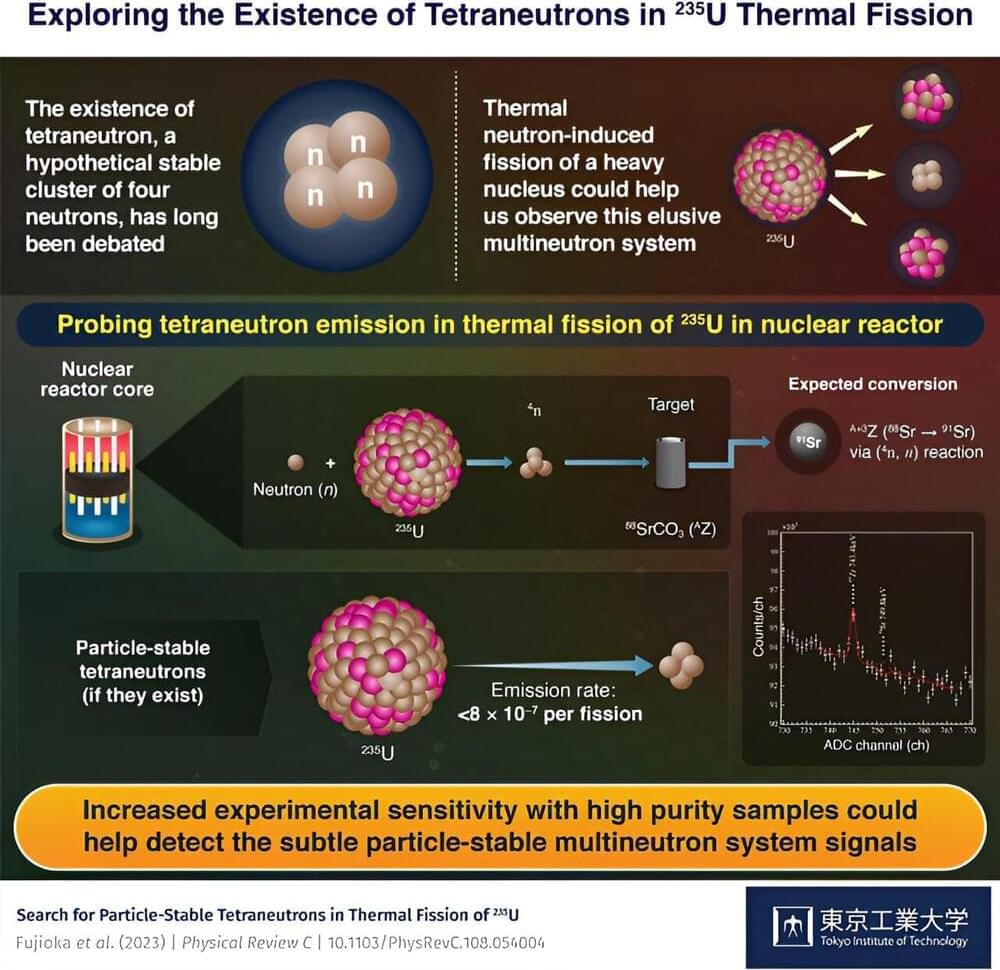
The possible emission rate of particle-stable tetraneutron, a four-neutron system whose existence has been long debated within the scientific community, has been investigated by researchers from Tokyo Tech. They looked into tetraneutron emission from thermal fission of 235 U by irradiating a sample of 88 SrCO3 in a nuclear research reactor and analyzing it via γ-ray spectroscopy.
Tetraneutron is an elusive atomic nucleus consisting of four neutrons, whose existence has been highly debated by scientists. This stems primarily from our lack of knowledge about systems consisting of only neutrons, since most atomic nuclei are usually made of a combination of protons and neutrons. Scientists believe that the experimental observation of a tetraneutron could be the key to exploring new properties of atomic nuclei and answering the age-old question: Can a charge-neutral multineutron system ever exist?
Two recent experimental studies reported the presence of tetraneutrons in bound state and resonant state (a state that decays with time but lives long enough to be detected experimentally). However, theoretical studies indicate that tetraneutrons will not exist in a bound state if the interactions between neutrons are governed by our common understanding of two or three-body nuclear forces.