I found this on NewsBreak: How Food Changes Your Brain.



I found this on NewsBreak: Scientists finally make ‘goldene’, potentially breakthrough new material.
Researchers have managed to create “goldene”, an incredibly thin version of gold.
The work follows the successful production of graphene, which is made out of a single layer graphite atoms. That has been hailed as a miracle material: it is astonishingly strong, and much better at conducting heat and electricity than copper.
Goldene is built on the same principle, with researchers spreading out gold so it is just one atom layer thick. And, similar to graphene, scientists say that the process gives it a variety of new properties that could lead to major breakthroughs.
I found this on NewsBreak: The big idea: are we about to discover a new force of nature?
Intriguingly, both disciplines are grappling with unexplained results that could be pointing to the existence of a new force of nature. If such a new force were to be confirmed, the implications for our understanding of the universe, its history and makeup would be profound.
There are four forces that we already know about. Gravity governs the grandest scales, marshalling the planets in their orbits and shaping the evolution of the universe as a whole. Electromagnetic force gives rise to a vast range of phenomena, from the magnetic field of the Earth to radio waves, visible light and X-rays, while also holding atoms, molecules and, by extension, the physical world together. Deep within the atomic nucleus, two further forces emerge: the vice-like “strong force”, which binds atomic nuclei, and the “weak force”, which among other things causes radioactive decay and enables the nuclear reactions that power the sun and the stars.
Studying these forces has transformed our understanding of nature and generated revolutionary new technologies. Work on electromagnetism in the 19th century gave us the electric dynamo and radio broadcasts, the discovery of the strong and weak forces in the 1930s led to nuclear energy and atomic bombs, while understanding gravity has made it possible to put astronauts on the moon and to develop GPS satellites that can tell us our location anywhere on Earth to within a few metres. Uncovering a fifth force would be one hell of a prize.

I found this on NewsBreak: Decoding the Mysteries of Life and the Cosmos: A Journey Through the Last Decade of Science.
By: Jason St Clair.
It’s worth reflecting on the scientific breakthroughs that have shaped our understanding of the universe and ourselves from 2010 to 2019. From the creation of synthetic life to the first glimpse of a black hole, these discoveries remind us of the indomitable human spirit and our unending quest for knowledge.
In 2010, scientists at the J. Craig Venter Institute played the role of cosmic composers, creating the first living organism with a completely synthetic genome. This milestone marked the first step in producing artificial life, a symphony of genetic notes designed in a computer, assembled in a lab, and brought to life in a donor cell. It was a testament to our growing mastery over the building blocks of life itself.
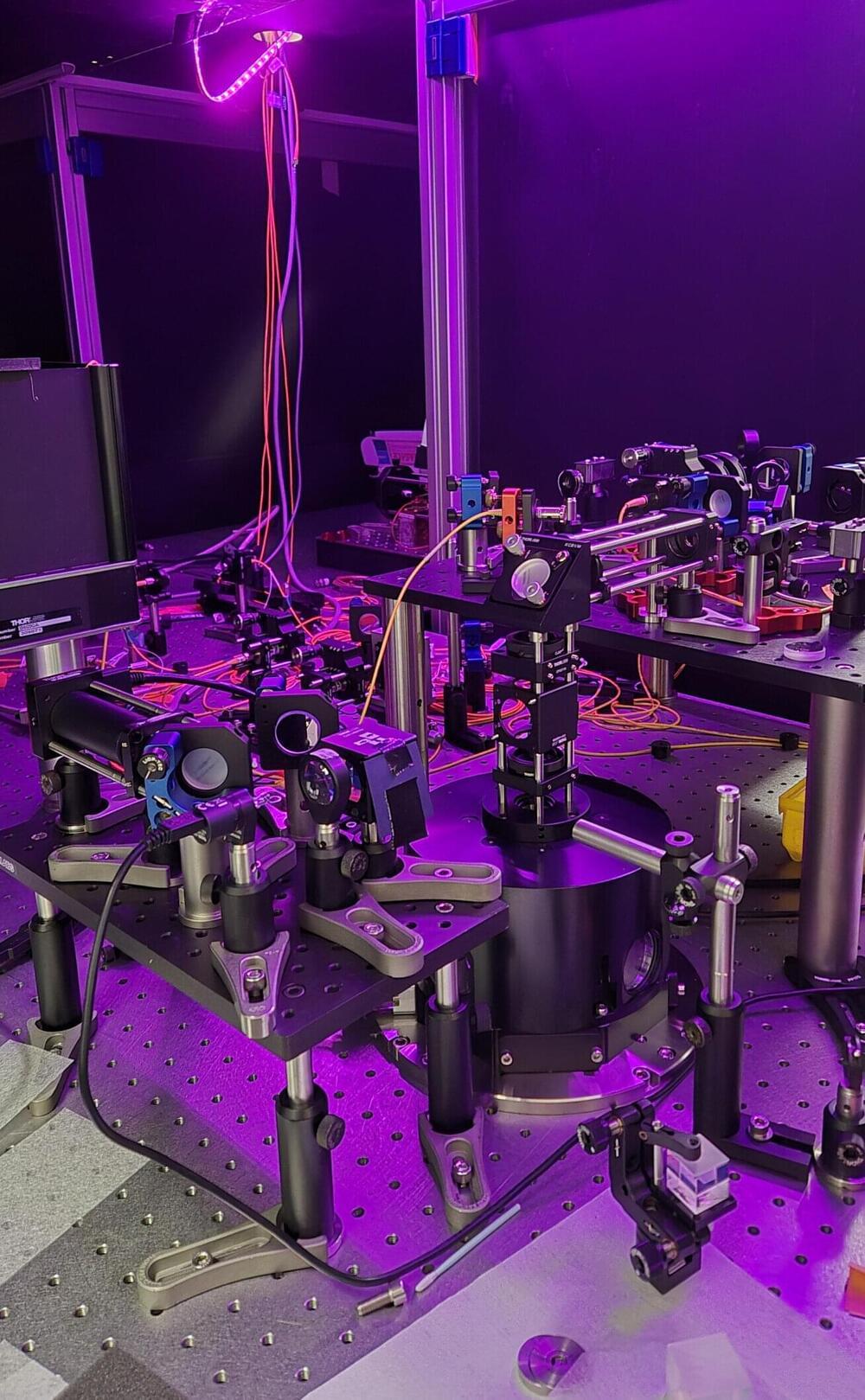





I found this on NewsBreak: Crucial connection for ‘quantum internet’ made for the first time.
However, this development is being held up because quantum information can be lost when transmitted over long distances. One way to overcome this barrier is to divide the network into smaller segments and link them all up with a shared quantum state.
To do this requires a means to store the quantum information and retrieve it again: that is, a quantum memory device. This must ‘talk’ to another device that allows the creation of quantum information in the first place.
For the first time, researchers have created such a system that interfaces these two key components and uses regular optical fibers to transmit the quantum data.